The three treatment modalities for patients with hyperthyroidism are antithyroid drugs (ATDs), surgery, and radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy. The study aims to determine the predictors of a response to RAI in patients with hyperthyroidism.
Materials and methodsWe retrospectively assessed 914 patients who received RAI for the treatment of hyperthyroidism between January 2000 and December 2023, with a follow-up of at least 6 months after the first dose.
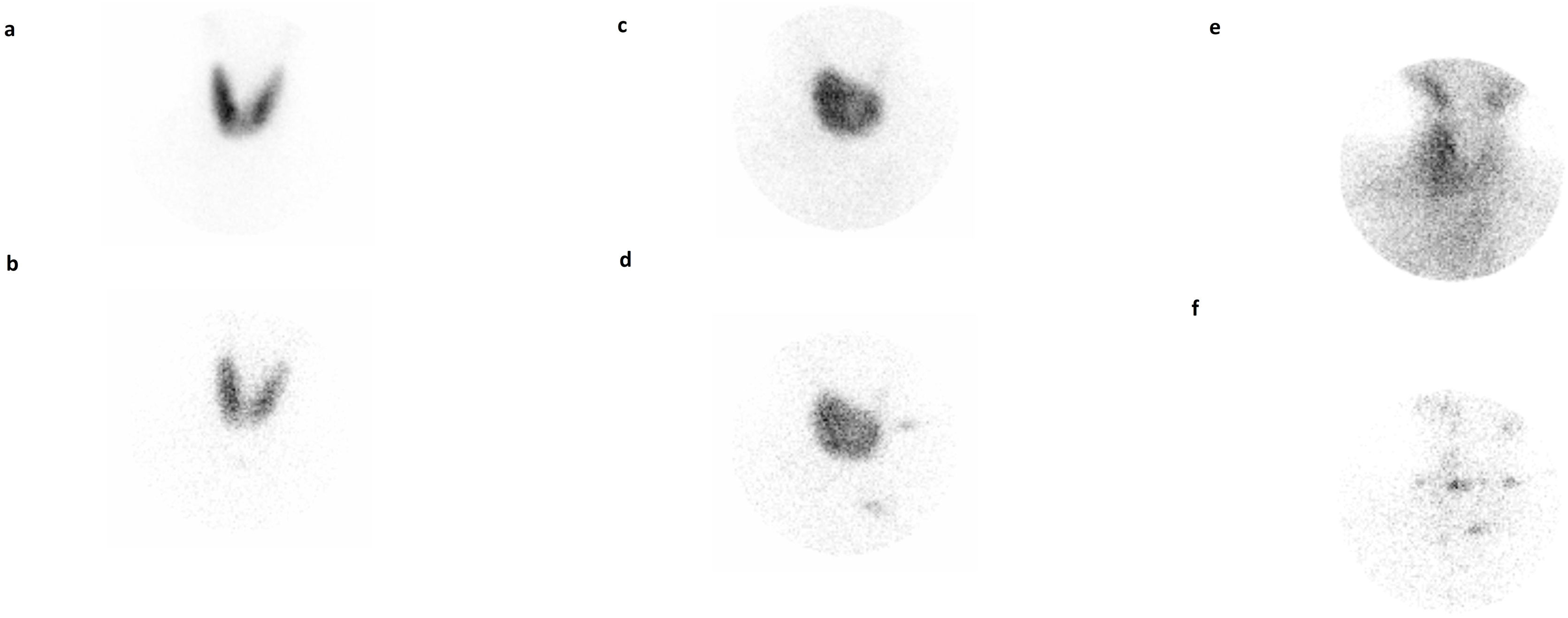
