We performed a meta-analysis to evaluate the effect of en-bloc transurethral resection vs. conventional transurethral resection for primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
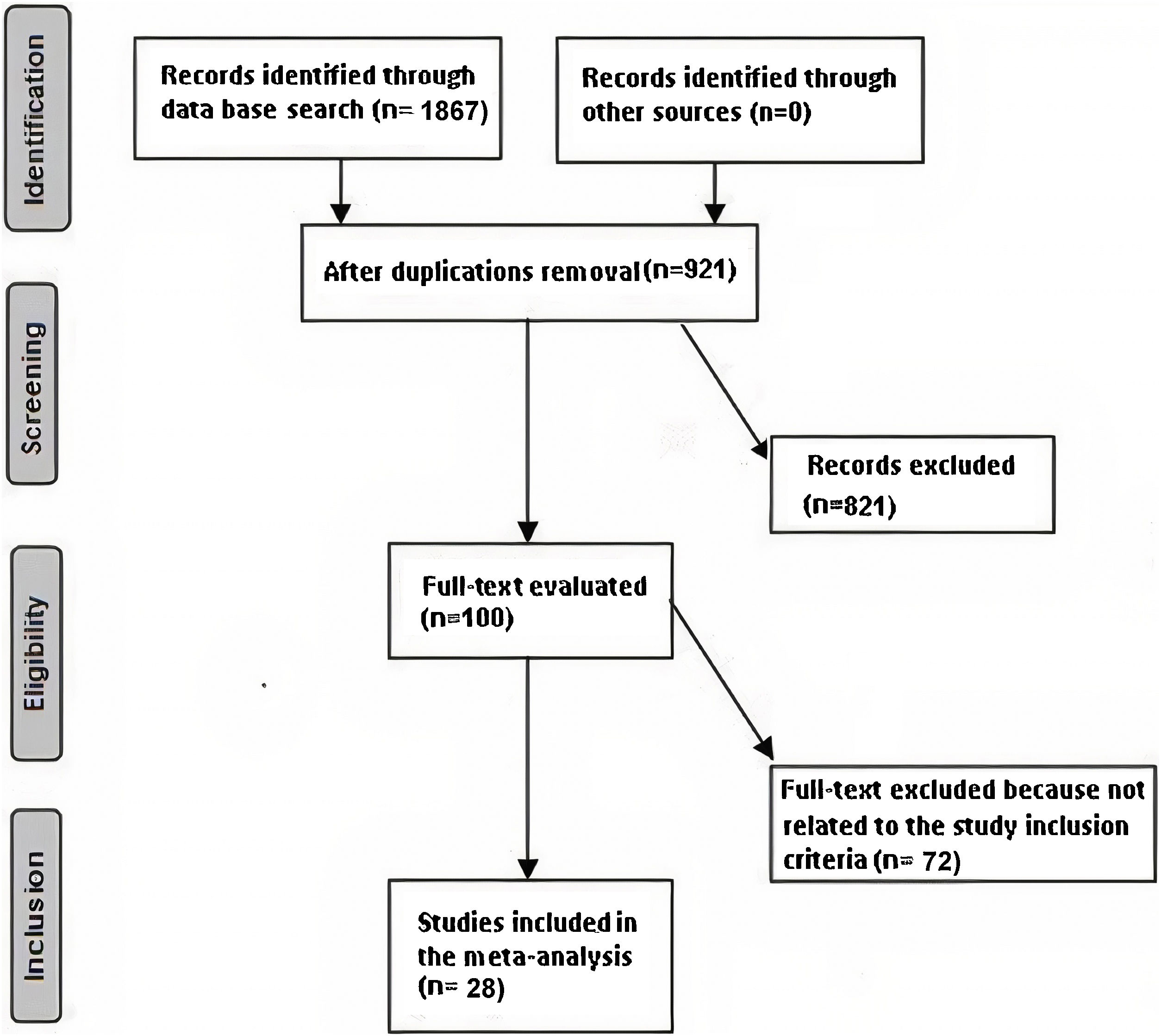
MethodsA systematic literature search up to January 2022 was done and 28 studies included 3714 primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer subjects at the start of the study; 1870 of them were en-bloc transurethral resection, and 1844 were conventional transurethral resection for primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. We calculated the odds-ratio (OR) and mean-difference (MD) with 95% confidence-intervals (CIs) to evaluate the effect of en-bloc transurethral resection compared with conventional transurethral resection for primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer by the dichotomous or continuous methods with random or fixed-effects models.
