Substance use disorder (SUD) has become a major concern in public health globally, and there is an urgent need to develop an integrated psychosocial intervention. The aims of the current study are to test the efficacy of the integrated treatment with neurofeedback and mindfulness-based therapy for SUD and identify the predictors of the efficacy.
MethodsThis study included 110 participants with SUD into the analysis. Outcome of measures includes demographic characteristics, severity of dependence, quality of life, symptoms of depression, and anxiety. Independent t test is used to estimate the change of scores at baseline and three months follow-up. Generalized estimating equations are applied to analyze the effect of predictors on the scores of dependence severity over time by controlling for the effects of demographic characteristics.
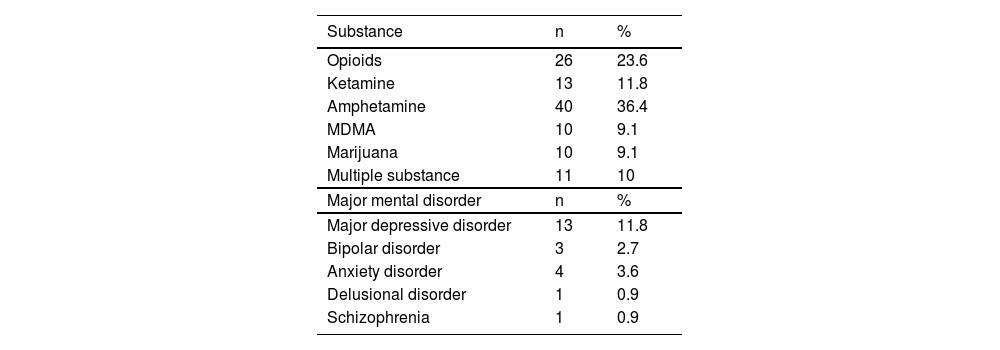
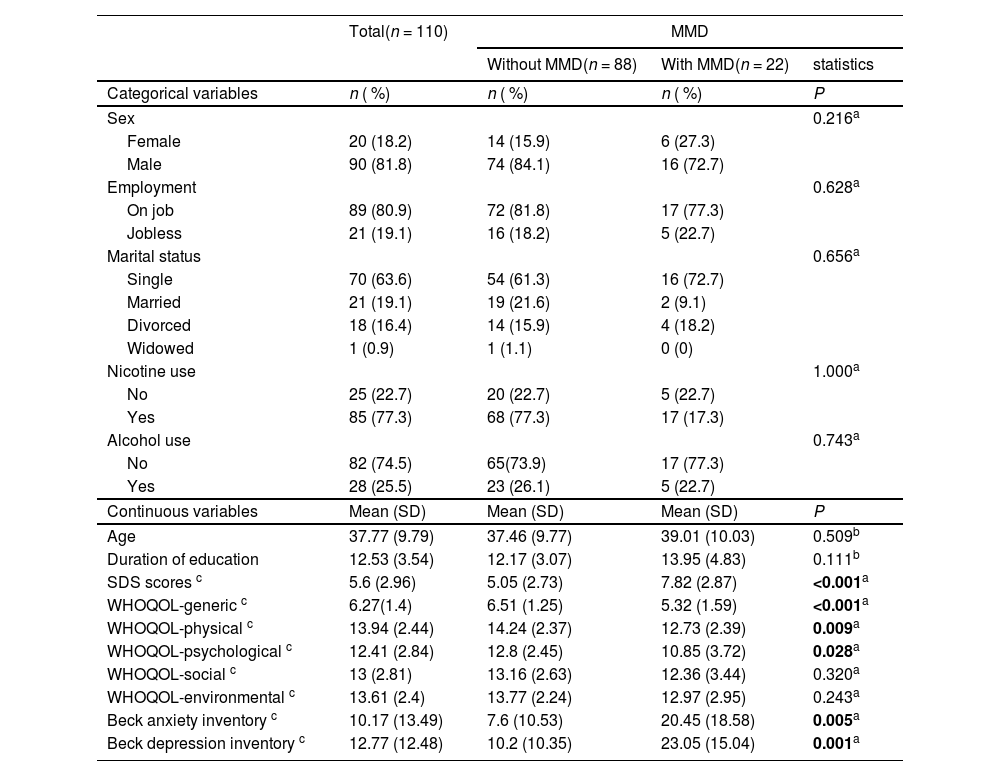
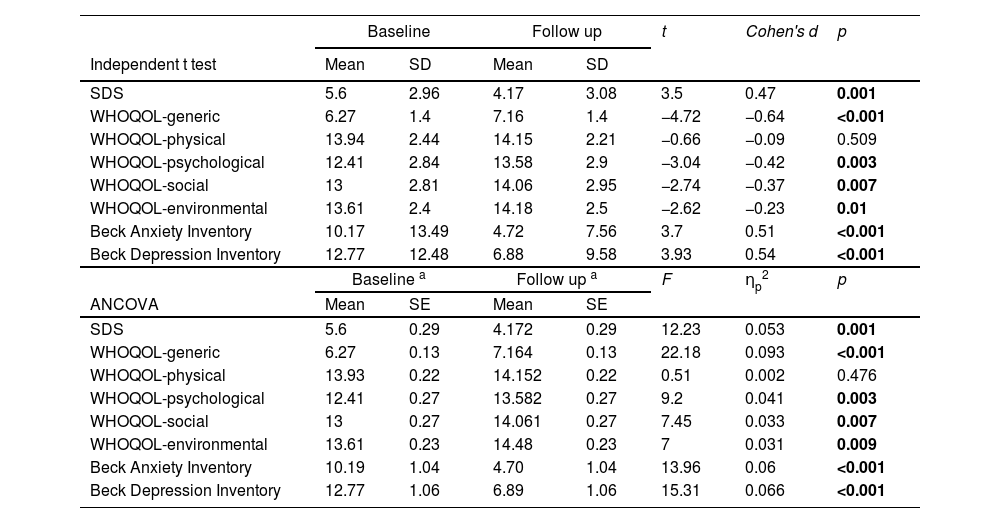
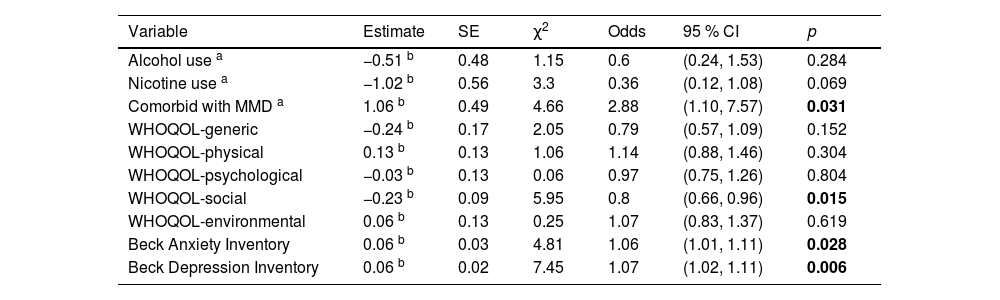
ResultsA total of 22 (20 %) participants were comorbid with major mental disorder (MMD). The decrement of the severity in dependence, anxiety, and depression after treatment are identified. Improved scores of qualities of life in generic, psychological, social, and environmental domains are also noticed. After controlling for the effects of demographic characteristics, the predictors of poorer outcome are comorbid with MMD, lower quality of life, and higher level of depression and anxiety.
ConclusionThe present study implicates the efficacy of integrated therapy. Early identification of predictors is beneficial for healthcare workers to improve the treatment efficacy