To analyze the influential factors in the response in prostatectomized patients with subsequent biochemical relapse (BCR) and treated with salvage radiotherapy (RTP).
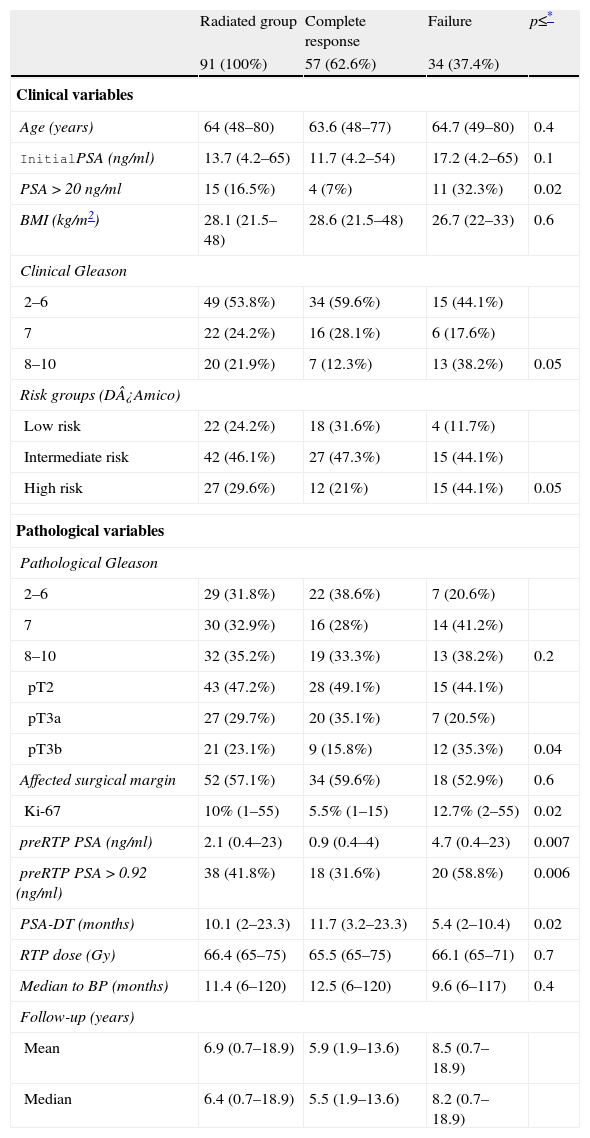
Materials and methodsWe analyzed 313 patients with pT2/pT3 prostate cancer who were receiving salvage therapy due to biochemical relapse (from a series of 1310 radical prostatectomies between 1989 and 2012). Of the 313 patients, 159 (50.8%) only received androgen deprivation (AD), 63 (20.1%) radiotherapy (RTP) plus concomitant AD and 91 (29.1%) only RTP. Of these, 57 (62.6%) have maintained complete response and 34 (37.4%) had failure response with post-RTP BCR.
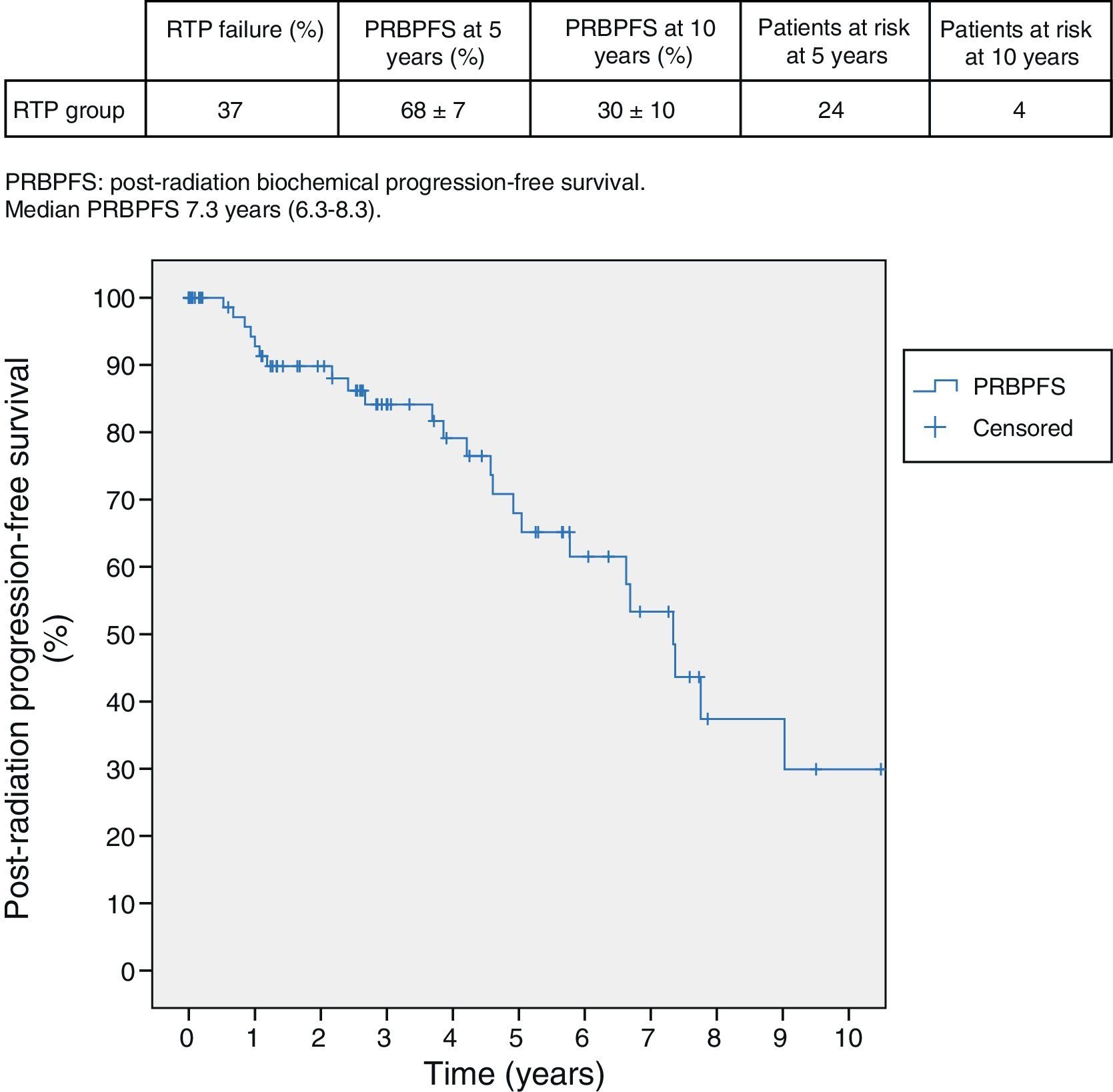
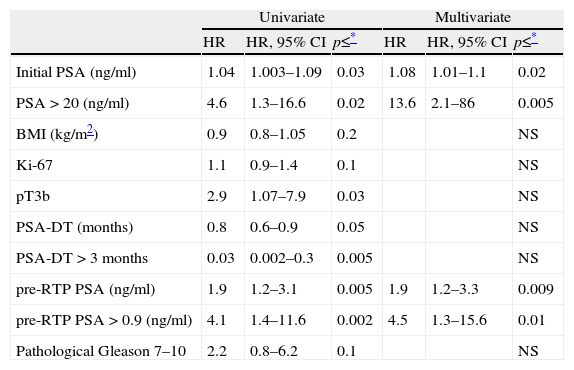
ResultsStudy of the group treated exclusively with salvage RTP. Ninety-one patients were treated with salvage RTP. Median follow-up was 6.4 years and median to recurrence 11 months. Post-RTP biochemical relapse-free survival (PRBRFS) was 68±7% and 30±10% in 5–10 years. Median PRBRFS was 7.3 years (6.3–8.3). Initial PSA (HR: 1.08; 95% CI: 1.01–1.1 P=0.02) with best PSA cut-off point PSA>20ng/ml (HR: 13.6; 95% CI: 2.1–86 P=0.005) and PSA pre-RTP (HR: 1.9; 95% CI: 1.2–3.3; P=0.009), best PSA cut-off point PSA preRTP 0.92ng/ml (HR: 4.5; 95% CI: 1.3–15.6; P=0.01) showed independent influence in the response in the multivariate study. PRBRFS at 5 years was 81±9% versus 58±9% with initial PSA<20 or >20ng/ml (P=0.03). PRBRFS at 5 years was 93±5% versus 53±10% according to PSA pre-RTP<0.9 or >0.9ng/ml (P=0.02).
ConclusionsIn patients treated with salvage RTP after radical prostatectomy, the preoperative PSA>20ng/ml and PSA preRTP>0.92ng/ml show an independent influence on the response.
