To address the effect of resveratrol and other red wine polyphenols on cell proliferation, apoptosis and androgen receptor (AR) expression in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells.
Materials and methodsLNCaP cells (5×102) were cultured in microtiter plate modules and treated with gallic acid, tannic acid and quercetin (1, 5 and 10μM), rutin and morin (25, 50 and 75μM) and resveratrol (5, 10 and 25μM). To address the extent of proliferation at 24, 48, 72 and 96h, a colorimetric immunoassay method was used. An activity caspase 3/7 detection assay was used to disclose apoptosis at 24, 48 and 72h. AR mARN levels were determined by real time RT-PCR.
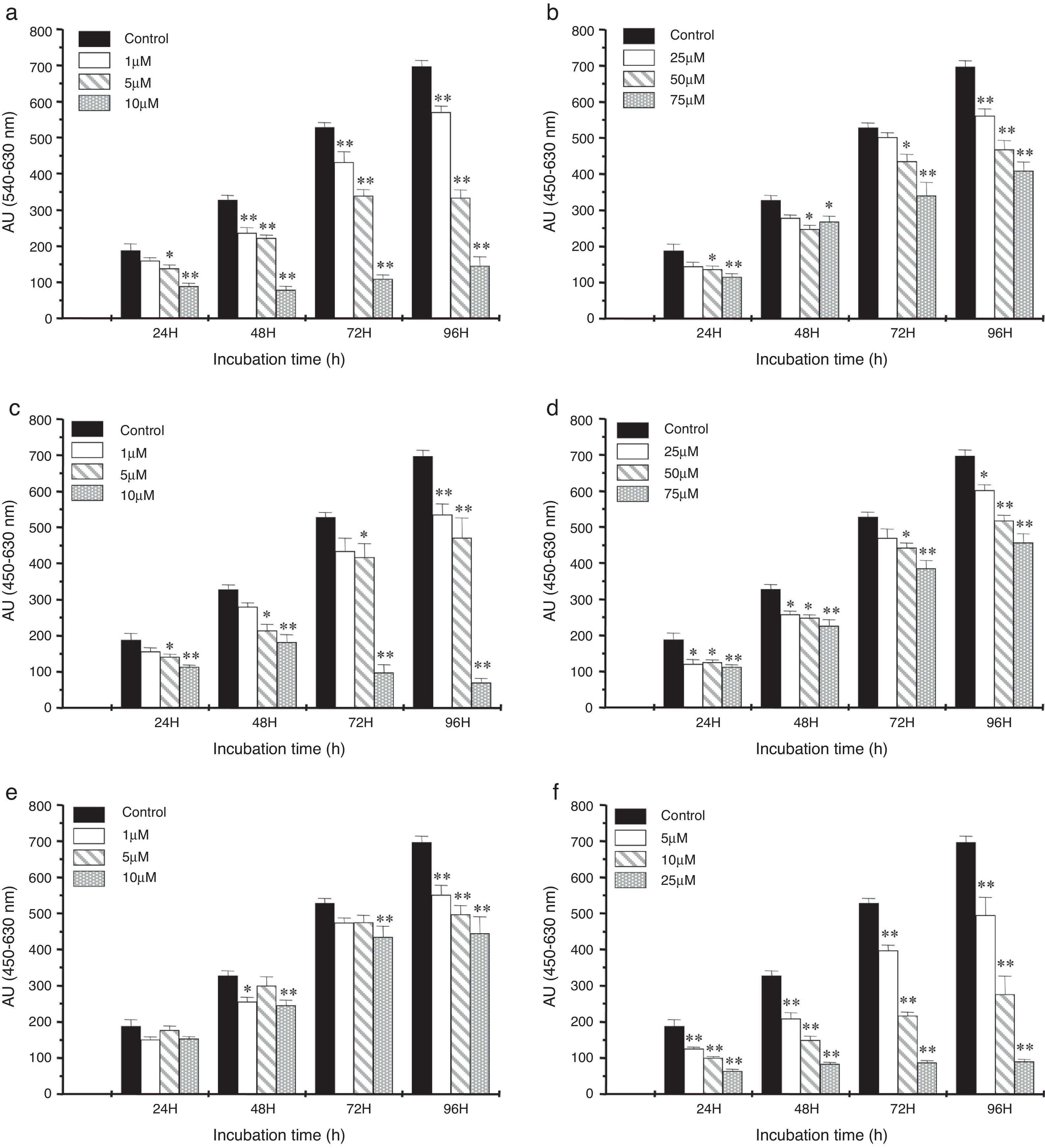
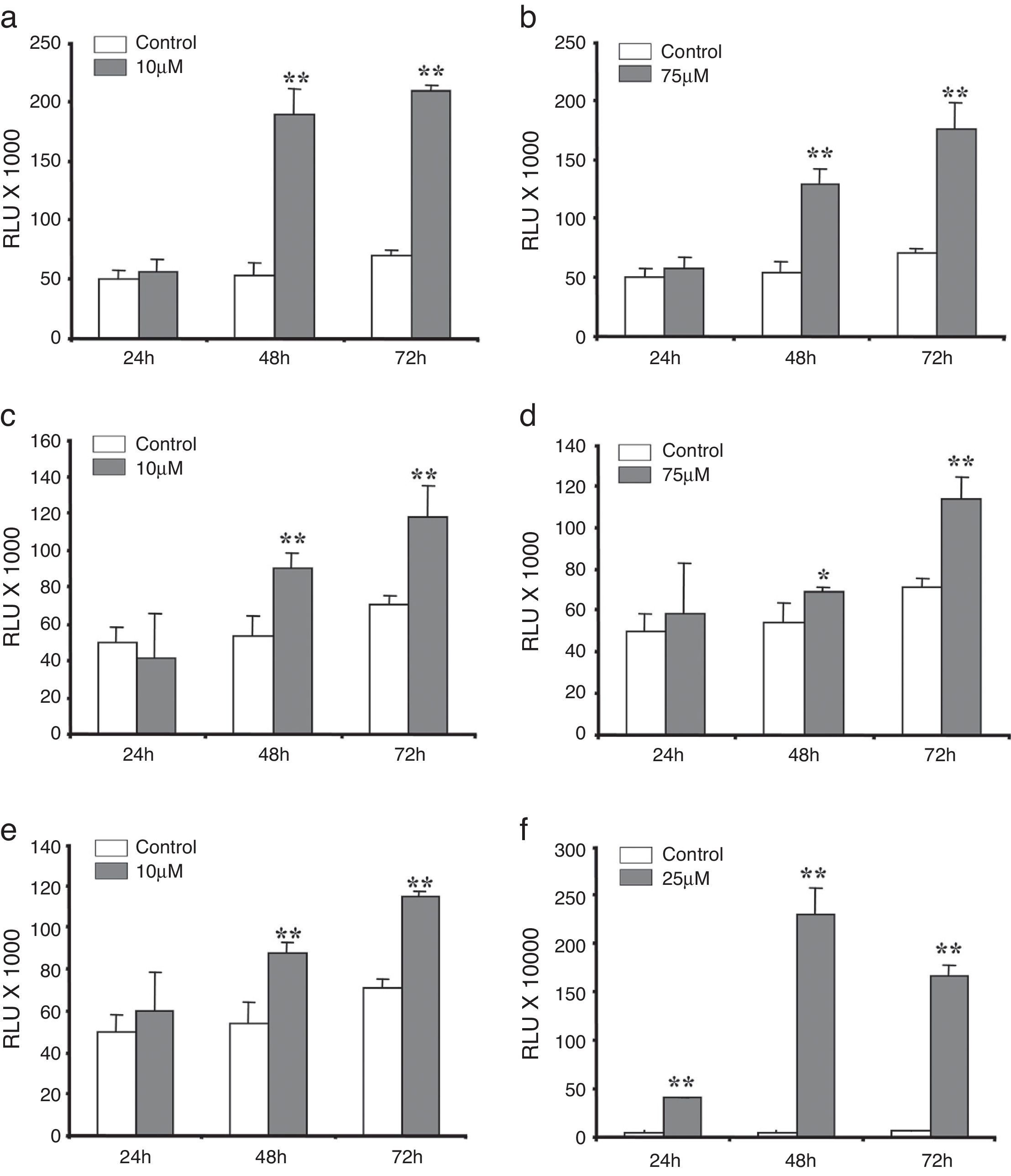
ResultsAll polyphenols studied significantly inhibited (P<.05) cell proliferation compared to control. However, there were moderate differences between them. Resveratrol was the strongest inhibitor at different times and doses. Also, caspase-3 and caspase-7 activity was significantly higher (P<.05) than control in the presence of all the compounds, but the earlier response was achieved by resveratrol. Resveratrol, quercetin and morin were the only nutrients that significantly inhibited AR mRNA expression. Again resveratrol produced the highest inhibition (90–250 times less than control), followed by morin (67–100 times) and quercetin (55–91 times).
ConclusionsAll polyphenols studied showed important antiproliferative effects and induced apoptosis when added to LNCaP cells culture. We confirm that resveratrol, morin and quercetin may achieve such effect through reduced expression of AR. The synergistic effects of these compounds and their potential to prevent progression of hormone-dependent prostate cancer merit further study.
