This study aims to systematically review the performance of red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio (RPR) in the diagnosis of significant or advanced fibrosis, and cirrhosis associated with hepatitis B virus (HBV).
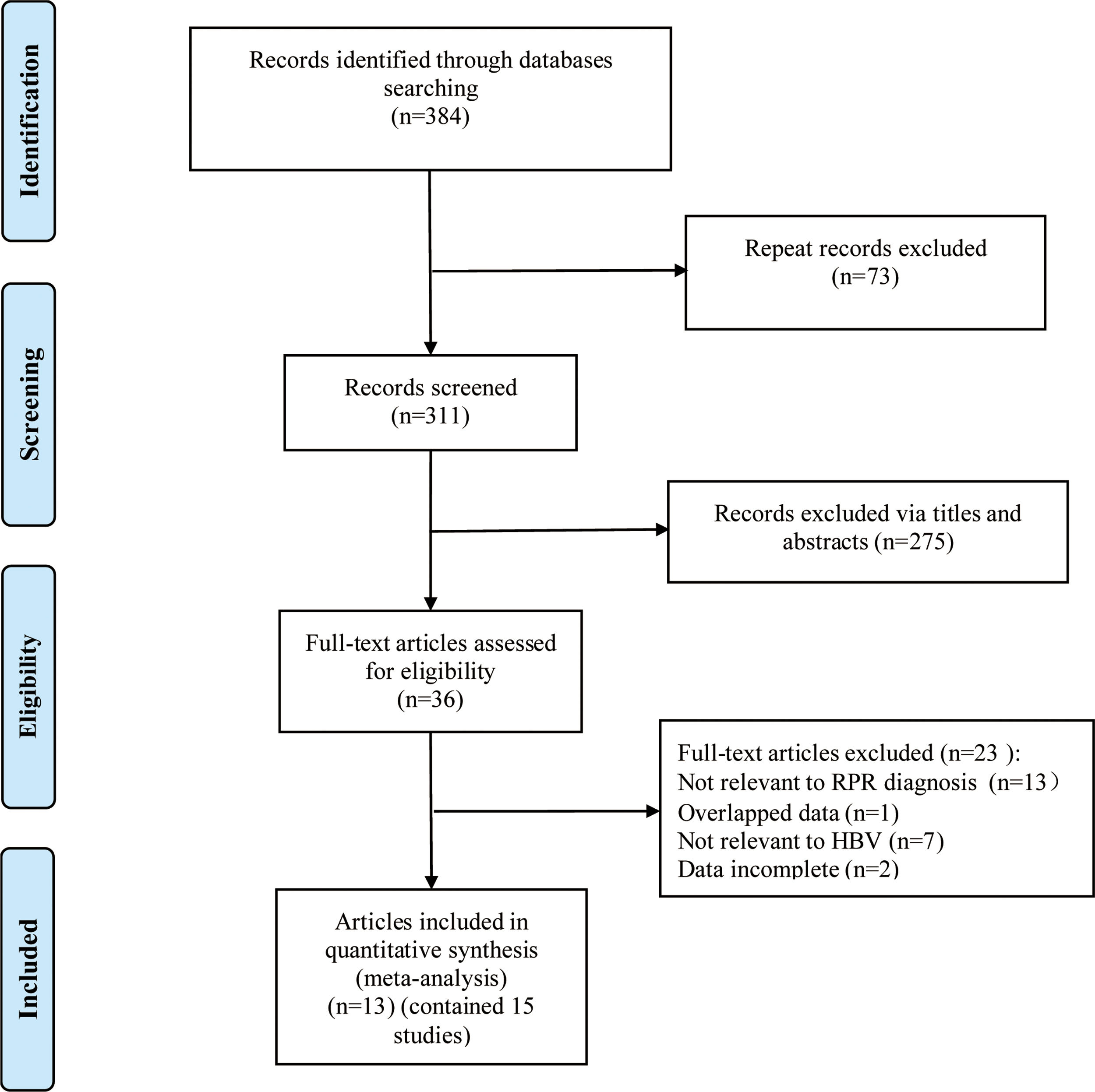
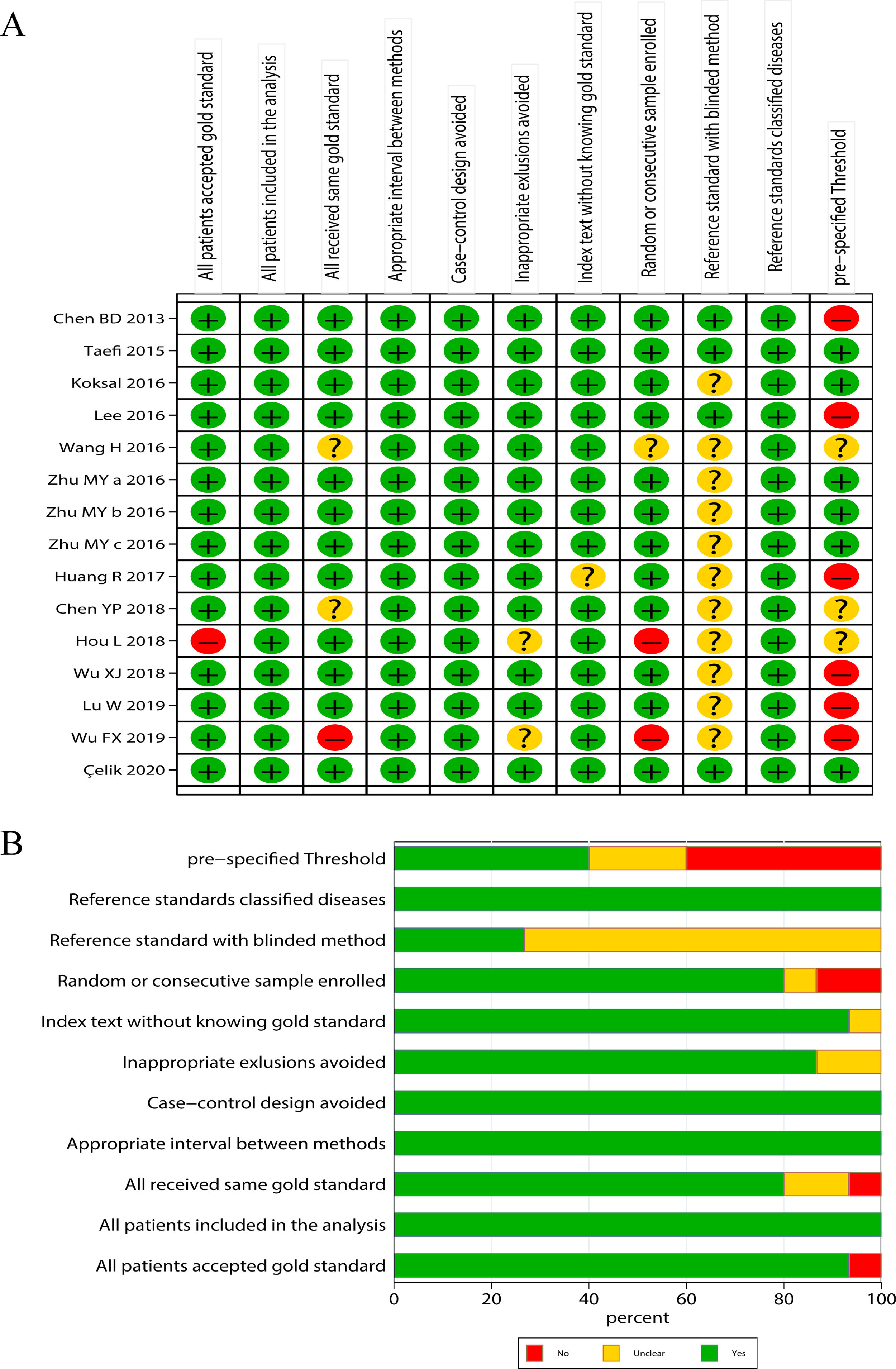
