Las alteraciones motoras de la parálisis cerebral generan alteraciones del control postural y equilibrio. Los videojuegos y la realidad virtual trabajan sobre esos aspectos lúdicamente. El objetivo fue evaluar su efectividad en el control postural y equilibrio en población infantil con parálisis cerebral en Atención Temprana.
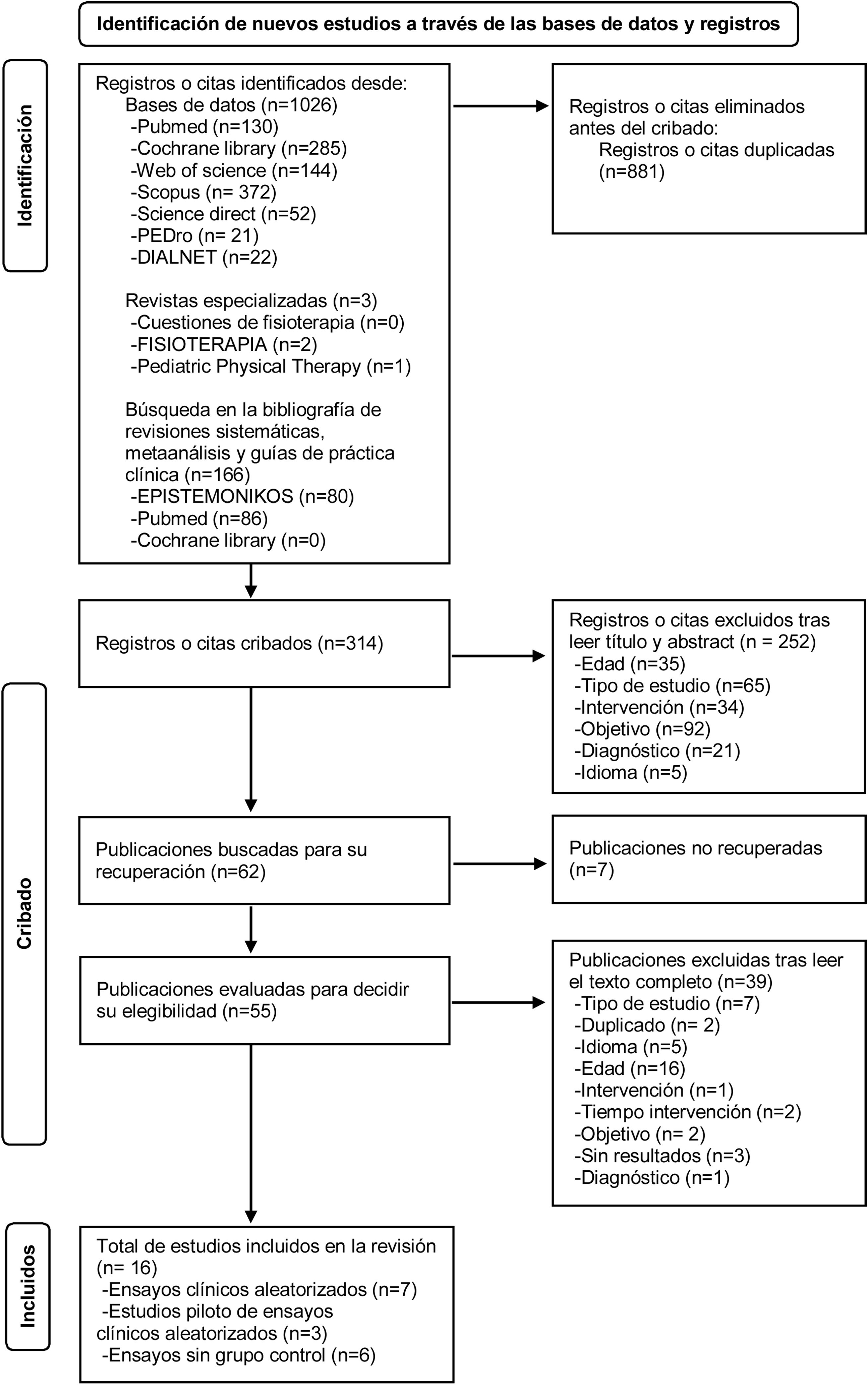
Material y métodosEntre enero y febrero del 2021 se realizó la búsqueda de ensayos clínicos aleatorizados y sin grupo control en Epistemonikos, Pubmed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, Science Direct, PEDro y Dialnet. Se revisó la bibliografía de guías clínicas, revisiones sistemáticas y metaanálisis. Se complementó con las revistas Fisioterapia, Cuestiones de Fisioterapia y Pediatric Physical Therapy. Tras la elección de artículos utilizándose la Declaración PRISMA, se analizó su calidad con las escalas CONSORT, TREND y SIGN.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 16 estudios que evaluaban el control postural, equilibrio y función motora gruesa en población infantil entre 3 y 13 años con parálisis cerebral. La realidad virtual utilizada fue: Wii, XBOX, PlayStation2, TYROMOTION y ordenador. Los estudios obtuvieron mejoras significativas en variables que median el control postural, equilibrio y función motora gruesa al finalizar y se mantuvieron 4-8 semanas. No indicaron efectos adversos reseñables. La calidad fue variable incluyéndose estudios 1+ y 1− de la escala SIGN.
ConclusionesLos estudios reportan cierto grado de efectividad en la mejora del control postural y equilibrio en población infantil con parálisis cerebral en diferentes rangos de edad. Son necesarios estudios con mayor muestra, calidad y población centrada en Atención Temprana para generalizar estos resultados.
Motor disorders in cerebral palsy cause alterations in postural control and balance. Video games and virtual reality work on these aspects in a playful way. The objective was to evaluate their effectiveness on postural control and balance in children with cerebral palsy in Early Intervention.
Material and methodsBetween January and February 2021 we searched in Epistemonikos, Pubmed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus, Science Direct, PEDro and Dialnet for randomised clinical trials and trials without a control group. Bibliographies of clinical guidelines, systematic reviews and meta-analyses were reviewed. It was complemented with the journals Fisioterapia, Cuestiones de Fisioterapia and Pediatric Physical Therapy. We use PRISMA Statement. After selecting articles, their quality was analysed using CONSORT, TREND and SIGN scales.
ResultsSixteen studies were included that assessed postural control, balance and gross motor function in children aged 3–13 years with cerebral palsy. The virtual reality used was Wii, XBOX, PlayStation2, TYROMOTION and computer. The studies showed significant improvements in variables that evaluate postural control, balance and gross motor function at the end and maintained for 4–8 weeks. Motivation and participation levels increased. No notable adverse effects were reported. Quality was variable, including 1+ and 1− on the SIGN scale.
ConclusionsStudies report a certain degree of effectiveness in improving postural control and balance in children with cerebral palsy in different age ranges. Studies with a larger sample, quality and a study population focused on Early Intervention are needed to generalise these results.
Article
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".