The impact of inactivated vaccines for COVID-19, BBIBP-CorV COVID-19, on the human immune system was not studied. This study investigates the immune response induced by the BBIBP-CorV COVID-19 vaccine.
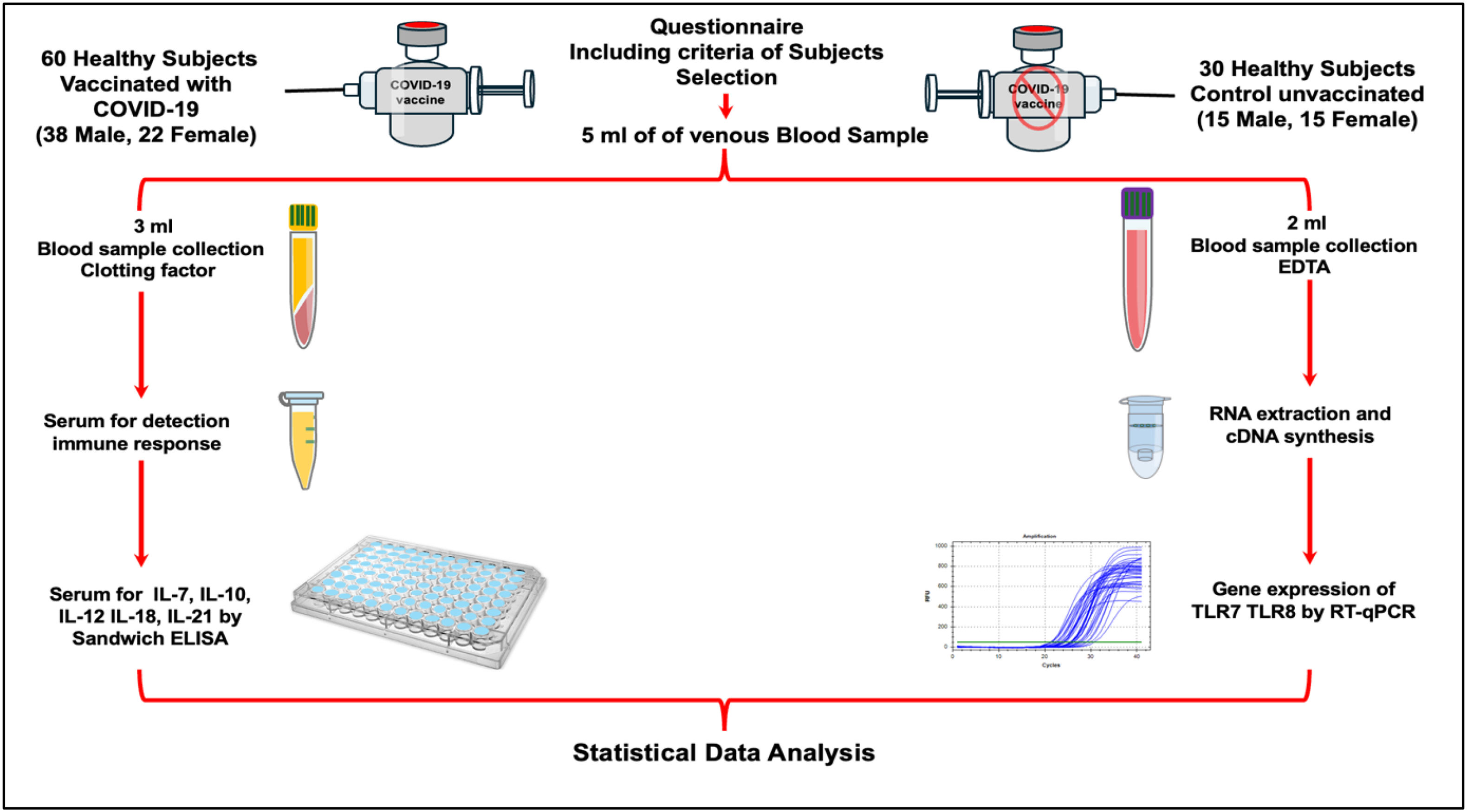
MethodA total of 90 blood samples (5 ml each) were collected from participants (mean age: 20 years) in Basrah, Iraq. The study included 60 vaccinated individuals (38 males, 22 females), 60 days post-BBIBP-CorV vaccination and 30 unvaccinated controls (15 males, 15 females). Blood was divided: 2 ml in EDTA tubes for TLR7/TLR8 mRNA expression (RT-qPCR) and 3 ml in clotting activator tubes for serum isolation to measure IL-7, IL-10, IL-12, IL-18, and IL-21 levels (sandwich ELISA). Data were compared with controls and analysed for statistical differences. Volunteers with flu, COVID-19 symptoms, fever, chronic diseases, or immunocompromised conditions were excluded.
