To evaluate the biomechanical properties of a type of monofilament polypropylene mesh used to repair vaginal prolapse, as well as the effects of the inclusion of standard size orifices, called “helper orifices,” on the interface resistance in the receiving area.
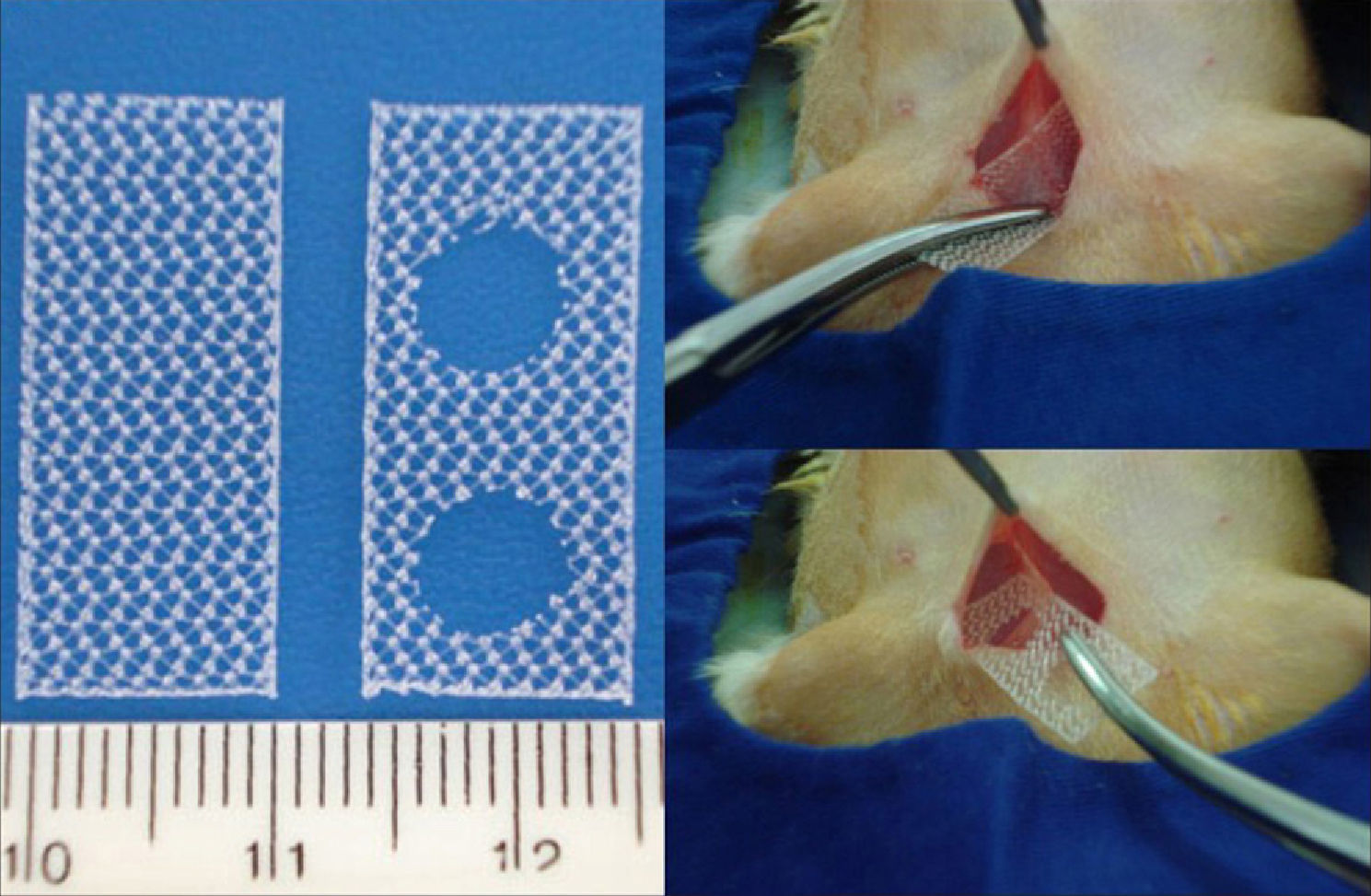
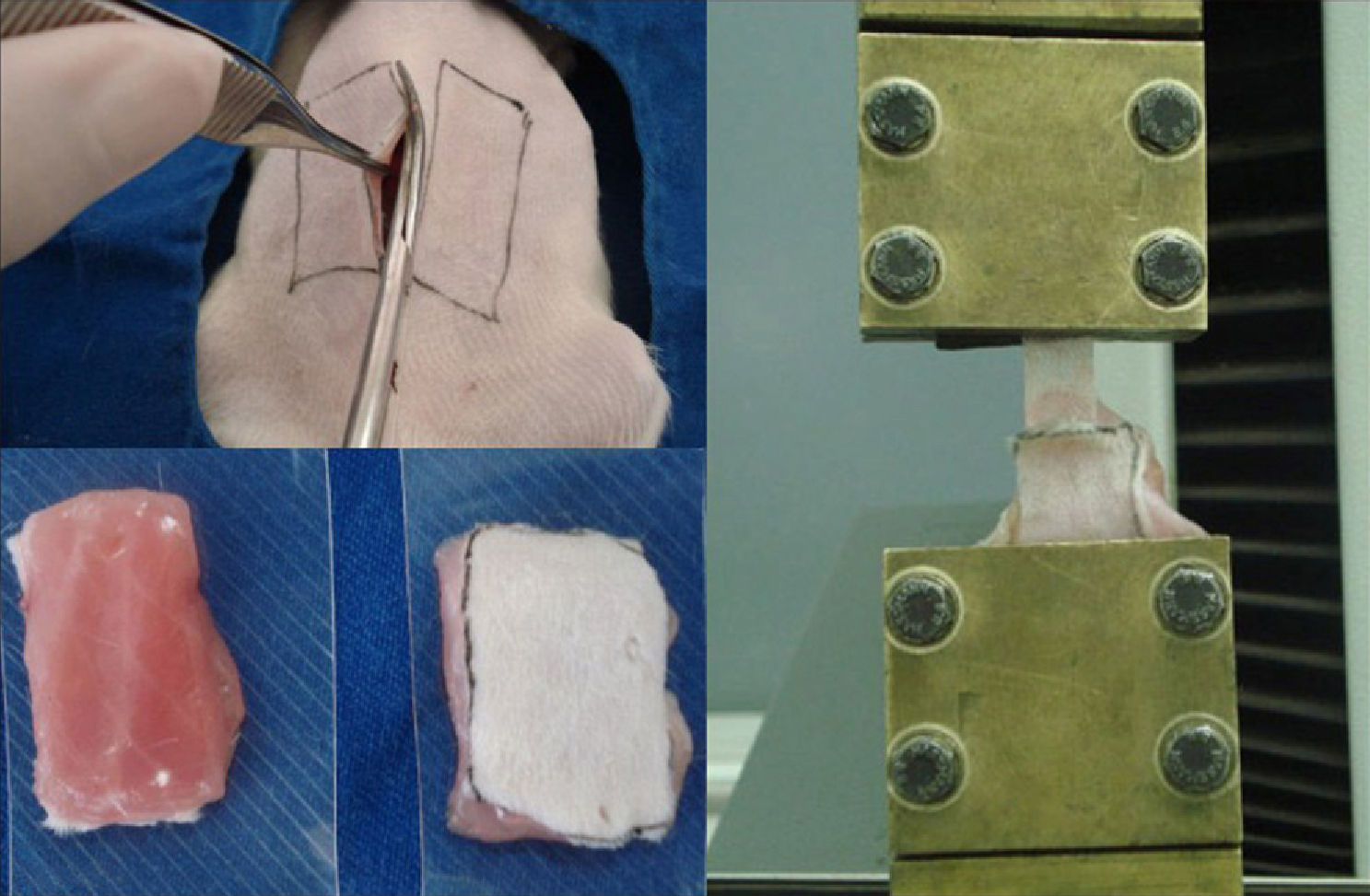
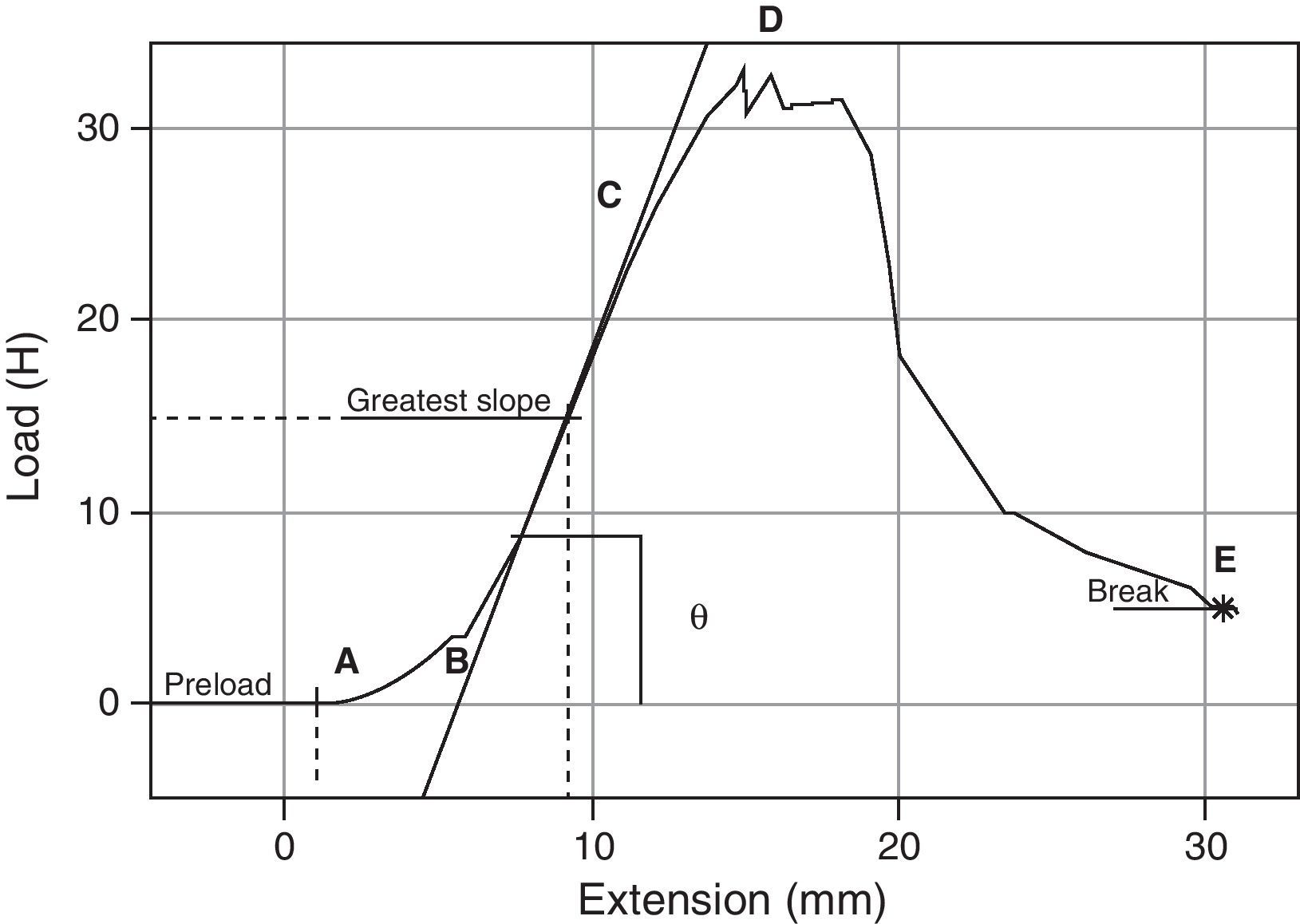
Material and methodsForty, 3 month-old, female Wistar rats received an implant of monofilament polypropylene mesh, measuring 24mm×11mm with no orifices, on the left side of the abdominal wall (block 1). On the right side, a similar mesh with two circular orifices (6mm diameter) was implanted (block 2). The rats were euthanized 90 days later and their abdominal walls were removed and divided into two blocks. The biomechanical study used a precision tensiometer in which the mesh was uniaxially tensioned until it was loosened from the tissue interface. In order to determine the tissue adherence and elasticity in each group, the following variables were analyzed: maximum load; deflection at maximum load; work to maximum load; stiffness as well as load, deflection and work at detachment of the mesh.