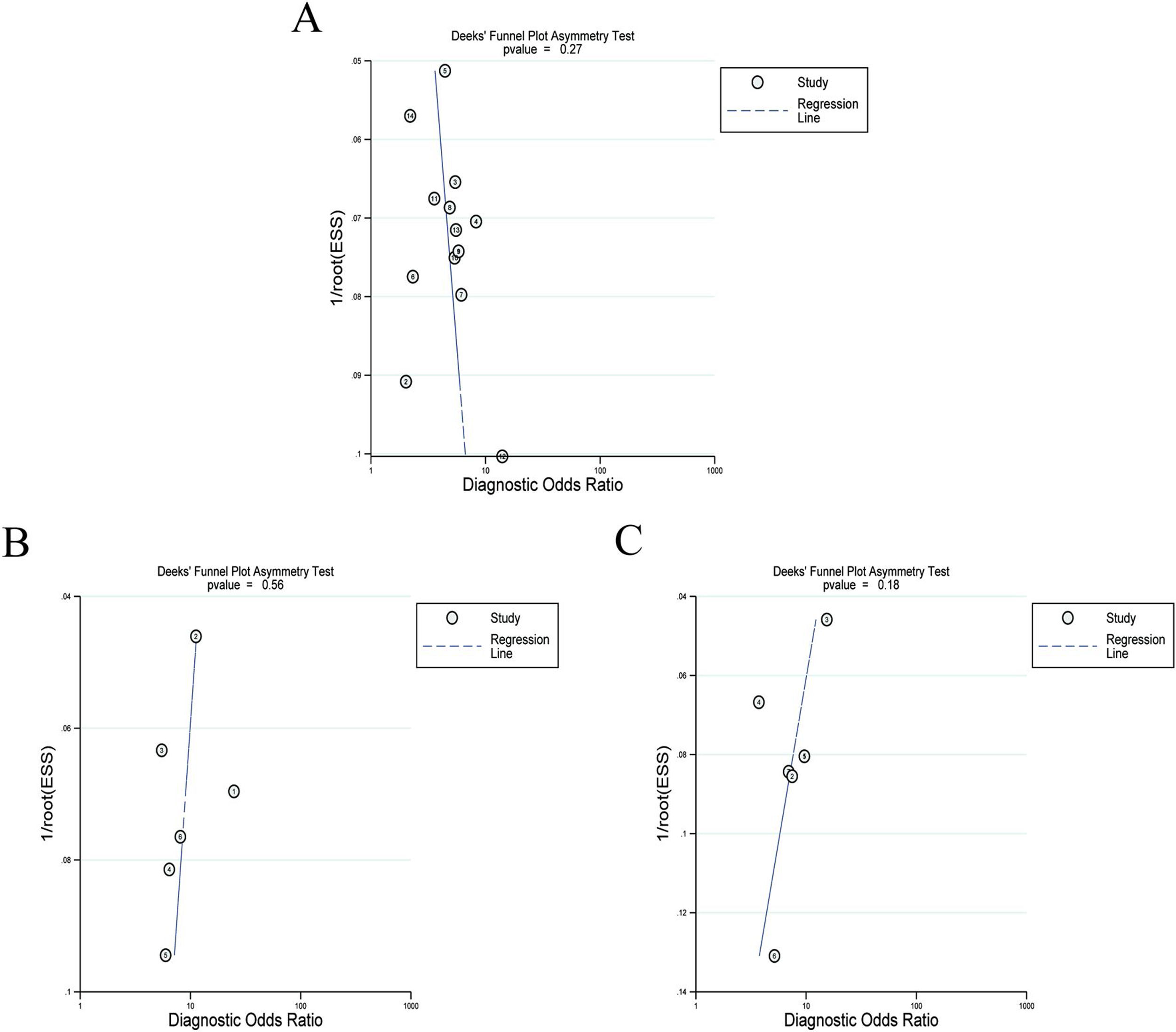
MethodsThe relevant studies were comprehensively searched in English databases such as Web of Science, PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, as well as Chinese databases such as China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang Data from the inception to March 2021. Accuracy of RPR in diagnosing significant or advanced fibrosis and liver cirrhosis was assessed by area under the curve (AUC), pooled sensitivity and specificity, as well as positive and negative likelihood ratios. Stata 15.0 software was applied to analyze the data.