Abordar el efecto del resveratrol y otros polifenoles del vino tinto sobre la proliferación celular, la apoptosis y la expresión del receptor androgénico (RA) en células LNCaP de cáncer de próstata humano.
Materiales y métodosLas células LNCaP (5×102) se cultivaron en módulos de placas de microtitulación y se trataron con ácido gálico, ácido tánico y quercetina (1, 5 y 10μM), rutina y morina (25, 50 y 75μM) y resveratrol (5, 10 y 25μM). Para abordar el alcance de la proliferación a las 24, 48, 72 y 96h se utilizó un método de inmunoanálisis colorimétrico. Se utilizó un ensayo de detección de actividad de caspasa 3/7 para revelar la apoptosis a las 24, 48 y 72h. Se determinaron niveles de ARNm de RA mediante RT-PCR a tiempo real.
ResultadosTodos los polifenoles estudiados inhibieron significativamente (p<0,05) la proliferación celular en comparación con el control. Sin embargo, hubo diferencias moderadas entre ellos. El resveratrol fue el inhibidor más fuerte en diferentes momentos y dosis. También la actividad de caspasa-3 y caspasa-7 era significativamente mayor (p<0,05) que el control en la presencia de todos los compuestos, pero la respuesta anterior se logró por el resveratrol. El resveratrol, la quercetina y la morina fueron los únicos nutrientes que inhibían significativamente la expresión de ARNm de RA. Una vez más el resveratrol produjo la inhibición más alta (90-250 veces menor que el control), seguido por morina (67-100 veces) y quercetina (55-91 veces).
ConclusionesTodos los polifenoles estudiados mostraron importantes efectos antiproliferativos y apoptosis inducida cuando se añadieron al cultivo de células LNCaP. Confirmamos que el resveratrol, la morina y la quercetina pueden lograr tal efecto a través de la reducción de expresión de RA. Los efectos sinérgicos de estos compuestos y su potencial para prevenir la progresión del cáncer de próstata hormono-dependiente merecen ser estudiados en profundidad.