This research aims to examine the efficacy of melatonin as an adjuvant therapeutic agent for COVID-19 patients in the intensive care unit.
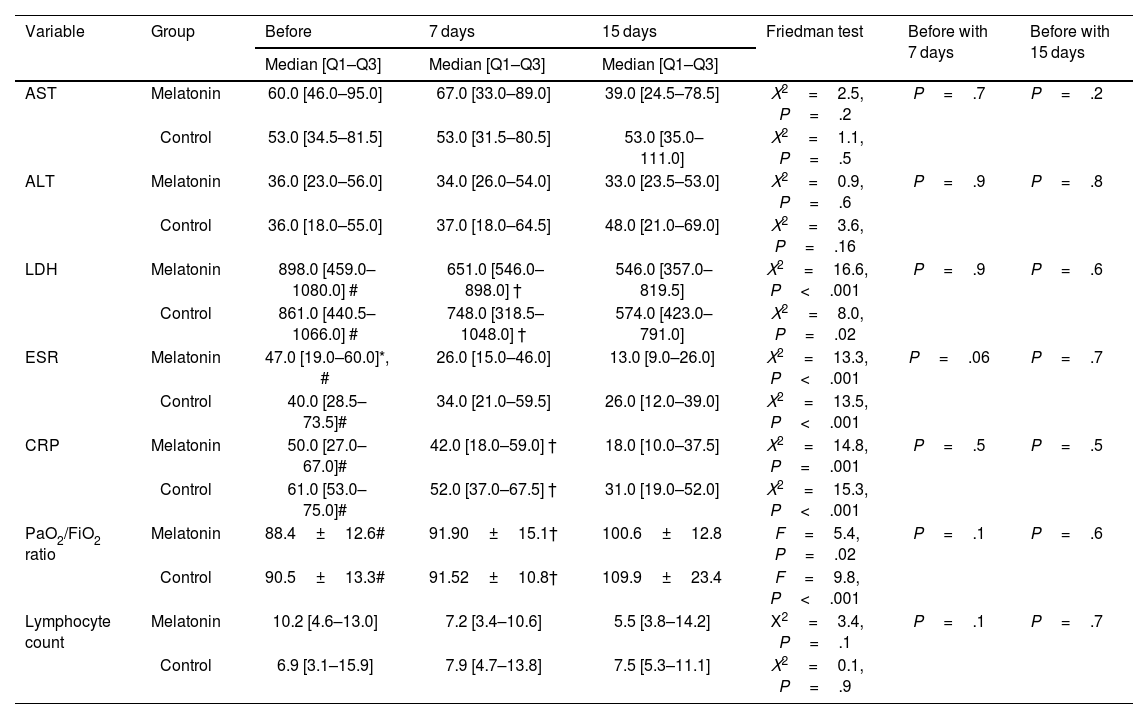
MethodsA randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation was conducted on a group of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Individuals were allocated into 2 groups: one group received a combination of 18 mg of melatonin and standard treatment for 14 days; the other group received a placebo in addition to standard treatment. Patients were evaluated at the beginning of the study as well as the 7th and 15th days to analyze changes in clinical symptoms, P/F ratio, and inflammatory markers.
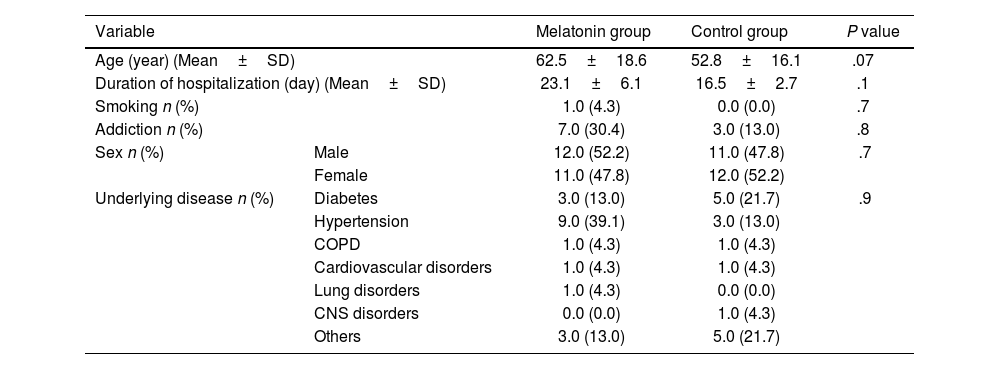
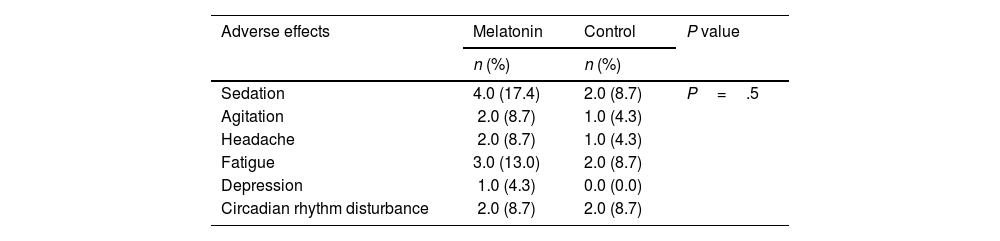
ResultsThe study included patients with an average age of 57.80±17.96 years, with an equal gender representation. The average length of hospital stay was 19.83±4.45 days. Hypertension and diabetes were commonly observed comorbidities. There were no significant differences in the demographic characteristics between the 2 groups (P>.05). Additionally, there were no significant distinctions between the 2 groups in terms of clinical symptom improvement, mortality rate, adverse effects, and various blood markers (P>.05).
ConclusionOur study's findings suggested that melatonin is unlikely to significantly affect the clinical status of COVID-19 patients.
El objetivo de este estudio es examinar la eficacia de la melatonina como agente terapéutico adyuvante para pacientes con COVID-19 en la unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI).
MétodosSe realizó un estudio aleatorizado, doble ciego, y controlado por placebo en un grupo de pacientes hospitalizados con COVID-19. Los individuos fueron asignados a dos grupos: uno de ellos recibió una combinación de 18 mg de melatonina y tratamiento estándar durante 14 días, y el otro grupo recibió un placebo además del tratamiento estándar. Se evaluó a los pacientes al inicio del estudio, así como transcurridos 7 y 15 días, para analizar los cambios de los síntomas clínicos, ratio P/F y marcadores inflamatorios.
ResultadosEl estudio incluyó pacientes con una edad media de 57,80 ± 17,96 años, con igual representación de sexos. La duración media de la estancia hospitalaria fue de 19,83 ± 4,45 días. Hipertensión y diabetes fueron comorbilidades comúnmente observadas. No existieron diferencias significativas en cuanto a características demográficas entre los dos grupos (p > 0,05). Además, no existieron diferencias significativas entre los dos grupos en términos de mejora de los síntomas clínicos, tasa de mortalidad, efectos adversos y marcadores sanguíneos diversos (p > 0,05).
ConclusiónLos hallazgos de nuestro estudio sugirieron la improbabilidad de que la melatonina afecte al estado clínico de los pacientes de COVID-19.