Cardiovascular mortality is the leading cause of death in patients with prostate cancer (PC), metabolic syndrome (MS) being related to it. The main objective of this study was to determine the prevalence of MS in patients with CP undergoing androgen suppression (AS).
Materials and methodsWe performed a retrospective study of cases and controls that included 159 patients. The study group was made up of 53 patients with PC undergoing SA for a period exceeding 12 months. The control group had 53 patients with PC at the time of diagnosis and 53 patients with negative prostate biopsy. All the patients were evaluated for presence of MS according to NCEP-ATPIII criteria.
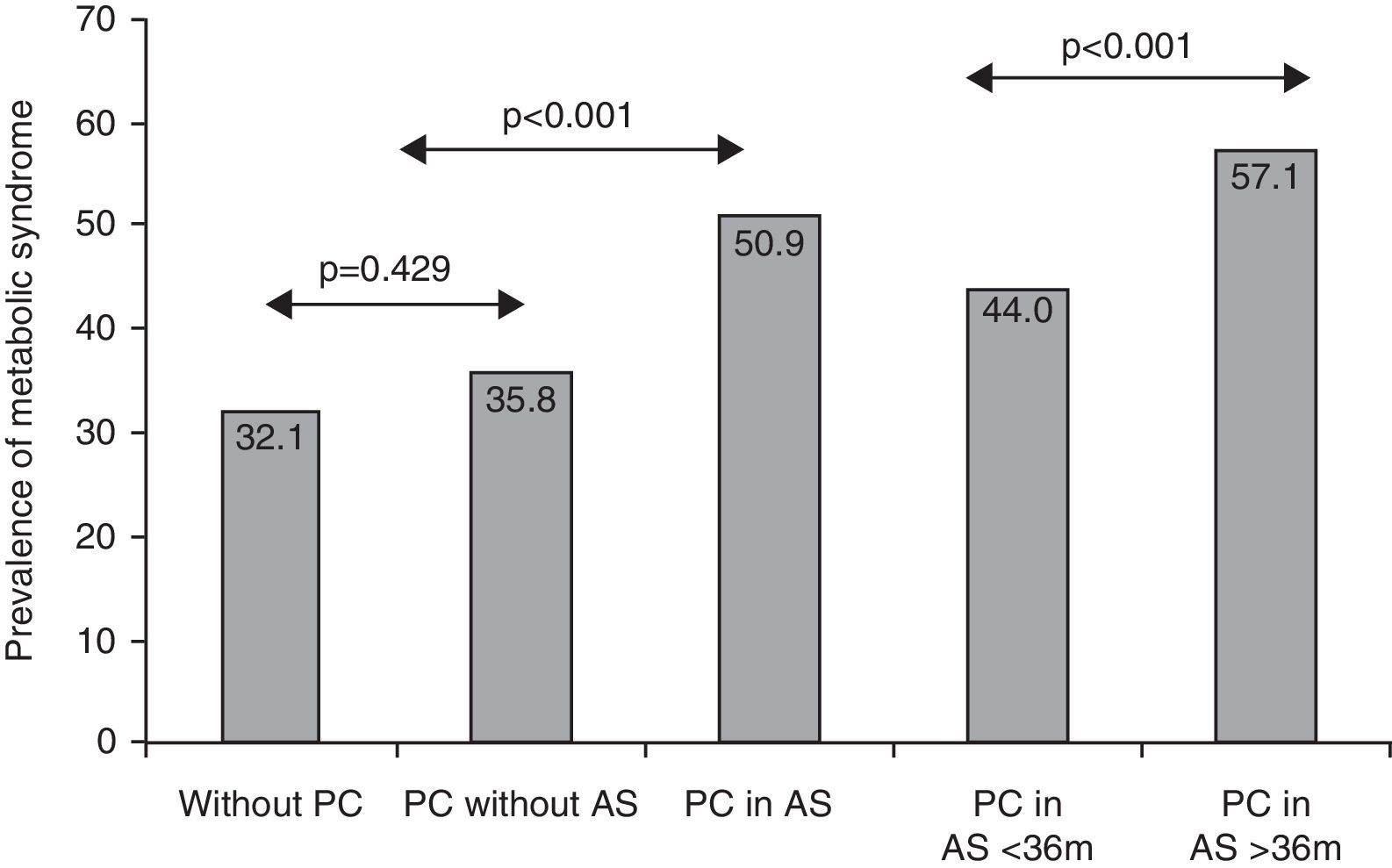
ResultsPrevalence of MS in patients without PC was 32.1% and in those with non-treated PC 35.8%, P=.324. In patients with PC undergoing AS, prevalence of MS was 50.9%, P<.001. When AS duration was less than 36 months, prevalence of MS was 44.0% and when greater than 36 months 57.1%, P<.001. Waist circumference and hyperglycemia were the two MS components that significantly increased. AS and its duration were independent predictors factors for the development of MS.
ConclusionsContinuous AS therapy increases the prevalence of MS and especially waist circumference and hyperglycemia. Development of MS increases according to AS duration.
La mortalidad cardiovascular es la primera causa de muerte en pacientes con cáncer de próstata (CP) y el síndrome metabólico (SM) está relacionado con ella. El objetivo principal de este estudio fue conocer la prevalencia del SM en pacientes con CP sometidos a supresión androgénica (SA).
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo de casos y controles que incluyó 159 pacientes. Cincuenta y tres pacientes con CP sometidos a SA durante un periodo superior a 12 meses formaron el grupo de casos; 53 pacientes con CP en el momento de su diagnóstico y 53 pacientes con biopsia prostática negativa formaron el grupo control. En todos los pacientes se evaluó la existencia de SM según los criterios del NCEP-ATPIII.
ResultadosLa prevalencia de SM en pacientes sin CP fue del 32,1% y en pacientes con CP no tratados fue del 35,8%; p=0,324. En pacientes con CP sometidos a SA la prevalencia de SM fue del 50,9%; p<0,001. Cuando la SA fue inferior a 36 meses se observó una prevalencia del 44,0% y cuando fue superior o igual a 36 meses del 57,1%; p<0,001. El perímetro abdominal (>102cm) y la hiperglucemia (>110mg/dl) fueron los 2 componentes del SM que se incrementaron significativamente. La SA y su duración fueron factores predictores independientes del desarrollo de SM.
ConclusionesLa SA continuada incrementa la prevalencia de SM y especialmente el perímetro abdominal y la hiperglucemia. Su desarrollo aumenta con la duración de la SA.