Some concerns persist regarding the safety of semaglutide. The objective of this updated meta-analysis is to assess the risk of acute pancreatitis with the use of semaglutide, assessing the results according to the different administration regimens.
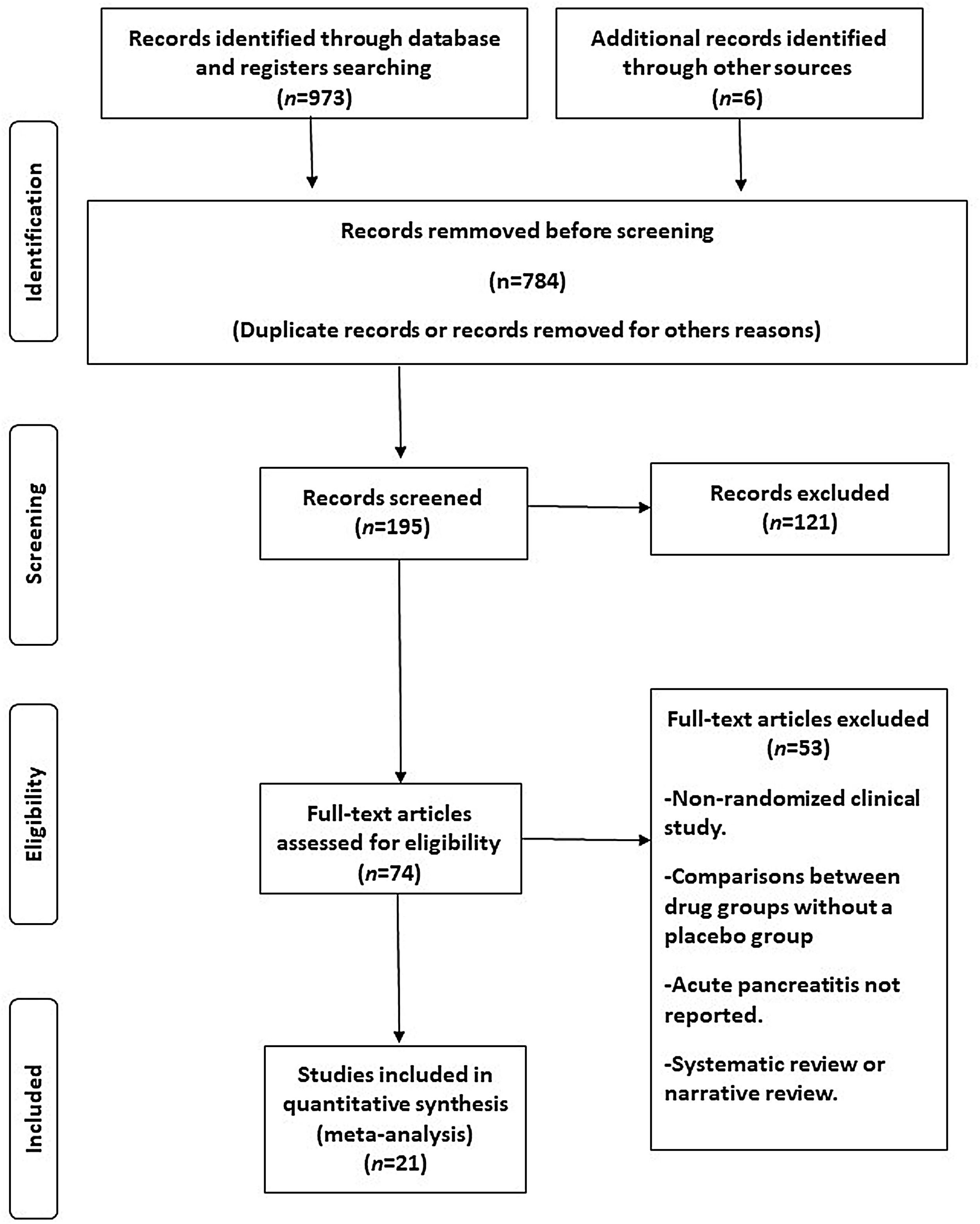
MethodsWe performed an updated meta-analysis of randomised, placebo-controlled studies of semaglutide therapy that report acute pancreatitis. This meta-analysis was performed in line with PRISMA guidelines. A global and stratified analysis according to the therapeutic scheme used was performed using the fixed-effects model.
