The Economic Activity Restriction (EAR) due to health conditions is being utilized as a foundational measure for the European indicator Healthy Life Years (HLY). The EAR group is experiencing limitations not only in economic activities but also in overall activities, and it is a population with a high likelihood of transitioning to mental illness due to health condition. However, few studies have investigated the relationship between EAR and mental illness. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to identify the association between EAR due to health conditions and mental illness for those aged 45 and older in South Korea.
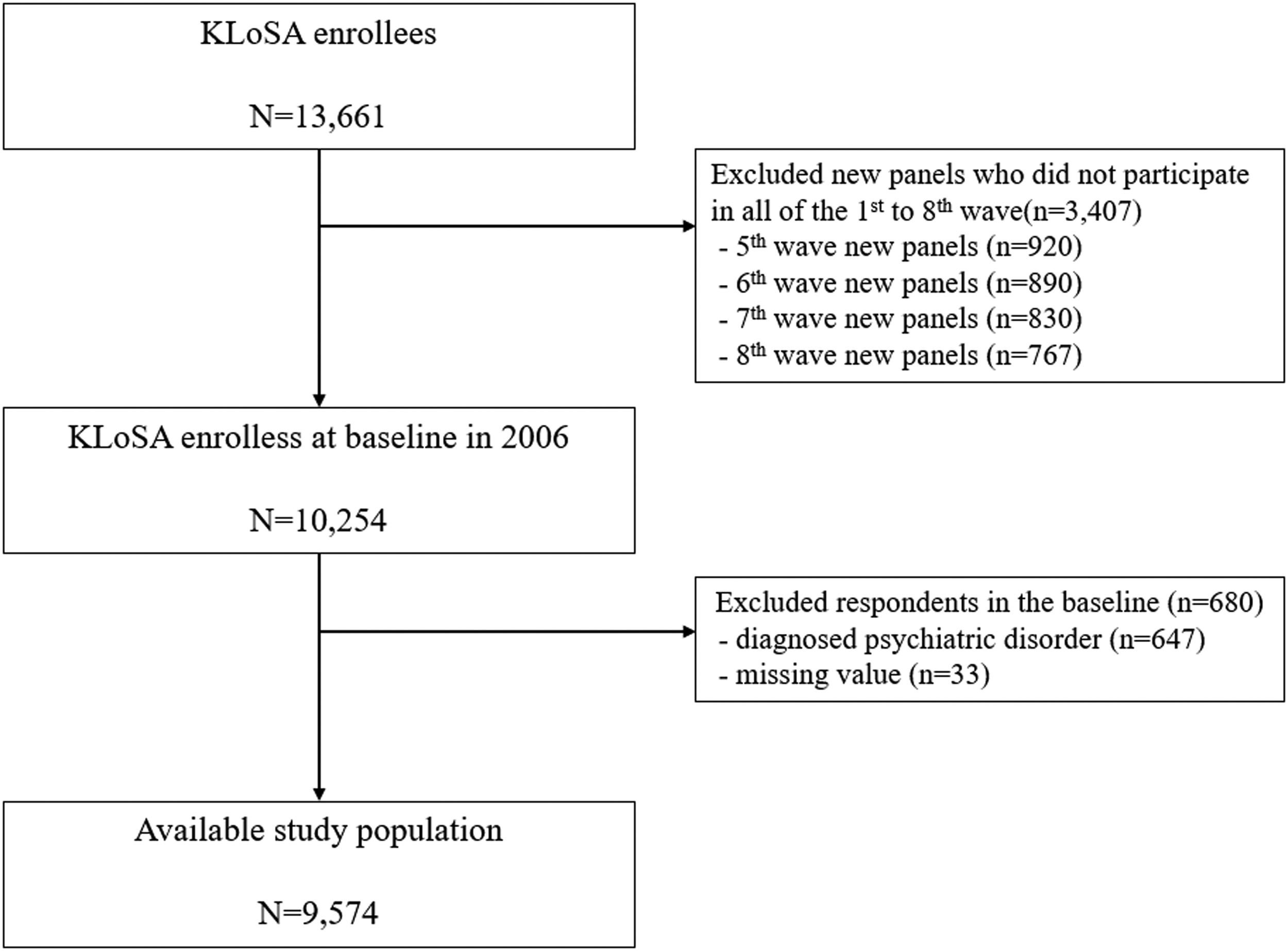
MethodsWe obtained data from the 2006–2020 Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging. EAR was assessed using self-reported questionnaires based on the Global Activity Limitation Indicator. mental illness was assessed based on the diagnosis data for participants who had been diagnosed. After excluding missing values, the data of 9,574 participants were analyzed using the chi-square test, log-rank tests, and time-dependent Cox proportional hazard model to evaluate the association between EAR and mental illness.
