To analyze gene expression profiles of prostate cancer (PCa) with the aim of determining the relevant differentially expressed genes and subsequently ascertaining whether this differential expression is maintained in post-prostatic massage (PPM) urine samples.
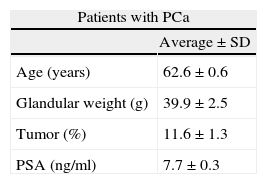
Materials and methodsForty-six tissue specimens (36 from PCa patients and 10 controls) and 158 urine PPM-urines (113 from PCa patients and 45 controls) were collected between December 2003 and May 2007. DNA microarrays were used to identify genes differentially expressed between tumor and control samples. Ten genes were technically validated in the same tissue samples by quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR). Forty-two selected differentially expressed genes were validated in an independent set of PPM-urines by qRT-PCR.
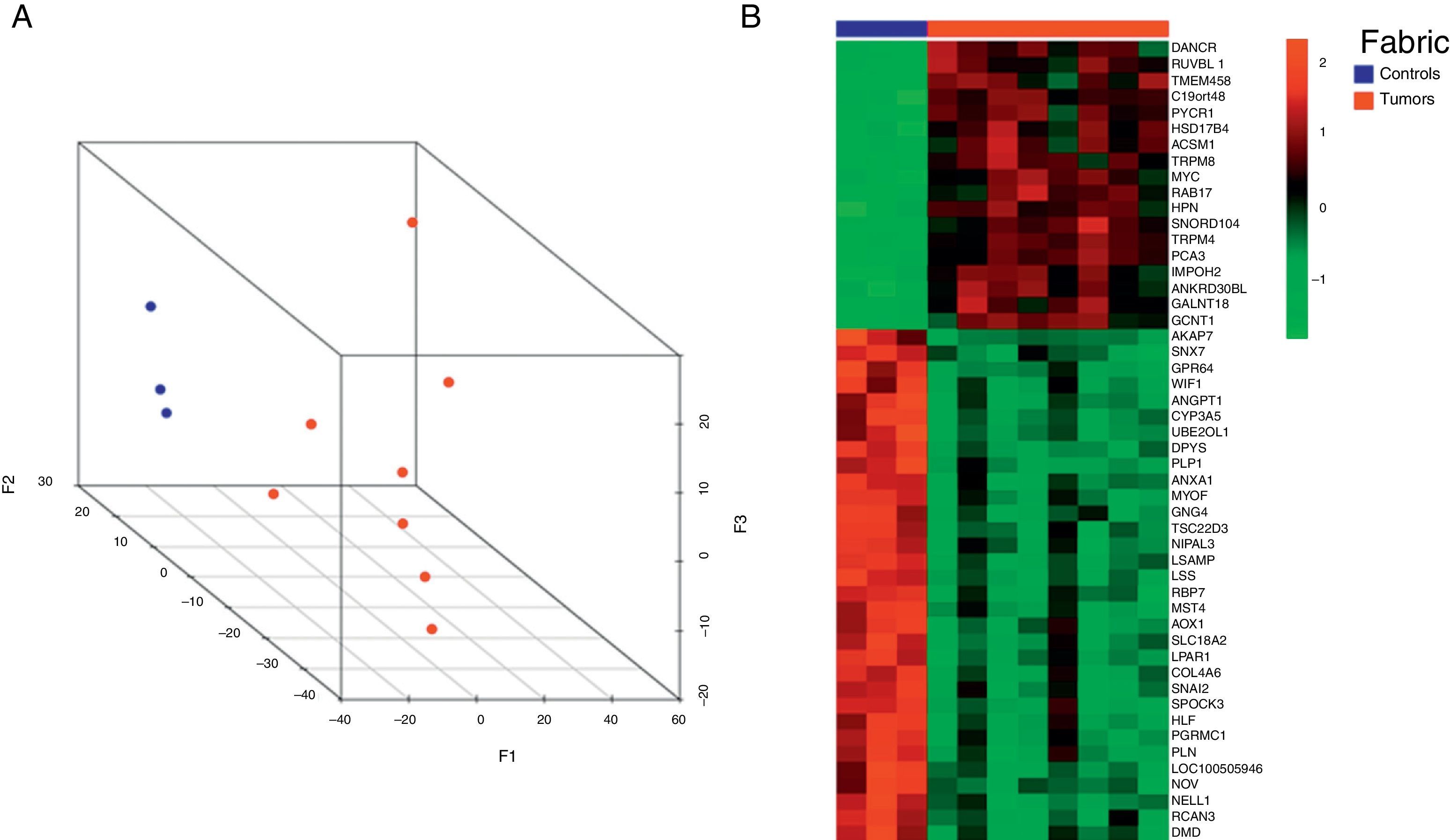
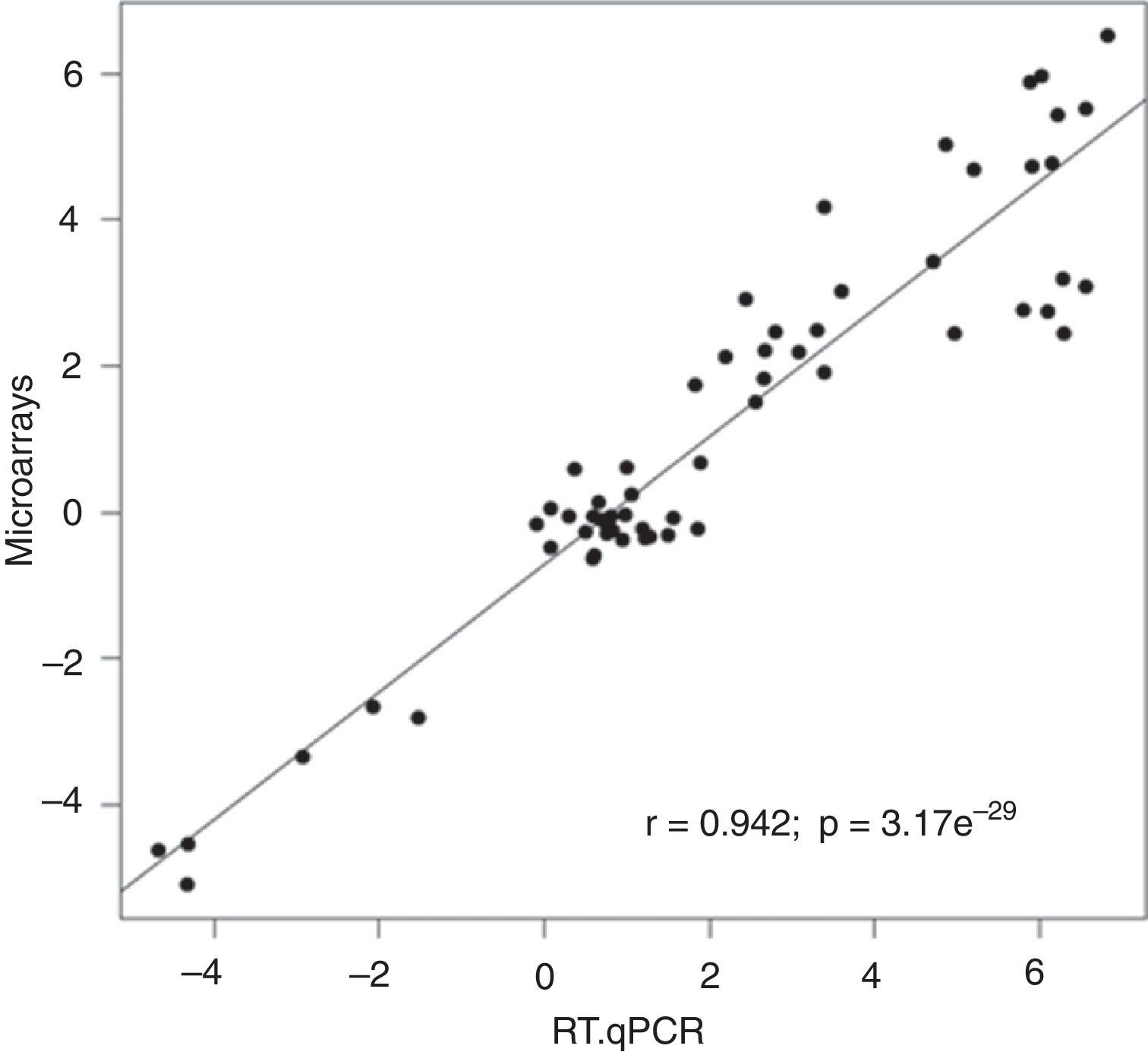
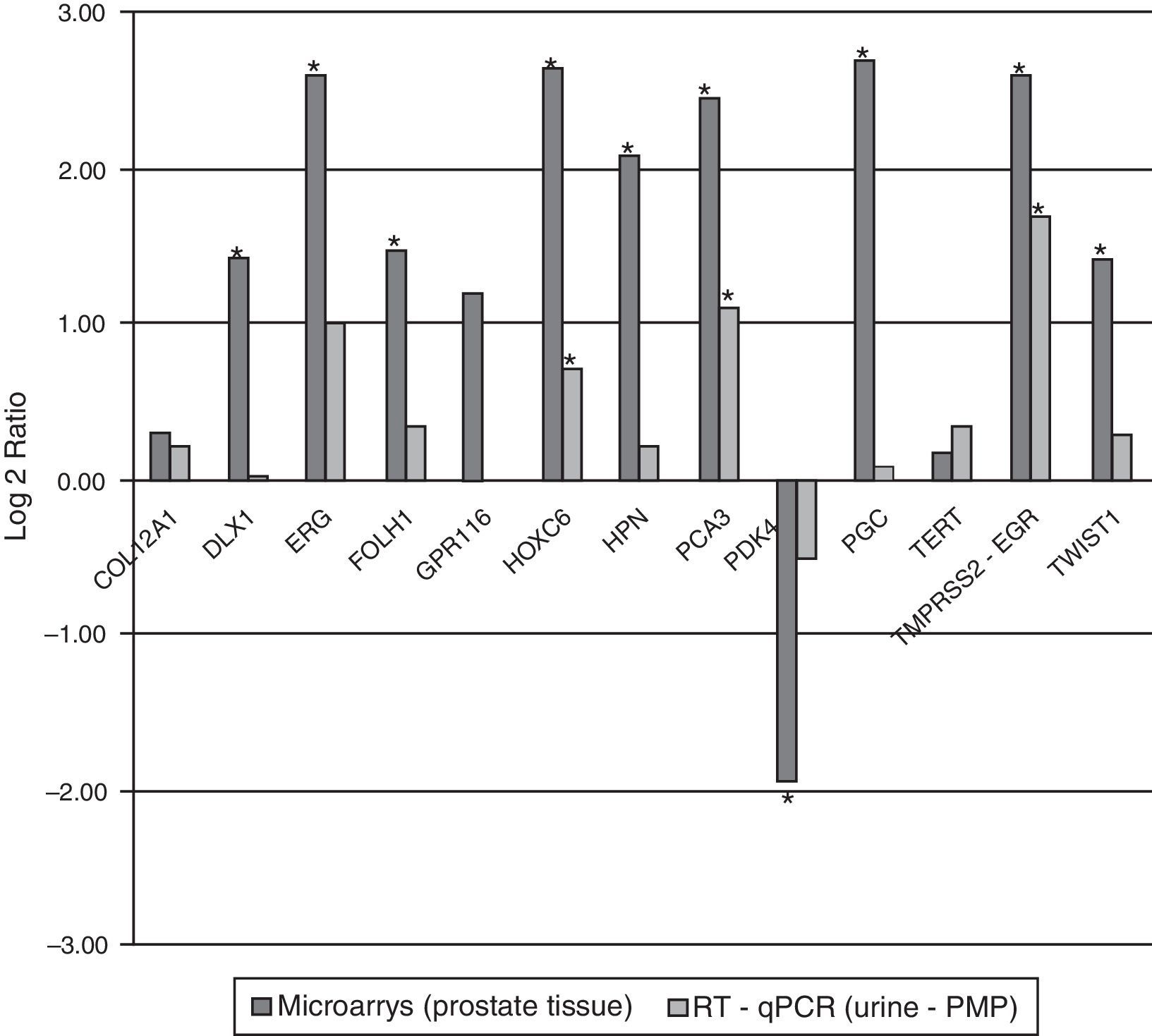