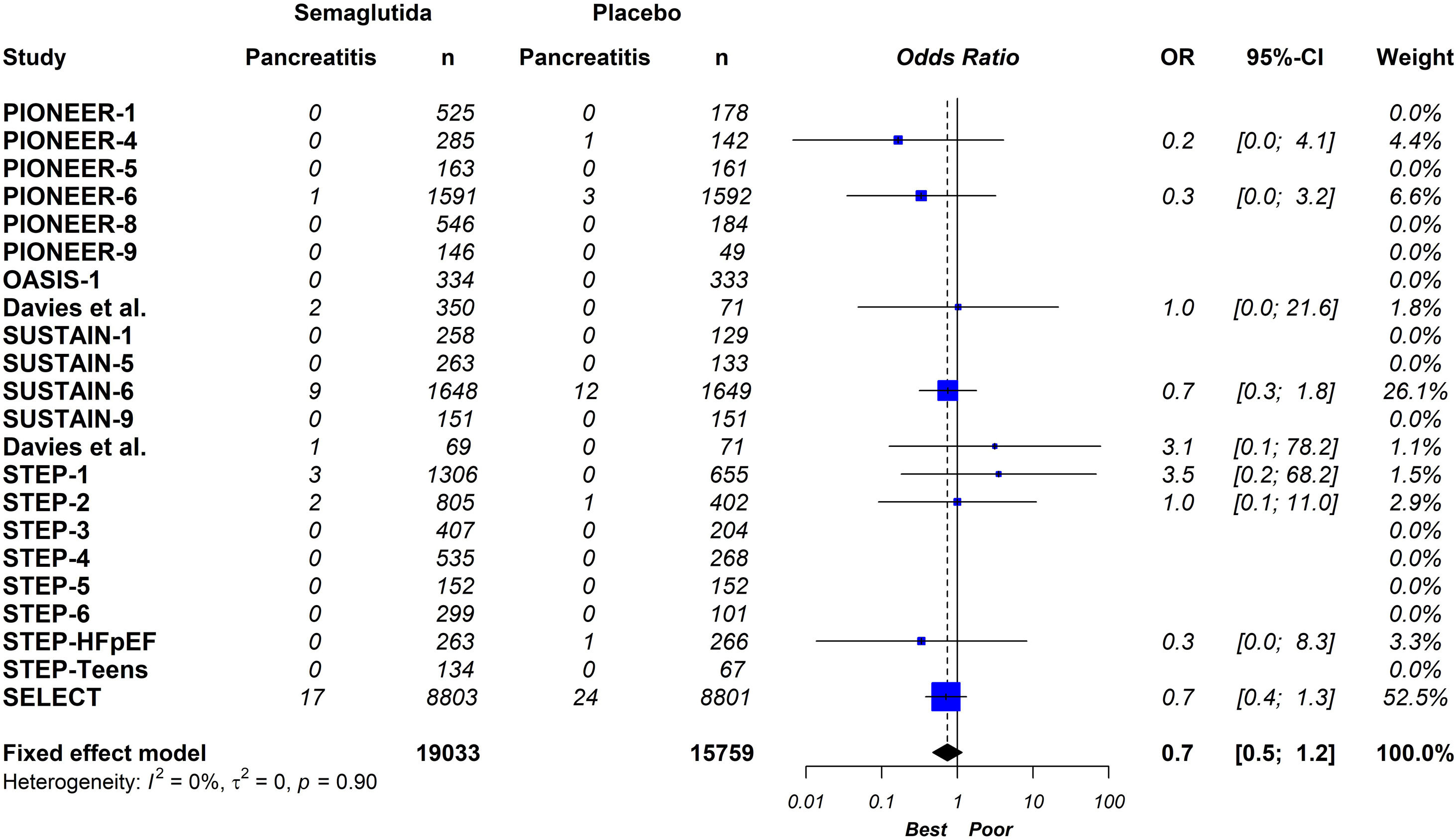
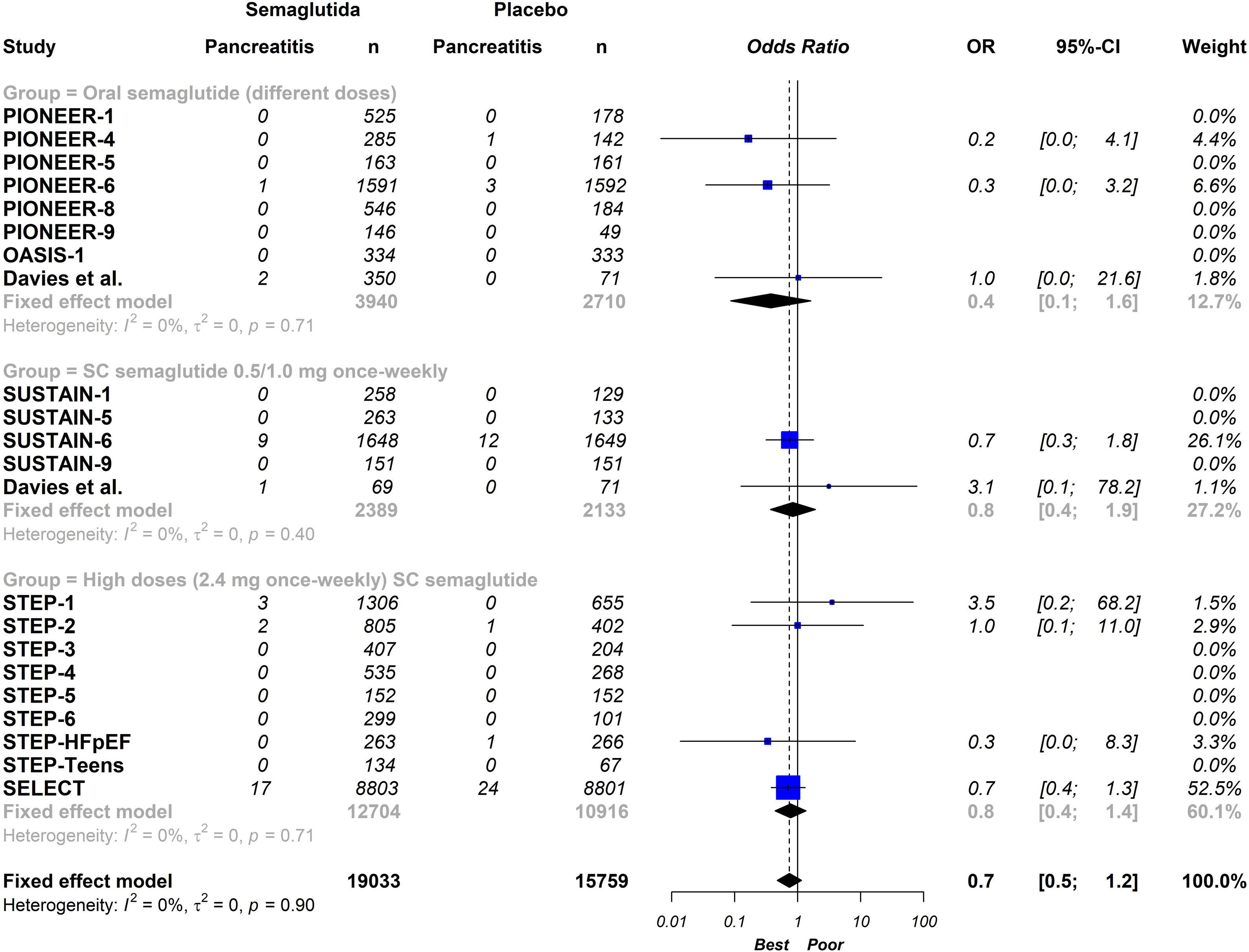
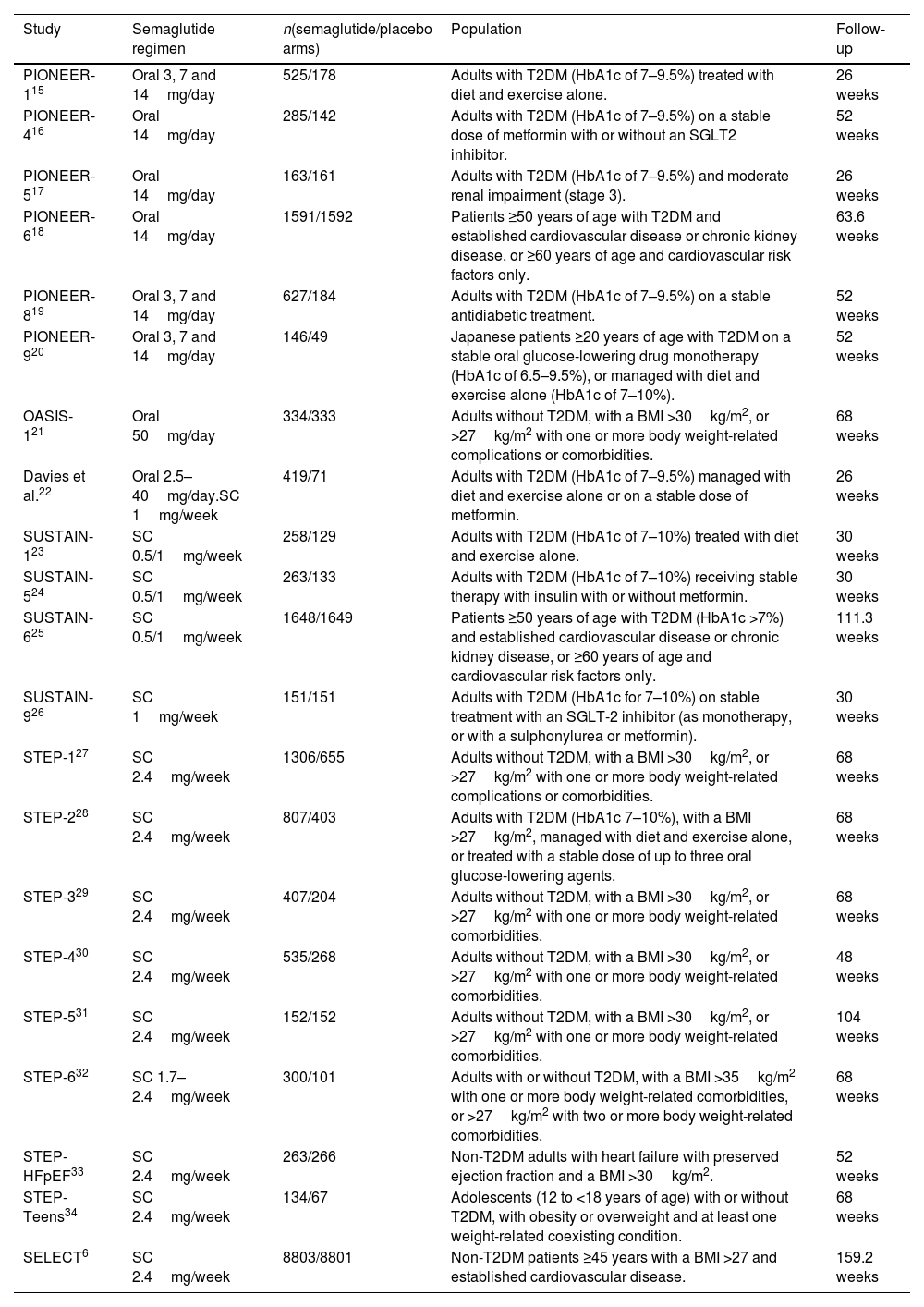
ResultsTwenty-one eligible trials of semaglutide, including 34,721 patients, were identified and considered eligible for the analyses. Globally, semaglutide therapy was not associated with an increased risk of acute pancreatitis (OR 0.7; 95% CI 0.5–1.2, I2 0%). When we analysed the studies according to the different schemes used, the results were similar (group with oral semaglutide: OR 0.40; 95% CI 0.10–1.60, I2 0%; group with low subcutaneous doses of semaglutide: OR 0.80; 95% CI 0.40–1.90, I2 0%; group with high subcutaneous doses of semaglutide: OR 0.70; 95% CI 0.50–1.20, I2 0%; interaction p-value=0.689).