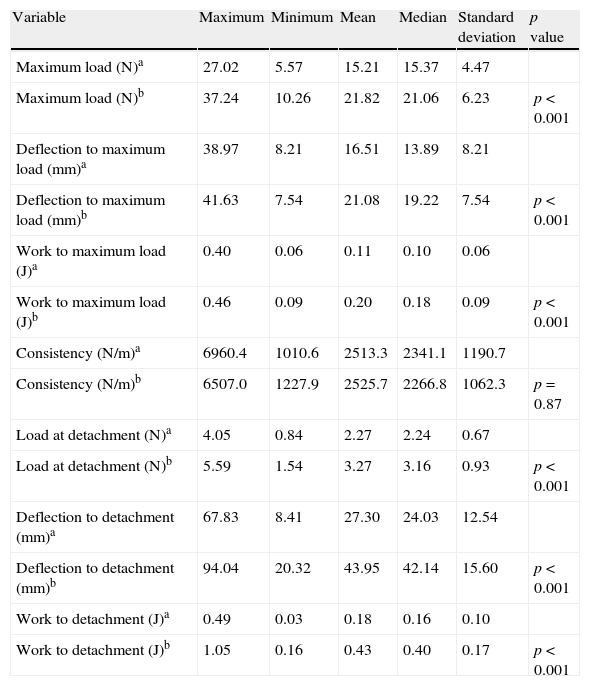
ResultsWith the exception of stiffness, all the other variables showed statistical differences between the groups, considering that they were increased in meshes with orifices (p<0.001). The inclusion of standard size orifices reduced 30% of the mesh weight.
ConclusionBesides reducing the weight and amount of material, the inclusion of standard size orifices in the monofilament macroporous polypropylene mesh improved the elasticity and adherence to the tissues when implanted in the interface of the abdominal wall in adult female rats.
Evaluar las propiedades biomecánicas de un tipo de malla de polipropileno monofilamento utilizada para la reparación de prolapsos vaginales y los efectos de la inclusión de orificios de tamaño estandarizado, que llamamos orificios facilitadores de la integración, sobre la resistencia en la interfaz con el lecho receptor.
Material y métodosEn 40 ratas Wistar, de 3 meses de edad (adultas), se implantó en la pared abdominal del lado izquierdo una malla de polipropileno monofilamento que medía 24 x 11mm sin orificios (bloque 1) y del lado derecho una malla similar con dos orificios circulares de 6mm de diámetro (bloque 2). Después de 90 días las ratas se sacrificaron y se les retiró la pared abdominal, dividiéndola en dos bloques. El estudio biomecánico se realizó con un tensiómetro de precisión con el cual se traccionó la malla en sentido uniaxial hasta que se desprendiera de la interfaz tisular. Para cuantificar en cada grupo la adherencia y elasticidad tisular se analizaron las siguientes variables: carga máxima, deflexión hasta la carga máxima, trabajo hasta la carga máxima y consistencia del material, además de carga, deflexión y trabajo en el desprendimiento de la malla.
ResultadosExceptuando la variable consistencia del material, para el resto de las variables hubo diferencia estadísticamente significativa entre ambos grupos, siendo superior en las mallas con orificios (p<0,001). La inclusión de orificios de tamaño estandarizado redujo en un 30% el peso de la malla.
ConclusiónLa inclusión de orificios de tamaño estandarizado en mallas de polipropileno macroporosas monofilamento, además de reducir su peso y la cantidad de material, aumentó la elasticidad y la adherencia a los tejidos al implantarse en la interfaz de la pared abdominal de ratas adultas.