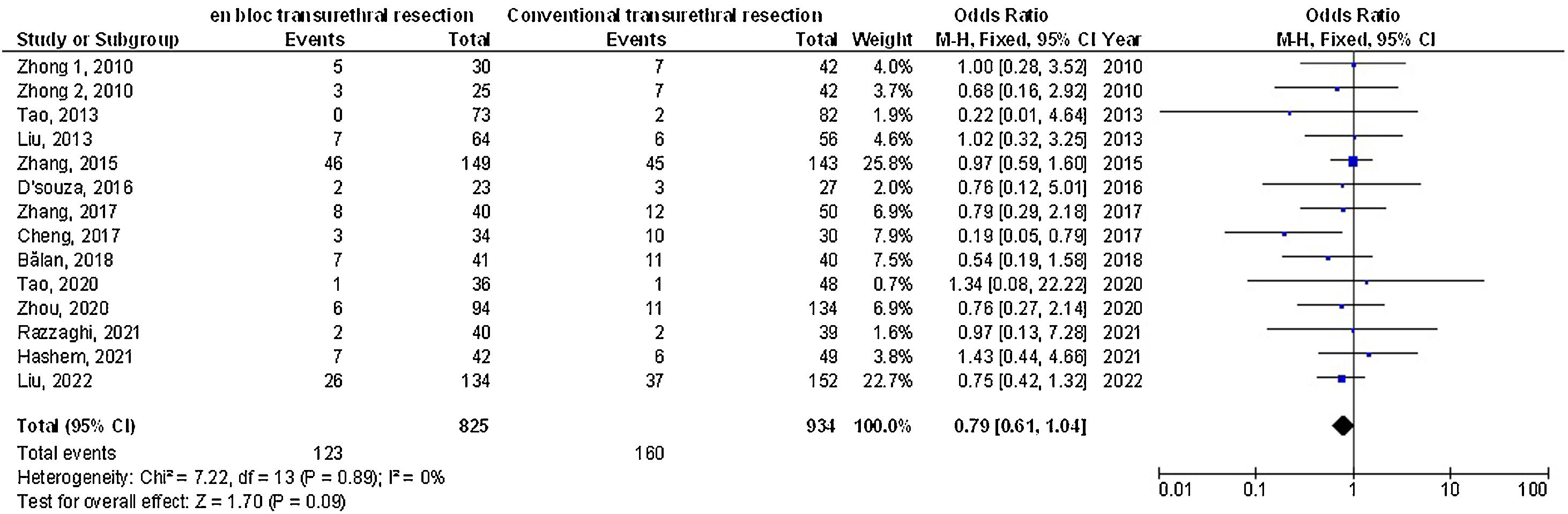
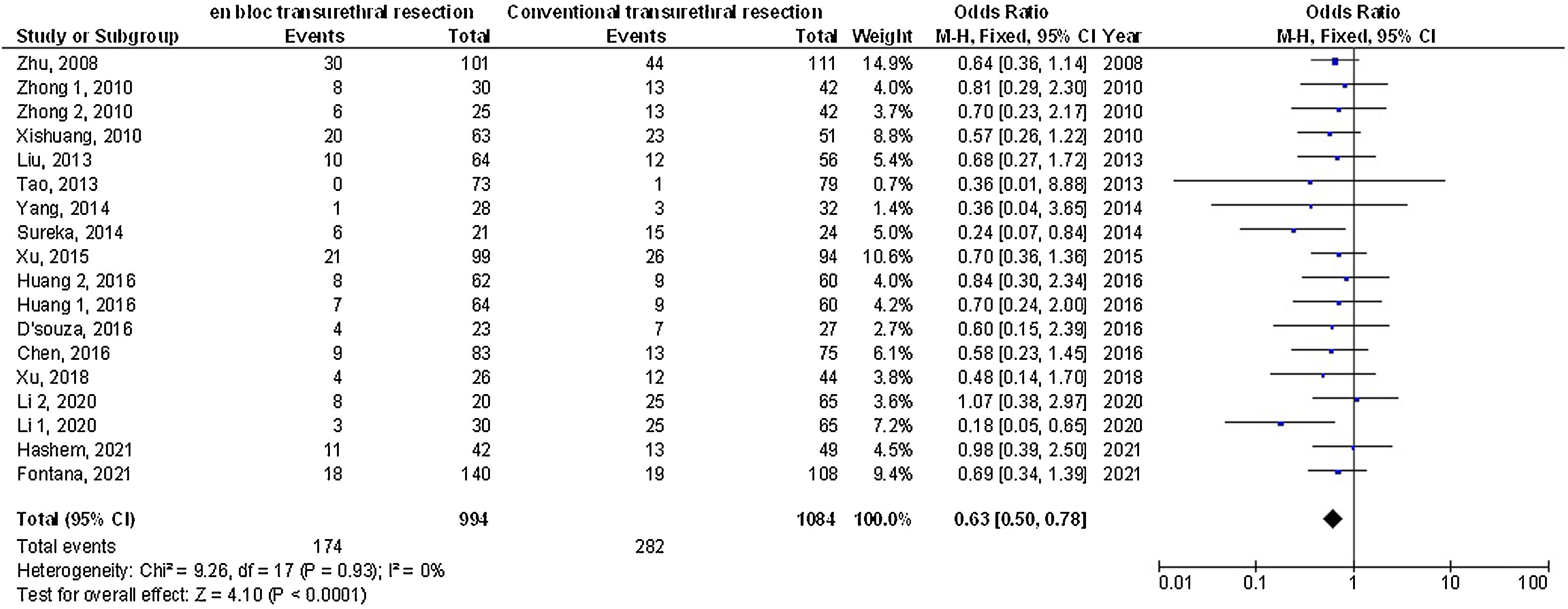
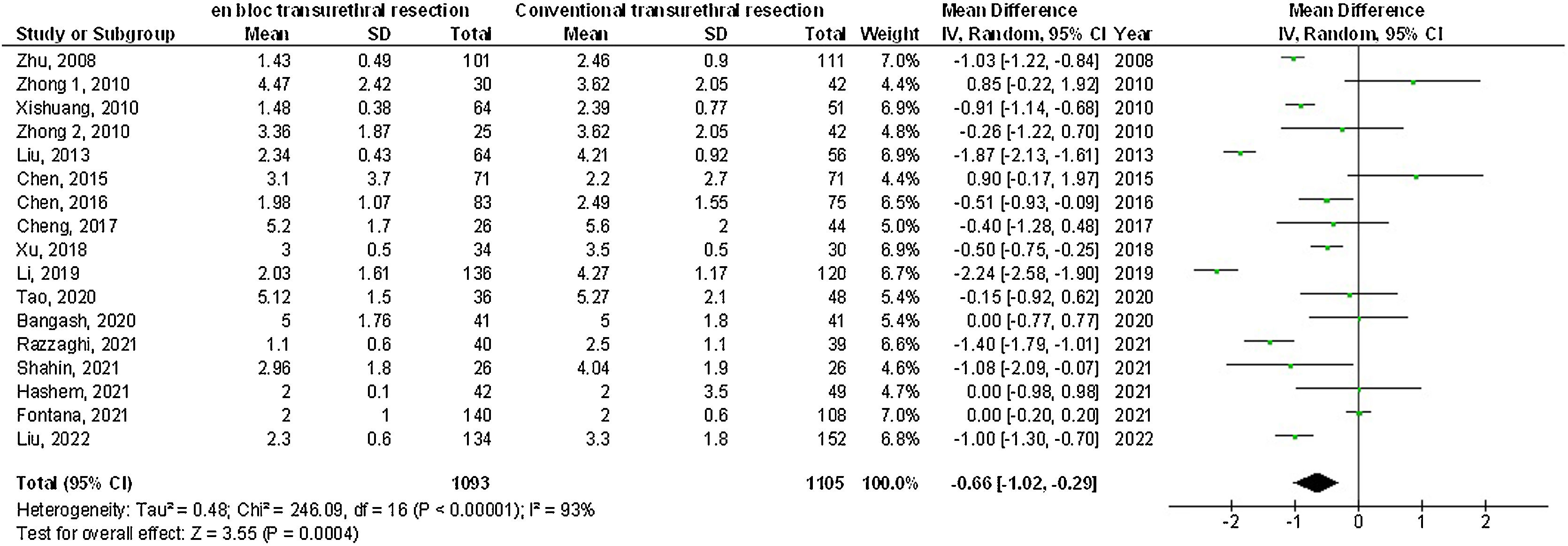
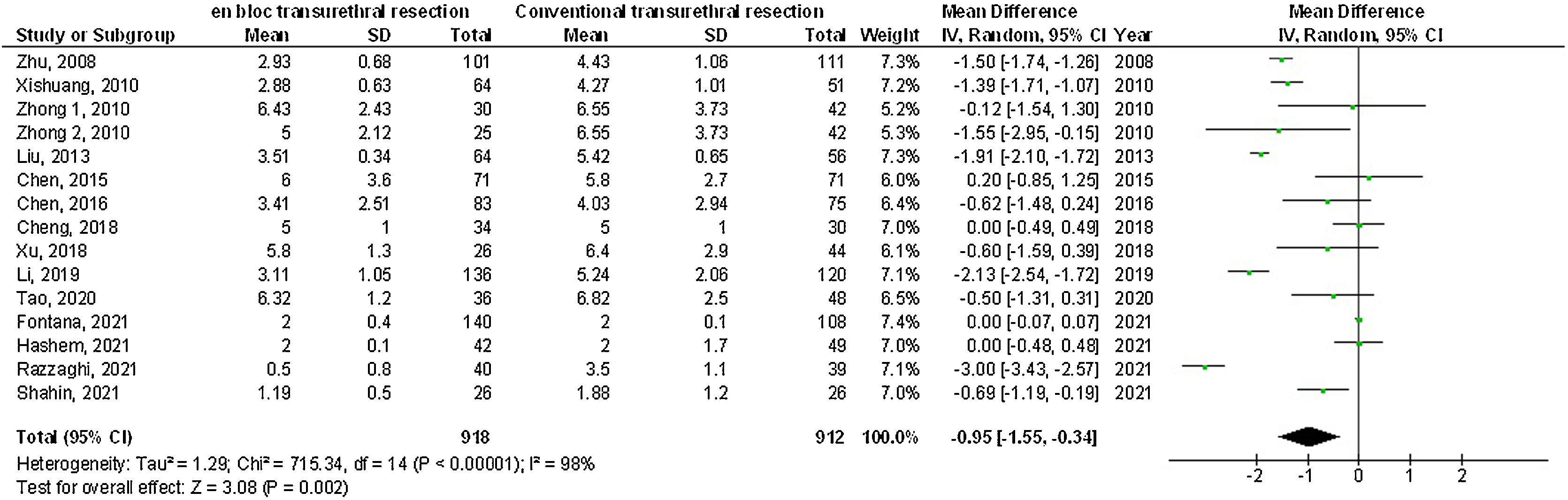
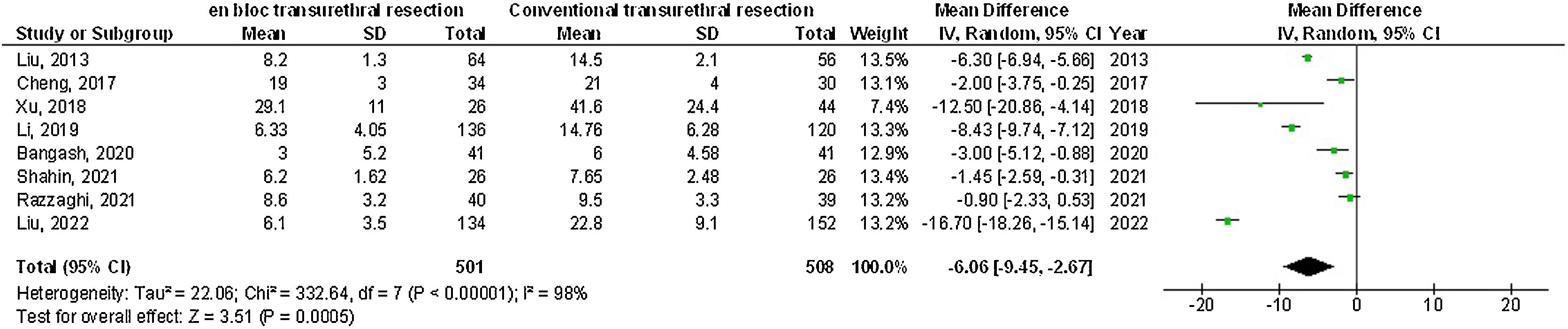
ResultsEn-bloc transurethral resection had significantly lower twenty-four-month recurrence (OR: 0.63; 95%CI: 0.50–0.78; p < 0.001), catheterization-time (MD: –0.66; 95%CI: –1.02–[–0.29]; p < 0.001), length of hospital stay (MD: –0.95; 95%CI: –1.55–[–0.34]; p = 0.002), postoperative bladder irrigation duration (MD: –6.06; 95%CI: –9.45–[–2.67]; p < 0.001), obturator nerve reflex (OR: 0.08; 95%CI: 0.02–0.34; p = 0.03), and bladder perforation (OR: 0.14; 95%CI: 0.06–0.36: p < 0.001) and no significant difference in the 12-month-recurrence (OR: 0.79; 95%CI: 0.61–1.04; p = 0.09), the operation time (MD: 0.67; 95%CI: –1.92 to 3.25; p = 0.61), and urethral stricture (OR: 0.46; 95%CI: 0.14–1.47; p = 0.0.19) compared with conventional transurethral resection for primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer subjects.