ConclusionThis updated meta-analysis demonstrates that the use of semaglutide is not associated with an increased risk of acute pancreatitis compared to placebo. In the stratified analysis, the results were similar with the different semaglutide regimens analysed.
Algunas preocupaciones con respecto a la seguridad de la semaglutida aún persisten. El objetivo del presente metaanálisis actualizado es evaluar el riesgo de pancreatitis aguda con el uso de semaglutida, valorando los resultados según los diferentes esquemas terapéuticos.
MétodosRealizamos un metaanálisis actualizado de estudios aleatorizados y controlados con placebo, que hayan evaluado el uso de semaglutida e informaran la incidencia de pancreatitis aguda. Este metaanálisis se llevó a cabo de acuerdo con las directrices PRISMA. Se realizó un análisis global y estratificado según el esquema terapéutico utilizado. Se utilizó un modelo de efectos fijos.
ResultadosVeintiún ensayos clínicos fueron identificaron y considerados elegibles para este metaanálisis (34.721 pacientes). A nivel global, el tratamiento con semaglutida no se asoció con un mayor riesgo de pancreatitis aguda (OR 0,7; IC 95%: 0,5-1,2; I2 0%). Cuando analizamos los estudios según los diferentes esquemas utilizados, los resultados fueron similares (grupo con semaglutida oral: OR 0,40; IC 95% 0,10-1,60, I2 0%; grupo con dosis subcutáneas bajas de semaglutida: OR 0,80; IC 95% 0,40-1,90, I2 0%; grupo con altas dosis subcutáneas de semaglutida; OR 0,70; IC 95% 0,50-1,20, I2 0%; valor de p de interacción=0,689).
ConclusiónEl presente metaanálisis demostró que el uso de semaglutida no se asoció con un mayor riesgo de pancreatitis aguda en comparación con el placebo. En el análisis estratificado, los resultados fueron similares con los diferentes esquemas de semaglutida analizados.