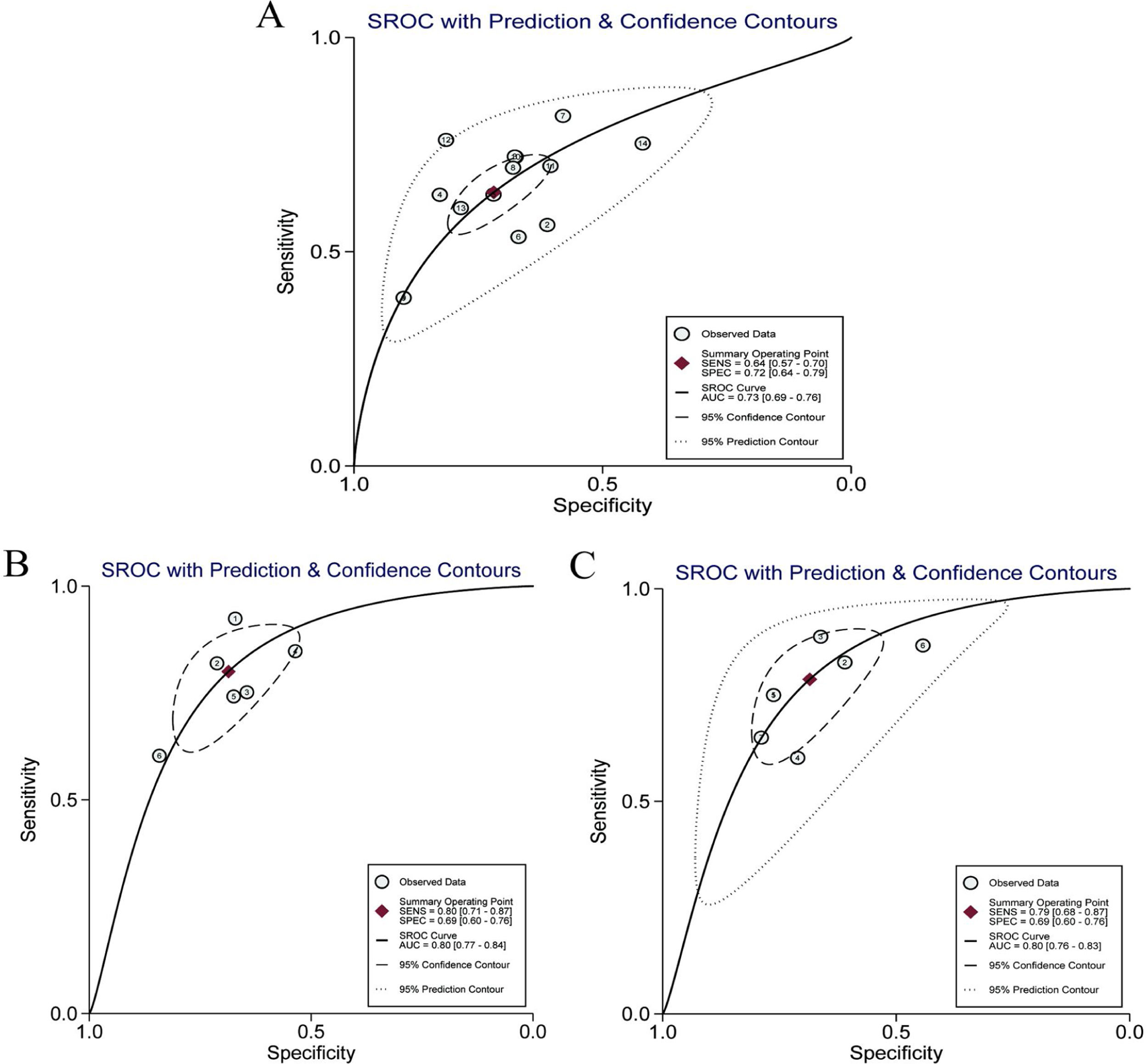
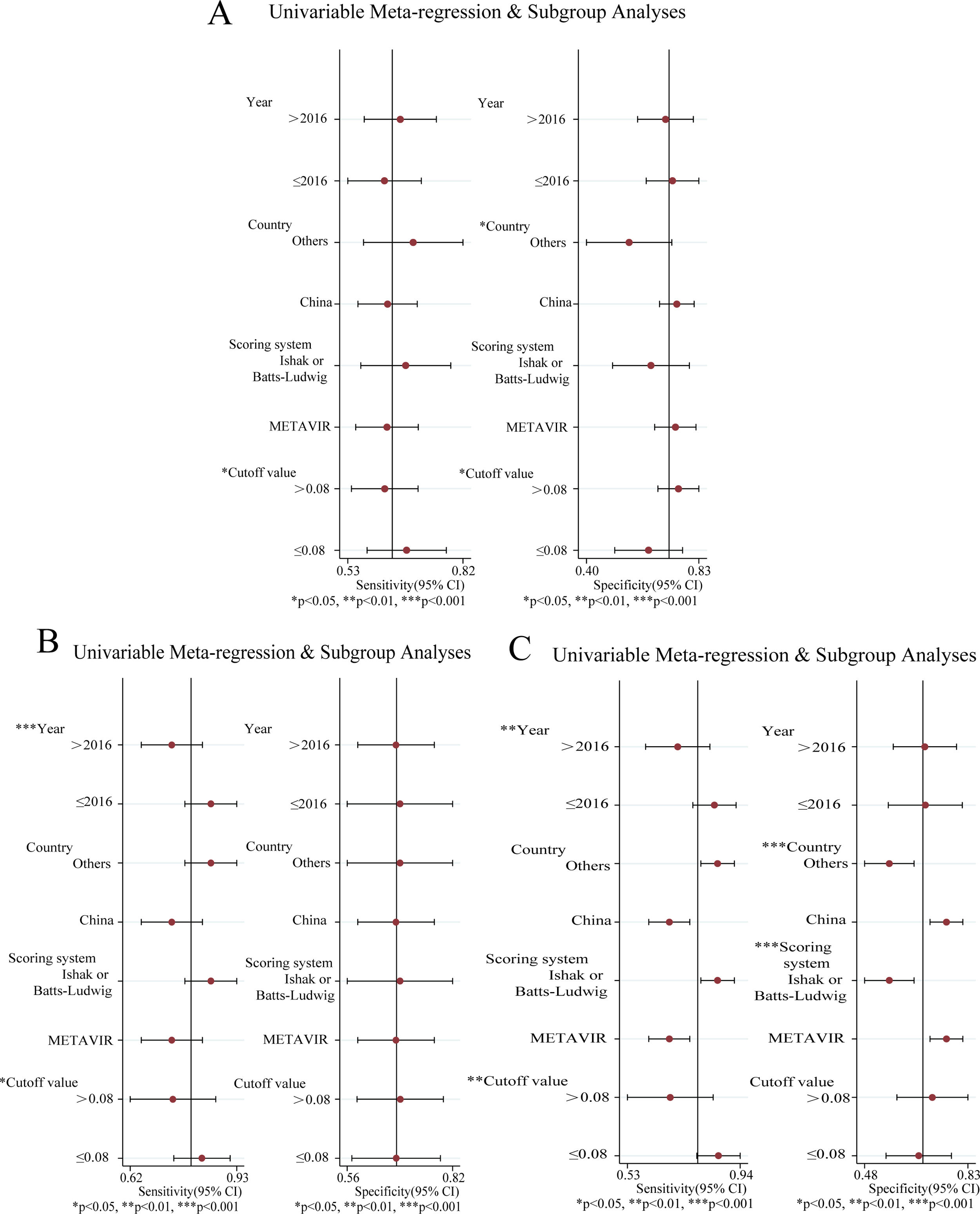
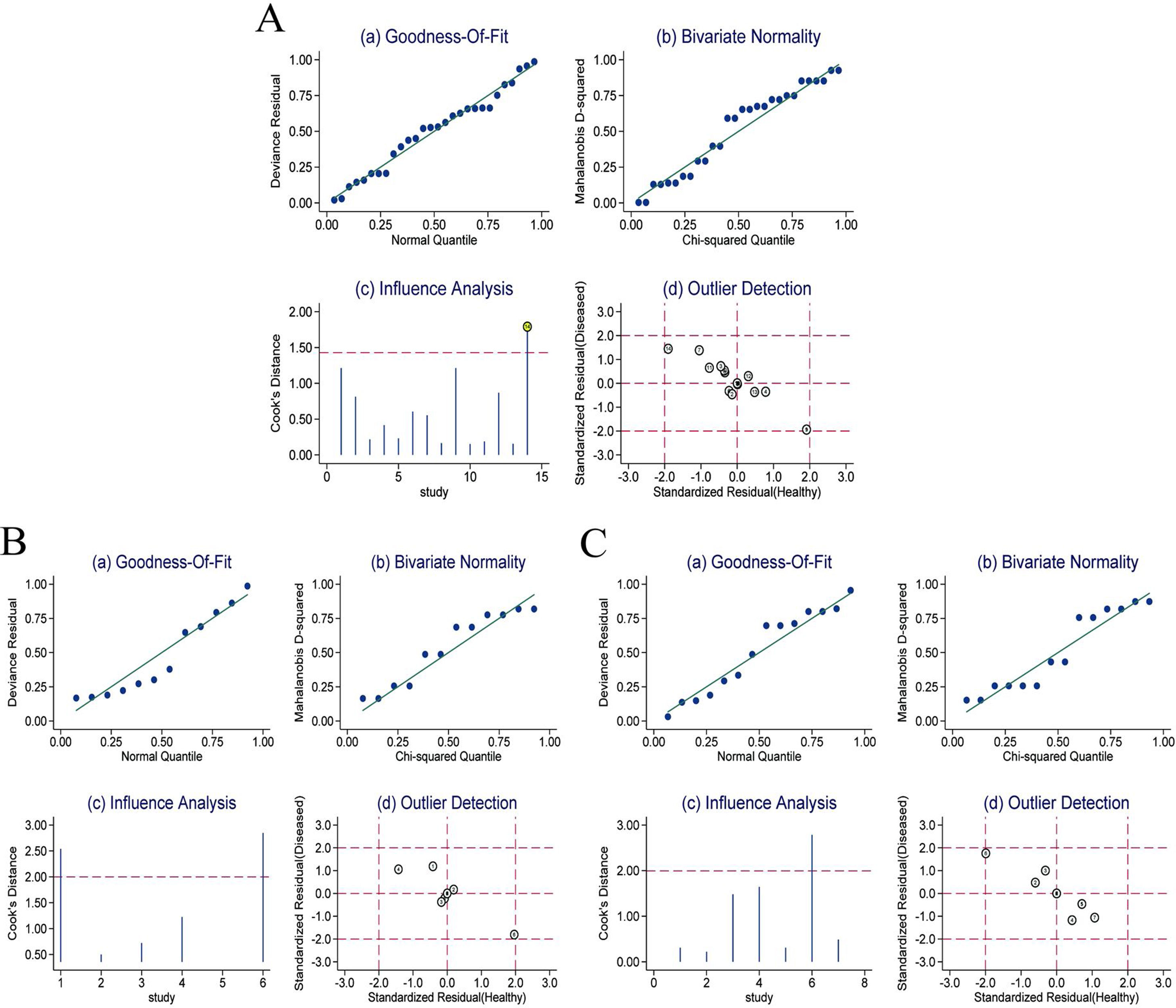
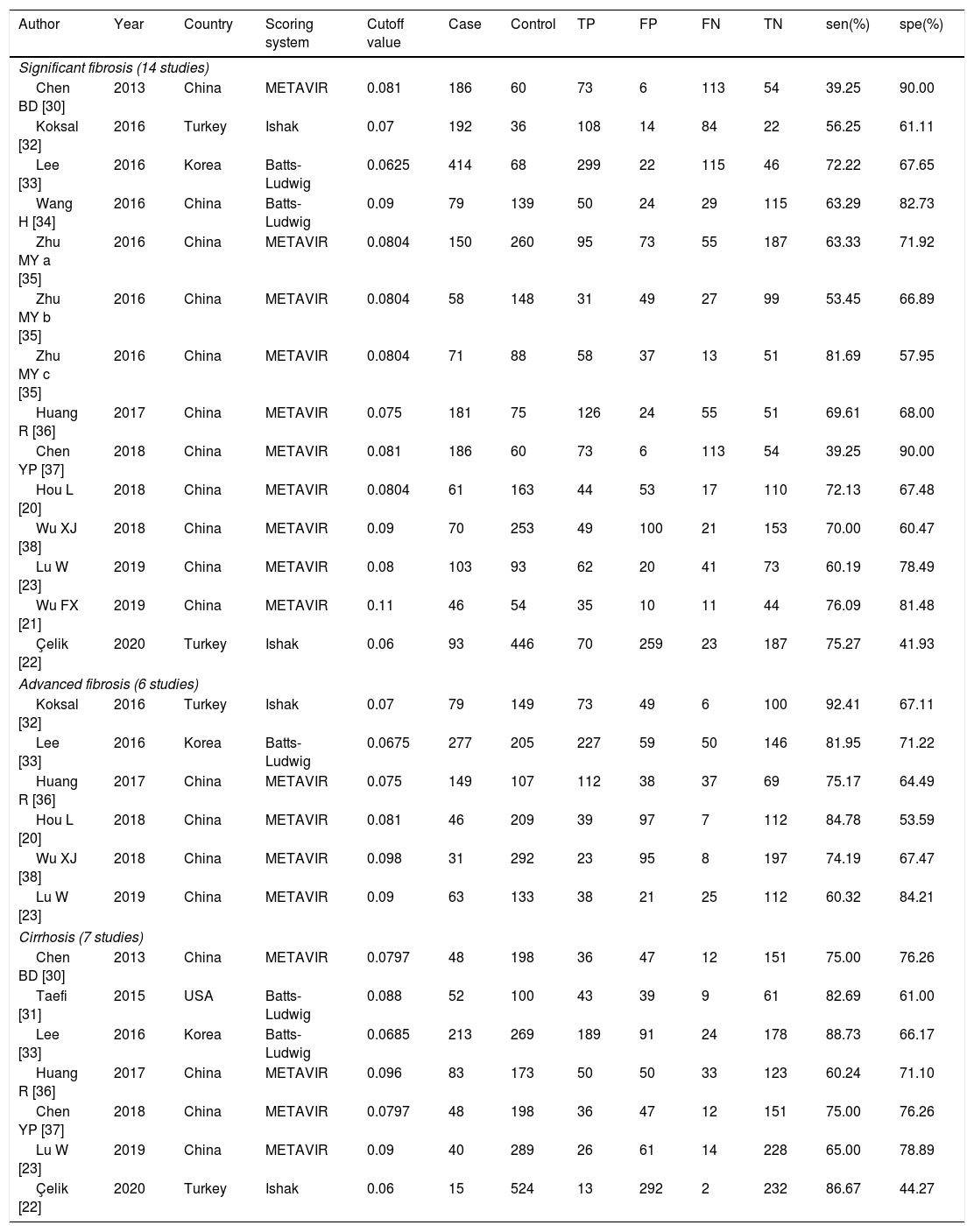
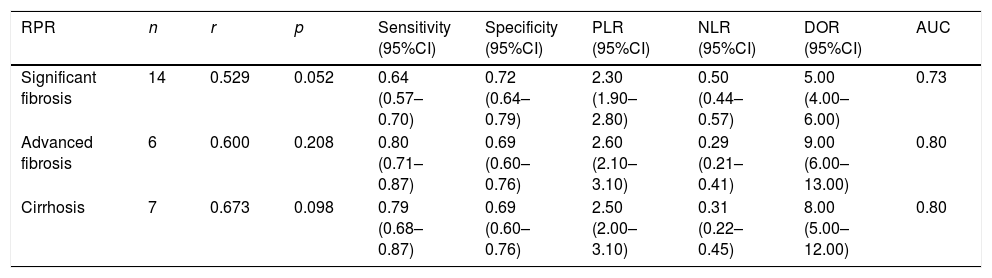
ResultsIn total, 13 literature met the requirements, including patients with significant fibrosis (n=1890), advanced fibrosis (n=645), and cirrhosis (n=499). The prevalence rates of significant fibrosis, advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis were 49.31% (range: 17.25–84.21%), 37.07% (range: 9.60–58.20%) and 2.18% (range: 