The study aims to compare individuals diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and healthy individuals in terms of psychosis-like experiences (PLEs) and investigate the relationship between PLEs and OCD severity.
MethodsSociodemographic information form, Yale-Brown Obsessive-Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS), the positive dimension of Community Assessment of Psychic Experiences (CAPE-P), Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D), and Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) were applied to 83 OCD patients and 83 healthy individuals. The 11th item of Y-BOCS (Y-BOCS-11) was used to evaluate the level of insight. The OCD group was compared with the healthy control group in terms of sociodemographic information and CAPE-P score. In the OCD group, mediation analyses were performed to evaluate the factors affecting the relationship between OCD severity and PLEs.
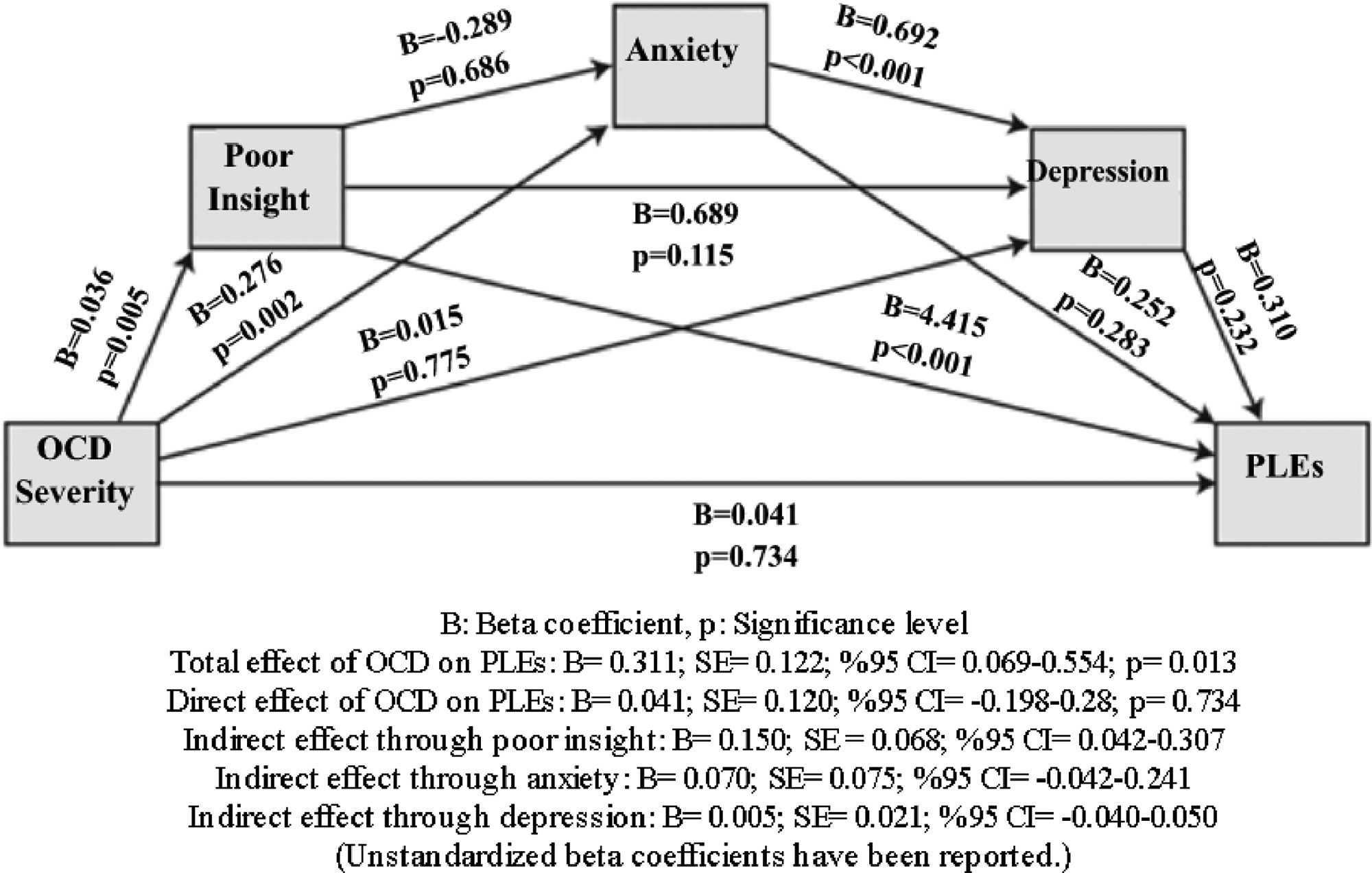
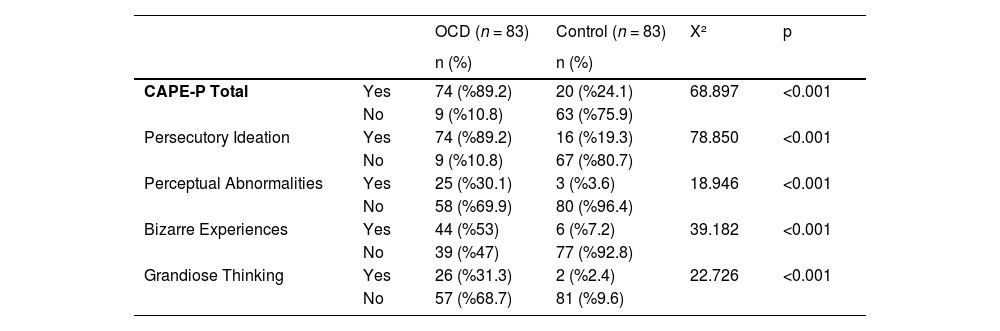
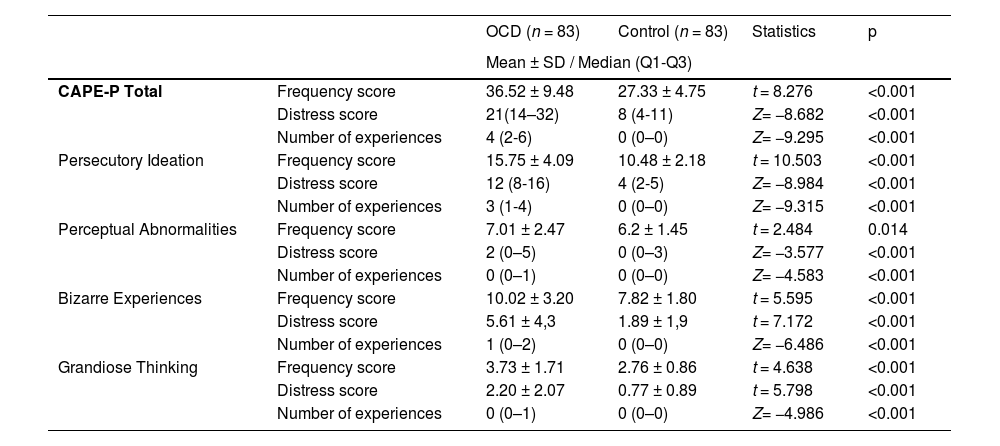
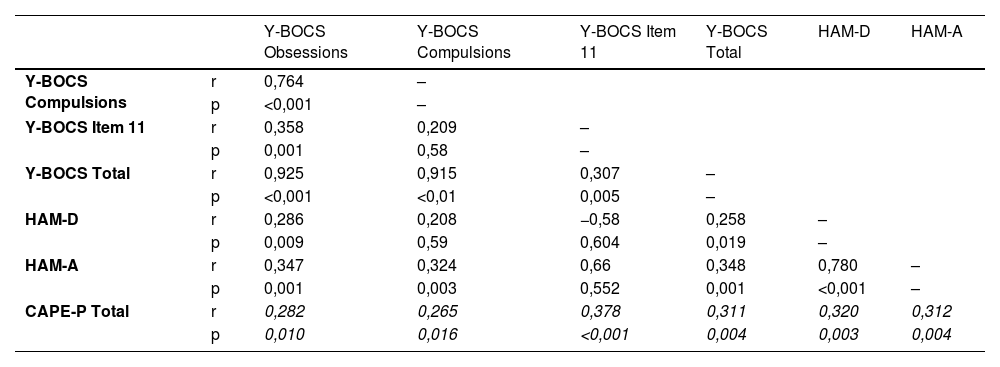
ResultsThe OCD group had higher CAPE-P scores than the healthy control group. CAPE-P scores were weakly correlated with Y-BOCS-11 and Y-BOCS total scores. It was found that the relationship between OCD severity and PLEs was mediated by poor insight; however, the scores of depression and anxiety did not.
ConclusionThe results show that the level of insight is a determinative factor for PLEs in OCD. The fact that PLEs are common in the OCD group and healthy individuals support the concept of the psychosis continuum. We emphasize that being aware of PLEs in OCD can provide new understandings of the phenomenon of OCD and psychosis.