ResultsThe BBIBP-CorV vaccine did not disrupt cytokine production, with no significant differences in IL-7, IL-10, IL-12, IL-18, and IL-21 levels between vaccinated and unvaccinated groups after 60 days (p > 0.05). However, TLR7 and TLR8 mRNA expression was significantly upregulated (p < 0.05) in vaccinated individuals compared to controls, indicating enhanced innate immune activation without affecting cytokine balance. These findings highlight the vaccine's ability to stimulate immunity while maintaining normal cytokine levels.
ConclusionsThese results are particularly significant as they demonstrate that the BBIBP-CorV COVID-19 vaccine successfully induces immunological responses via TLR7 and TLR8 activation without abnormal effects on cytokine production. As a pilot study, these findings lay a strong foundation for future research.
No se ha estudiado el impacto de las vacunas no activadas contra la COVID-19, tal como BBIBP-CorV COVID-19, en el sistema inmunitario humano. Este estudio investiga la respuesta inmunitaria inducida por la vacuna BBIBP-CorV contra la COVID-19.
MétodoSe recogió un total de 90 muestras de sangre (de 5 ml cada una) de los participantes (edad media: 20 años) en Basrah, Irak. El estudio incluyó 60 individuos vacunados (38 varones, 22 mujeres) 60 días tras la vacunación con BBIBP-CorV, y 30 controles no vacunados (15 varones, 15 mujeres). Se dividió la sangre del modo siguiente: 2 ml en tubos EDTA para estudiar la expresión del ARNm de TLR7/TLR8 (RT-qPCR), y 3 ml en tubos activadores de coagulación para aislamiento sérico, a fin de medir los niveles de IL-7, IL-10, IL-12, IL-18 e IL-21 (ELISA tipo sándwich). Se compararon los datos con los controles, y se analizaron para encontrar las diferencias estadísticas. Se excluyeron los voluntarios con gripe, síntomas de COVID-19, fiebre, enfermedades crónicas o condiciones inmunocomprometidas.
ResultadosLa vacuna BBIBP-CorV no alteró la producción de citocinas, ni reflejó diferencias significativas de los niveles de IL-7, IL-10, IL-12, IL-18 e IL-21 entre los grupos de vacunados y no vacunados transcurridos 60 días (p > 0,05). Sin embargo, la expresión del ARNm de TLR7 y TLR8 mRNA estuvo significativamente aumentada (p < 0,05) en los individuos vacunados, en comparación con los controles, lo cual indica el aumento de la activación inmunitaria innata sin afectar al equilibrio de las citocinas. Dichos hallazgos destacan la capacidad de la vacuna para estimular la inmunidad, a la vez que mantiene los niveles de citocinas normales.
ConclusionesEstos resultados son particularmente significativos, ya que demuestran que la vacuna BBIBP-CorV contra la COVID-19 induce exitosamente las respuestas inmunológicas a través de la activación de TLR7 y TLR8, sin efectos anormales en la producción de citocinas. Como estudio piloto, estos hallazgos establecen un fundamento sólido para la investigación futura.