Analizar en los pacientes prostatectomizados con posterior progresión bioquímica (PB) y tratados con radioterapia de rescate (RTP) los factores influyentes en la respuesta.
Material y métodosAnalizamos 313 pacientes con cáncer de próstata pT2/pT3 que reciben tratamiento de rescate por PB (de una serie de 1.310 pacientes operados entre 1989-2012). De los 313 pacientes 159 (50,8%) reciben solo deprivación androgénica (DA), 63 (20,1%) radioterapia (RTP) más DA concomitante y 91 (29,1%) solo RTP, de los cuales 57 (62,6%) mantienen respuesta completa y 34 (37,4%) fracaso del tratamiento.
ResultadosEstudio del grupo tratado solo con RTP de rescate: 91 pacientes son tratados con RTP de rescate. Mediana de seguimiento 6,4 años. Mediana hasta progresión 11 meses. La supervivencia libre de progresión bioquímica post-RTP (SLPBPR) es de 68±7% y 30±10% en 5 y 10 años y la mediana de SLPBPR 7,3 años (6,3-8,3). En el análisis multivariado presentan influencia independiente en la respuesta: el PSA inicial (HR: 1,08; IC 95%: 1,01-1,1; p=0,02) con mejor punto de corte PSA>20ng/ml (HR: 13,6; IC 95%: 2,1-86; p=0,005) y PSA pre-RTP (HR: 1,9; IC 95%: 1,2-3,3 p=0,009), mejor punto de corte PSA preRTP de 0,92ng/ml (HR: 4,5; IC95% 1,3-15,6; p=0,01). SLPBPR a 5 años 81±9% frente a 58±9% con PSA inicial <20 o >20ng/ml (p=0,03). SLPBPR a 5 años 93±5% frente a 53±10% según PSA pre-RTP <0,9 o >0,9ng/ml (p=0,02).
ConclusionesEn los pacientes prostatectomizados tratados con RTP de rescate el PSA preoperatorio >20ng/ml y el PSA preRTP >0,92ng/ml tienen influencia independiente en la respuesta.