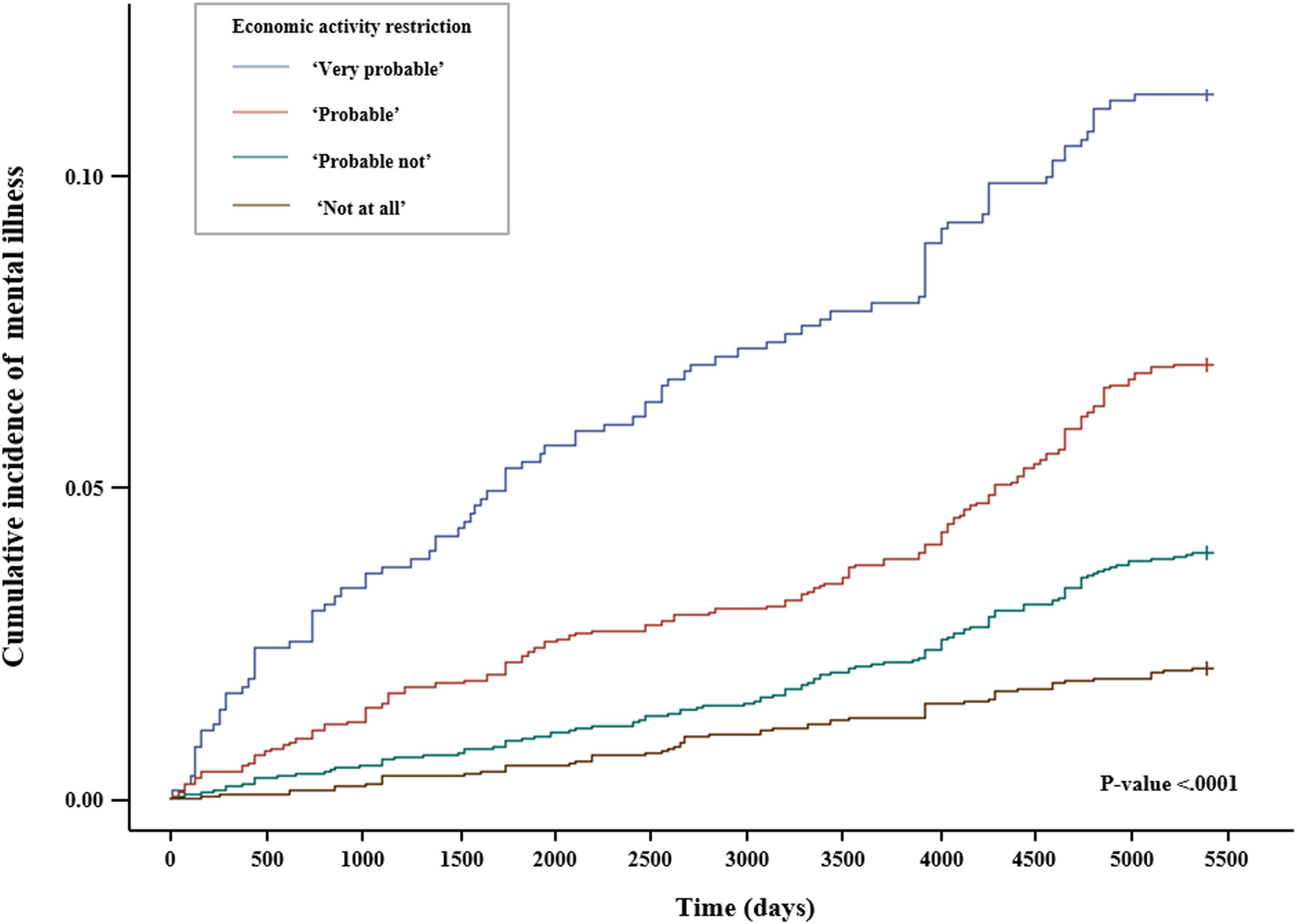
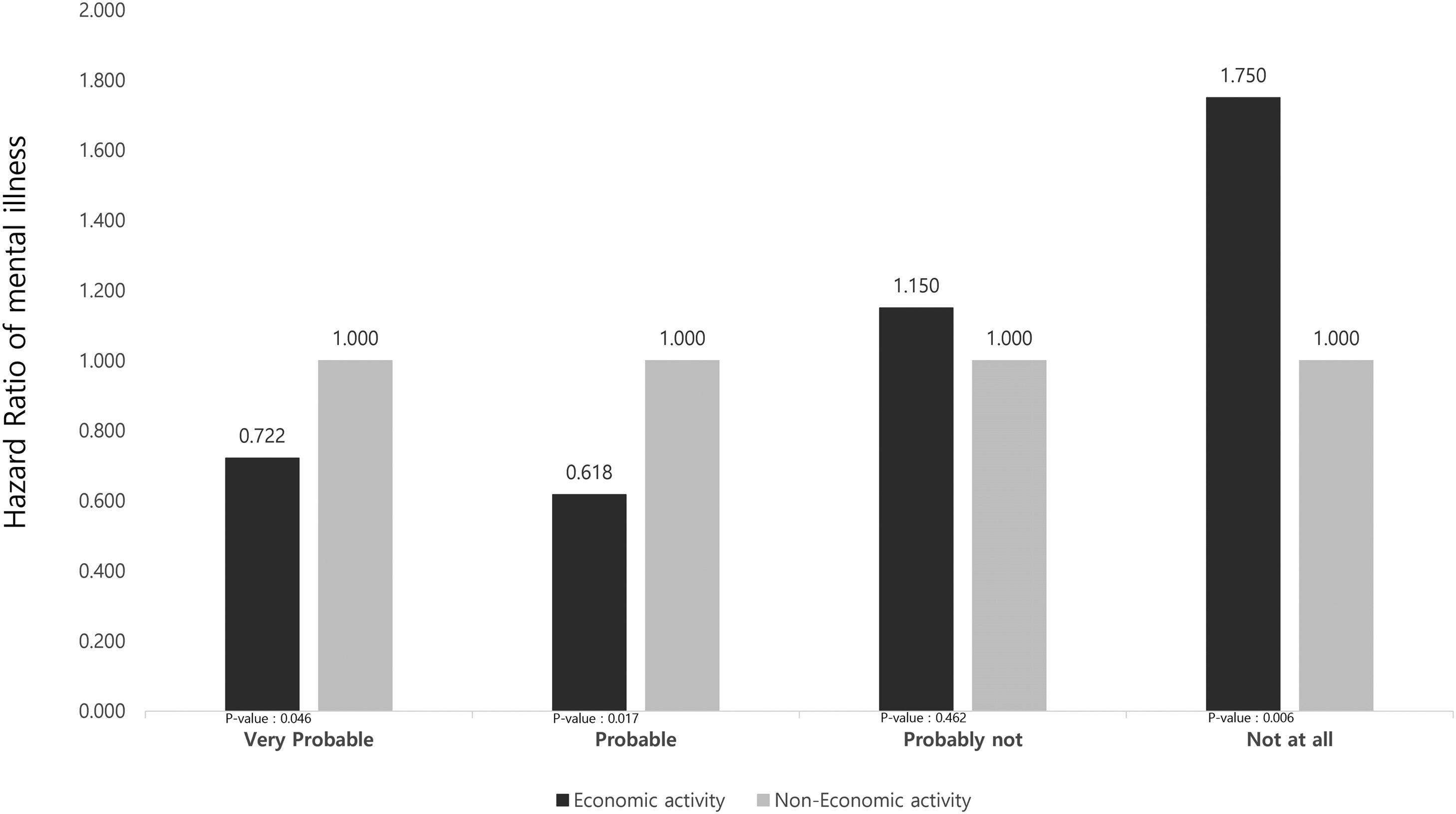
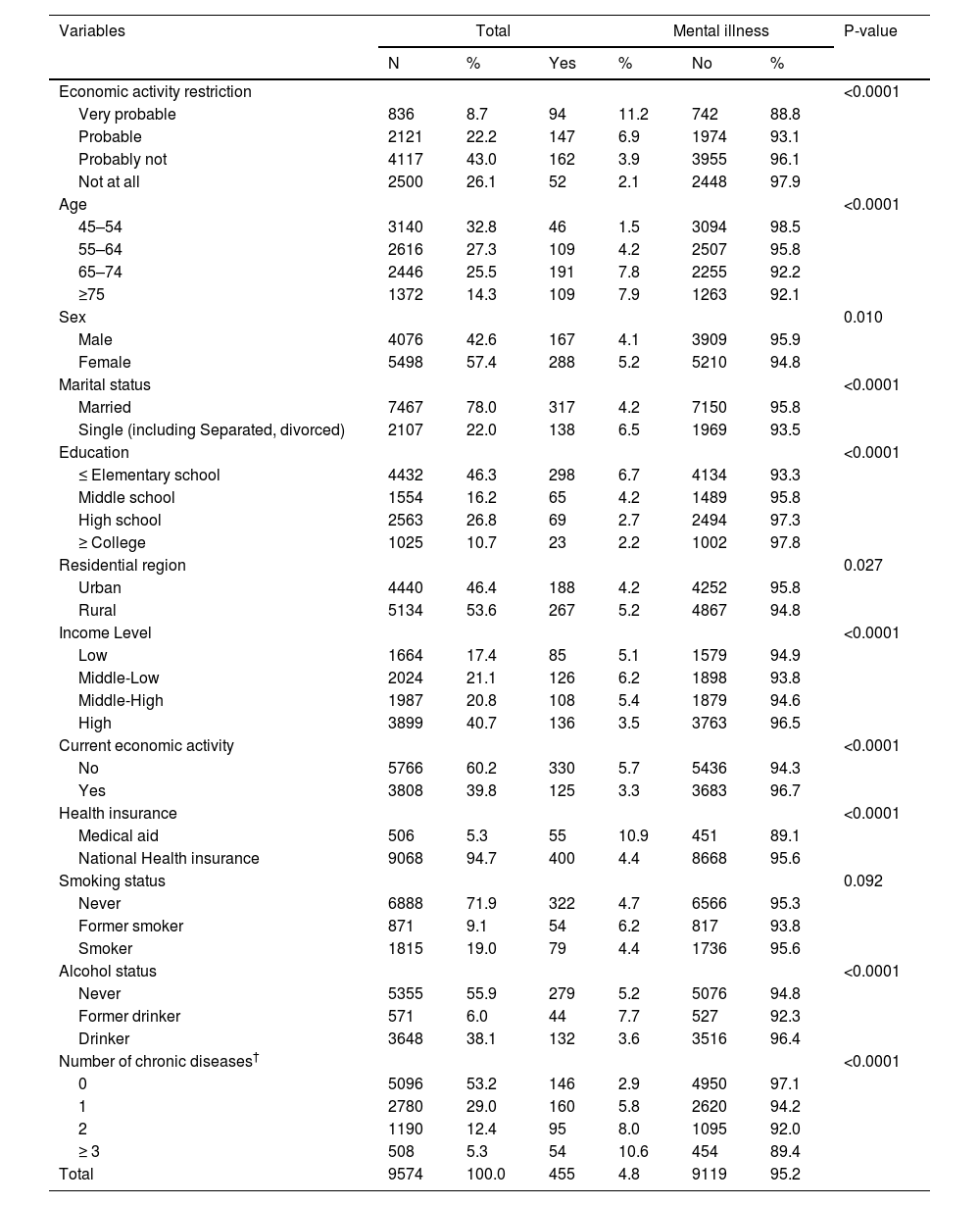
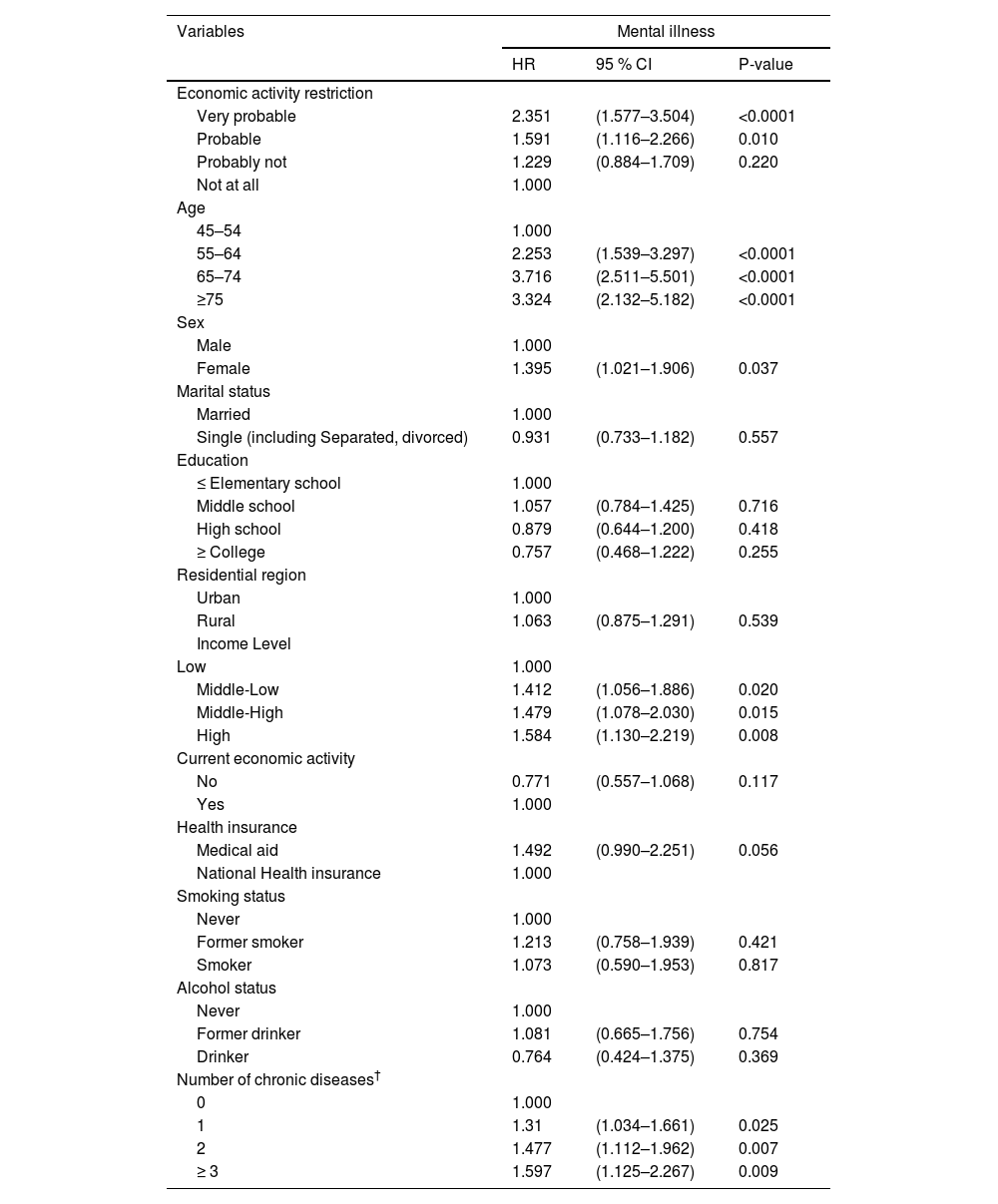
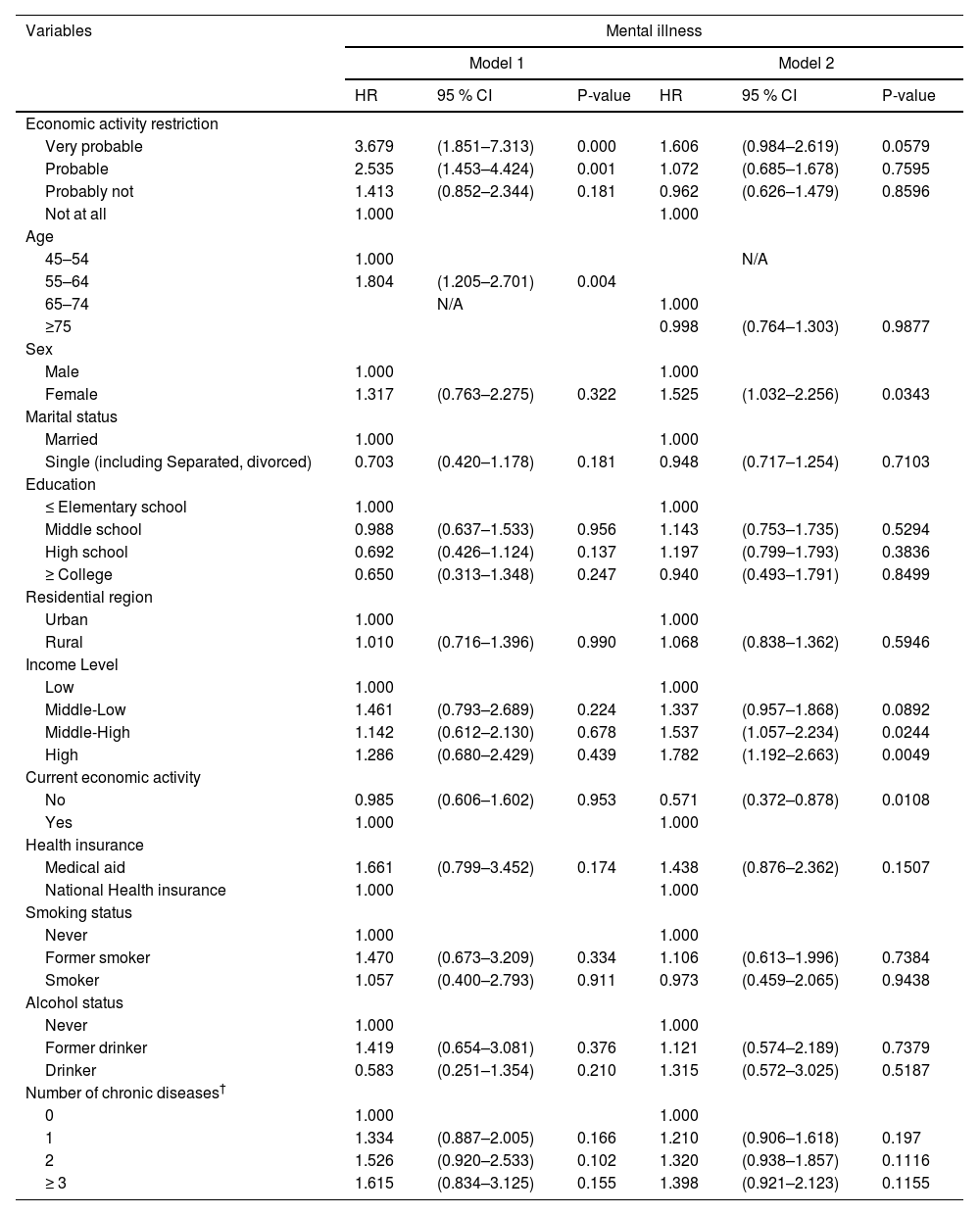
ResultsOut of the 9,574 participants gathered at baseline, the mental illness rate was 4.8 %. The hazard ratio (HR) of mental illness in those in the “very probable” of EAR was 2.351 times higher (p-value <0.0001) compared with “not at all” of EAR. In model 1 which includes under 64 years, HR of mental illness in “very probable” of EAR was 3.679 times higher (p-value: 0.000) and in “probable” of EAR was 2.535 time higher (p-value: 0.001) compared with “not at all” of EAR.
ConclusionIf we provide opportunities to participate in community activities or provide the mental health promotion programs for middle-aged population who are experiencing EAR due to health condition, it is expected to prevent the deterioration of mental health and reduce the incidence of mental illness among the middle-aged Korean population.