ResultsMultidimensional scaling plot according to the expression of all the microarray genes showed a clear distinction between control and tumor samples. A total of 1047 differentially expressed genes (FDR≤0.1) were identified between both groups of samples. We found a high correlation in the comparison of microarray and RT-qPCR gene expression levels (r=0.928, p<0.001). Thirteen genes maintained the same fold change direction when analyzed in PPM-urine samples and in four of them (HOXC6, PCA3, PDK4 and TMPRSS2-ERG), these differences were statistically significant (p<0.05).
ConclusionThe analysis of PCa by DNA microarrays provides new putative mRNA markers for PCa diagnosis that, with caution, can be extrapolated to PPM-urines.
Analizar los perfiles de expresión génica del cáncer de próstata (CaP) e identificar los genes diferencialmente expresados. Determinar si la expresión diferencial en tejido se mantiene en muestras de orina-posmasaje prostático (PMP).
Material y métodosUn total de 46 muestras de tejido prostático (36 de pacientes con CaP y 10 controles) y 158 orinas-PMP (113 de pacientes con CaP y 45 controles) se recogieron entre diciembre de 2003 y mayo de 2007. Se utilizaron microarrays de ADN para identificar los genes diferencialmente expresados entre las muestras de tejido tumorales y las controles. Diez genes fueron seleccionados para la validación técnica de los microarrays en las mismas muestras tisulares mediante PCR cuantitativa (RT-qPCR). Se seleccionaron 42 genes para ser validados en muestras de orina-PMP mediante RT-qPCR.
ResultadosEl gráfico de escalado multidimensional mostró una clara separación entre las muestras de tejido tumorales y las controles. Se han identificado 1.047 genes diferencialmente expresados (FDR≤0,1) entre los 2 grupos. La correlación entre los datos de microarrays y RT-qPCR fue alta (r=0,928, p<0,001). Trece genes mantuvieron el mismo sentido de expresión diferencial al ser analizados en orinas-PMP y 4 de ellos (HOXC6, PCA3, PDK4 y TMPRSS2-ERG) mostraron diferencias de expresión estadísticamente significativas entre orinas-PMP tumorales y controles (p<0,05).
ConclusiónExiste un perfil de expresión génica diferencial en el CaP. Aunque la extrapolación de la expresión génica obtenida en tejido prostático a orina-PMP se debe realizar con precaución, el análisis del tejido prostático permite la identificación de nuevos biomarcadores para diagnóstico no invasivo del CaP.