2.78–44.19%), respectively. The AUCs for predicting significant fibrosis, advanced fibrosis, and cirrhosis by RPR were 0.73 (95%CI: 0.69–0.76), 0.80 (95%CI: 0.77–0.84) and 0.80 (95%CI: 0.76–0.83), respectively.
ConclusionRPR is of some diagnostic value to the prediction of HBV-related significant fibrosis, advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis. This conclusion is urgently needed to be verified by further multi-center studies of large sample size and rigorous design.
Este estudio tiene como objetivo revisar sistemáticamente la capacidad del cociente entre el ancho de distribución de los glóbulos rojos y el recuento plaquetario (RPR) para discriminar en pacientes con infección crónica por virus de la hepatitis B la existencia de fibrosis significativa, avanzada y cirrosis.
MétodosSe realizaron búsquedas exhaustivas de los estudios relevantes en bases de datos en inglés, como Web of Science, PubMed, EMBASE y Cochrane Library, así como en bases de datos chinas, como China National Knowledge Infrastructure y Wanfang Data, desde el inicio hasta marzo de 2021. La precisión de RPR en el diagnóstico de fibrosis avanzada y cirrosis hepática se evaluó mediante el área bajo la curva, la sensibilidad y la especificidad combinadas, así como las razones de probabilidad positiva y negativa. Se aplicó el software Stata 15.0 para analizar los datos.
ResultadosUn total de 13 publicaciones cumplieron con los requisitos, incluyendo pacientes con fibrosis significativa (n=1.890), fibrosis avanzada (n=645) y cirrosis (n=499). Las tasas de prevalencia de fibrosis significativa, fibrosis avanzada y cirrosis fueron del 49,31% (rango: 17,25-84,21), 37,07% (rango: 9,60-58,20) y 2,18% (rango: 2,78-44,19), respectivamente. El área bajo la curva para predecir fibrosis significativa, fibrosis avanzada y cirrosis por RPR fue 0,73 (IC 95%: 0,69-0,76), 0,80 (IC 95%: 0,77-0,84) y 0,80 (IC 95%: 0,76-0,83), respectivamente.
ConclusiónLa RPR tiene algún valor diagnóstico para la predicción de fibrosis significativa relacionada con el virus de la hepatitis B, fibrosis avanzada y cirrosis. Y esta conclusión debe ser verificada con urgencia mediante más estudios multicéntricos de gran tamaño de muestra y diseño riguroso.