ConclusionsEn-bloc transurethral resection had a significantly lower twenty-four-month recurrence, catheterization time, length of hospital stay, postoperative bladder irrigation duration, obturator nerve reflex, bladder perforation, and no significant difference in the twelve-month recurrence, operation time, and urethral stricture compared with conventional transurethral resection for primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer subjects. Further studies are required.
Se realizó un metaanálisis para evaluar el efecto de la resección transuretral en bloque en comparación con la resección transuretral convencional para el cáncer de vejiga primario no músculo-infltrante.
MétodosSe realizó una búsqueda sistemática en la literatura hasta enero de 2022 y se incluyeron 28 estudios con 3.714 sujetos con cáncer de vejiga primario no músculo-infltrante al inicio del estudio; a 1.870 de ellos se les efectuó una resección transuretral en bloque y a 1.844 una resección transuretral convencional para el cáncer de vejiga primario no músculo-infltrante. Se calculó la odds-ratio (OR) y la diferencia de medias (DM) con intervalos de confianza (IC) del 95% para evaluar el efecto de una y otra en el cáncer primario de vejiga no invasivo por métodos dicotómicos o continuos con un modelo de efectos aleatorios o fijos.
ResultadosLa resección transuretral en bloque obtuvo valores significativamente menores en términos de recurrencia a los 24 meses (OR: 0,63; IC 95%: 0,50-0,78; p < 0,001), tiempo de sondaje (DM: –0,66; IC 95%: –1,02-[–0,29]; p < 0,001); duración de la estancia hospitalaria (DM: –0,95; IC 95%: –1,55-[–0,34]; p = 0,002), tiempo de irrigación vesical postoperatoria (DM: –6,06; IC 95%: –9,45-[–2,67]; p < 0,001), contracción del nervio obturador (OR: 0,08; IC 95%: 0,02–0,34; p = 0,03) y perforación de la vejiga (OR: 0,14; IC?95%: 0,06–0,36; p < 0,001) y no hubo diferencias significativas en cuanto a la recurrencia a los 12 meses (OR: 0,79; IC?95%: 0,61–1,04: p = 0,09), tiempo quirúrgico (DM: 0,67; IC?95%: –1,92–3,25; p = 0,61) y estenosis uretral (OR: 0,46; IC 95%: 0,14–1,47; p = 0,0,19) en comparación con la resección transuretral convencional para sujetos con cáncer de vejiga primario no invasivo.
ConclusionesLa resección transuretral en bloque tuvo resultados significativamente menores en recurrencia a los 24 meses, tiempo de sondaje, duración de la estancia hospitalaria, duración de la irrigación vesical postoperatoria, reflejo del nervio obturador y perforación de la vejiga y no tuvo ninguna diferencia significativa en la recurrencia a los 12 meses, el tiempo quirúrgico y la restricción uretral respecto a la resección transuretral convencional para sujetos con cáncer de vejiga primario no invasivo. Se necesitan más estudios.