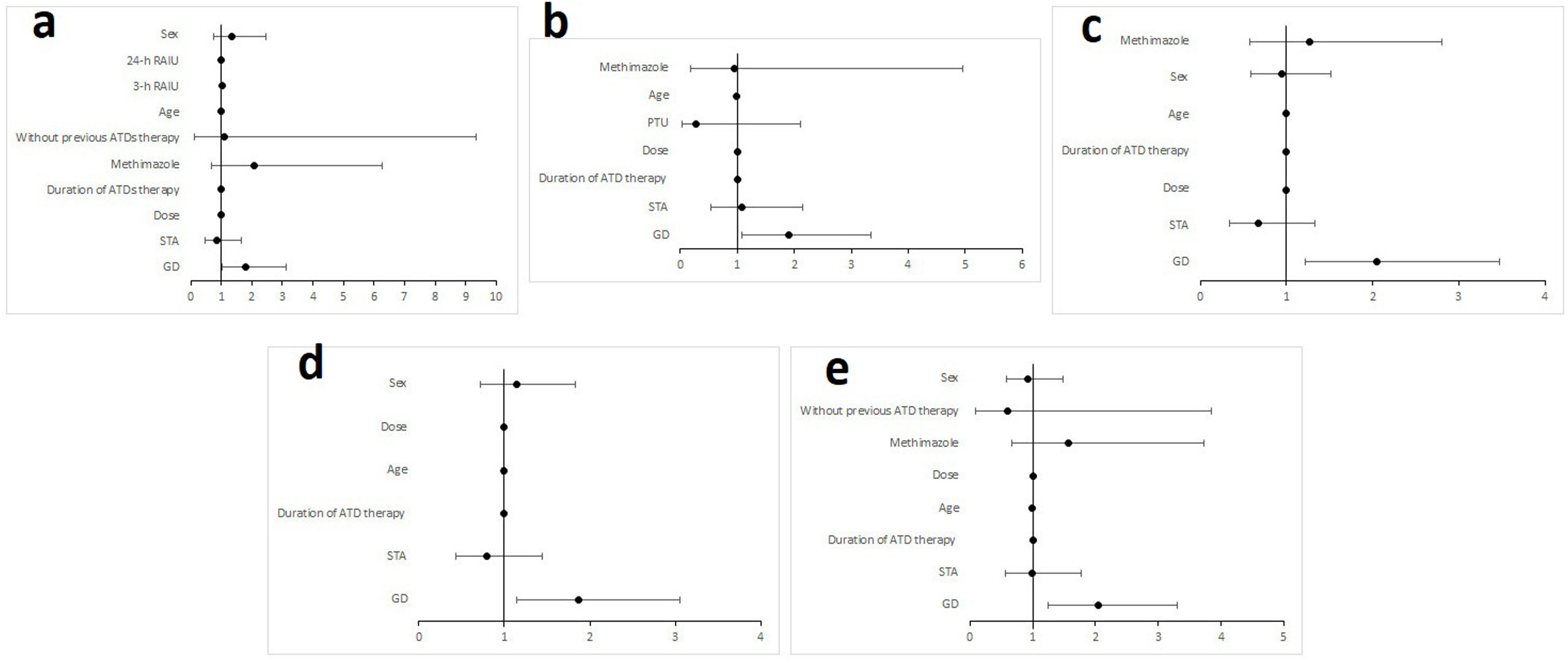
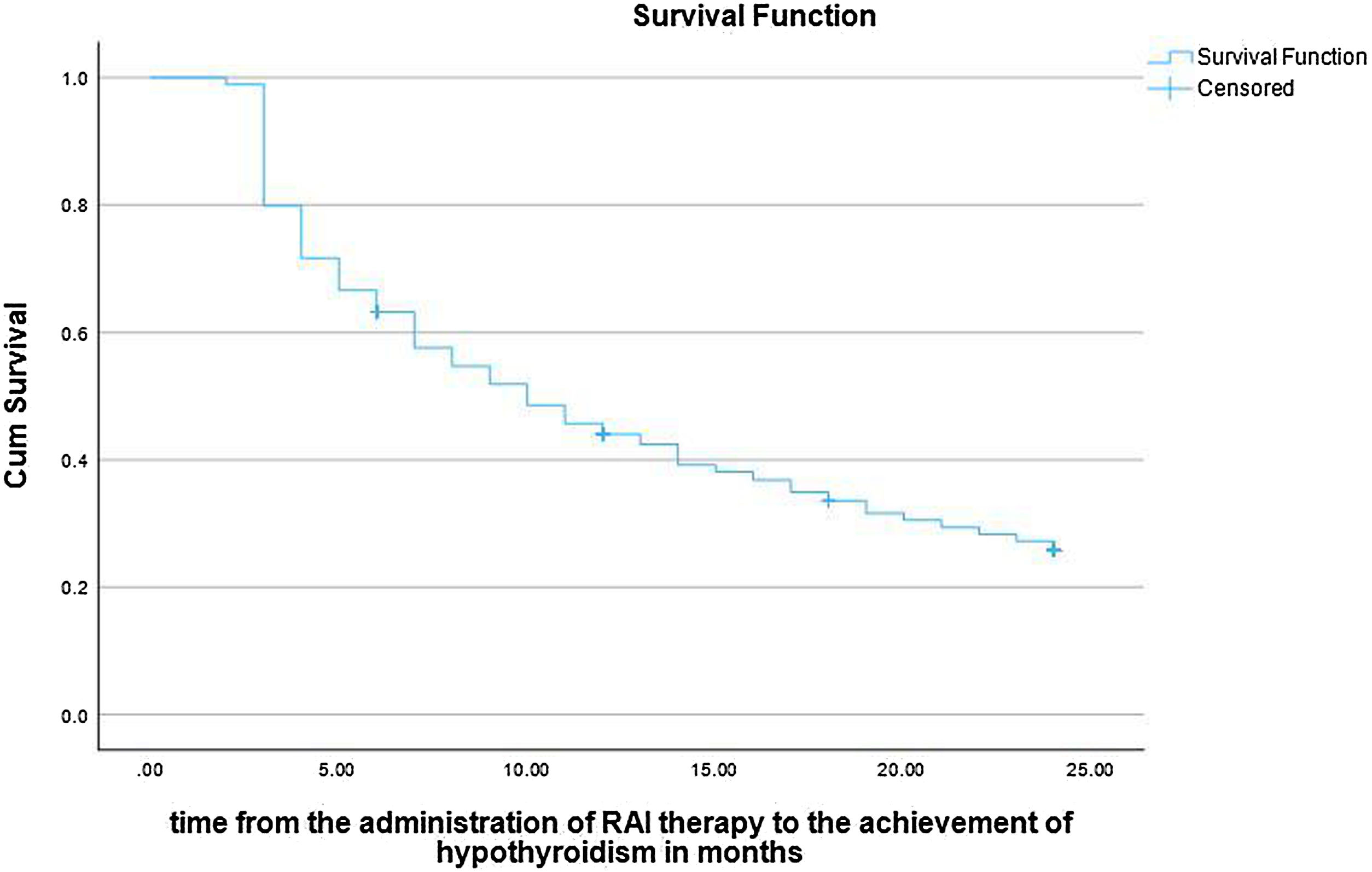
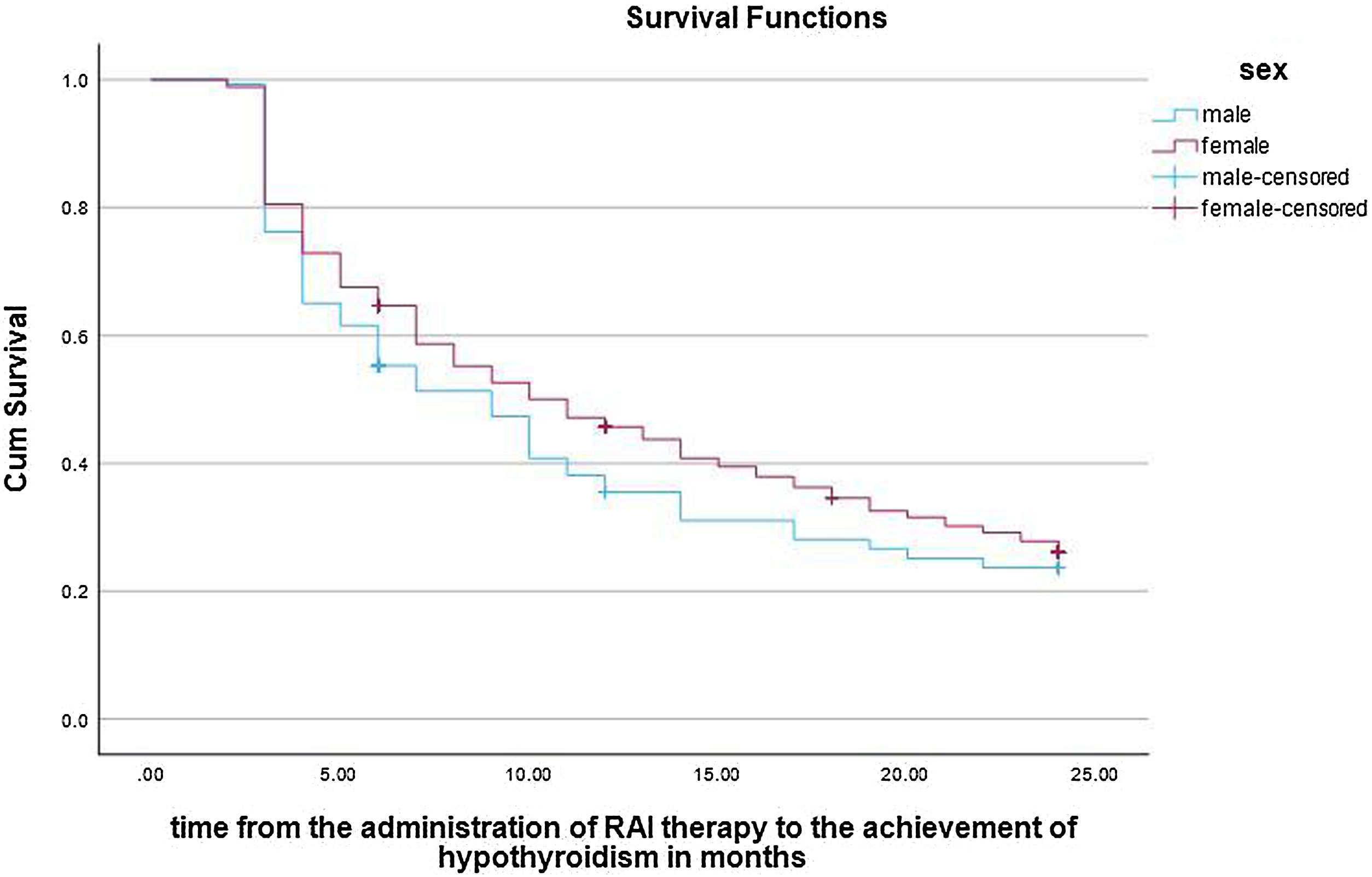
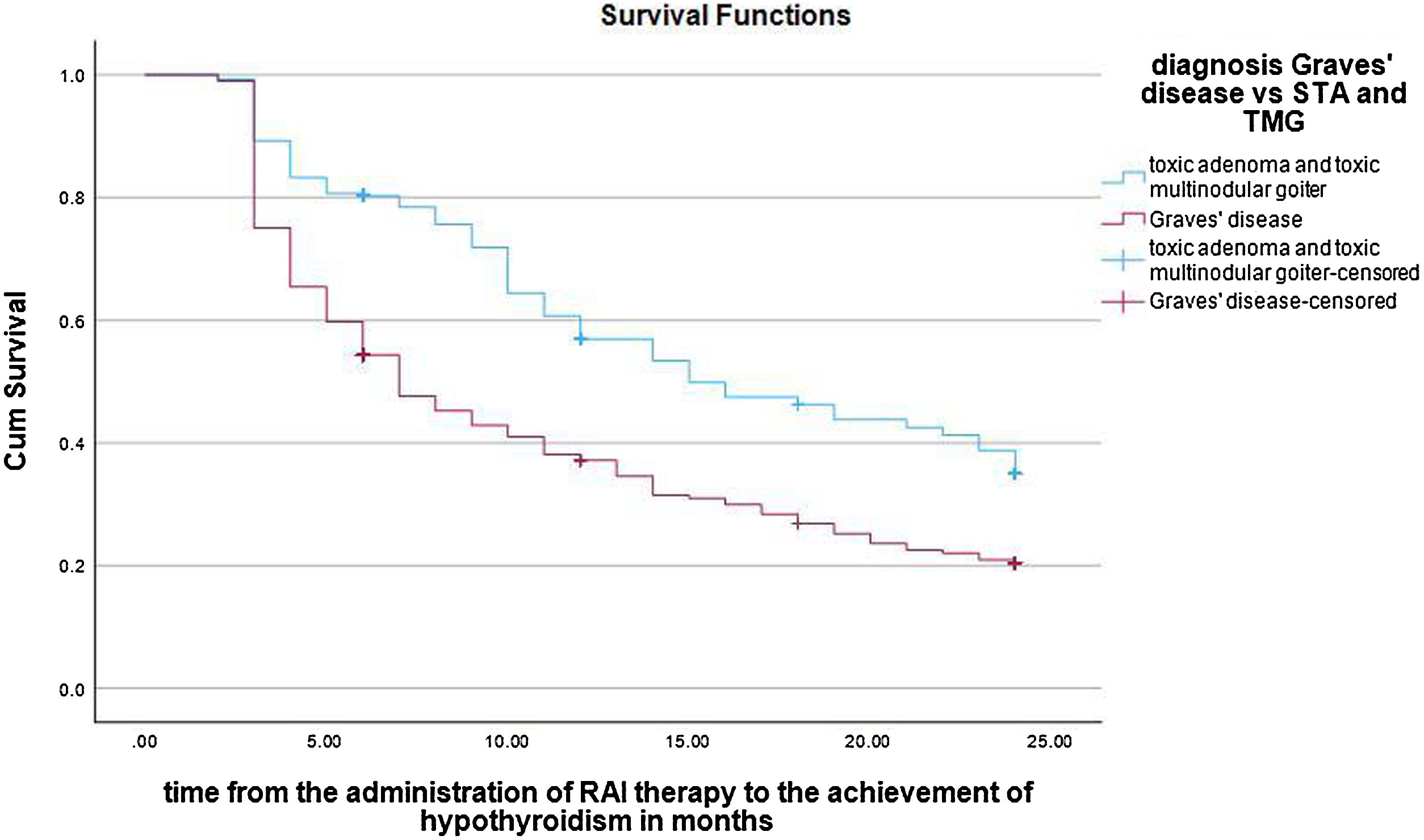
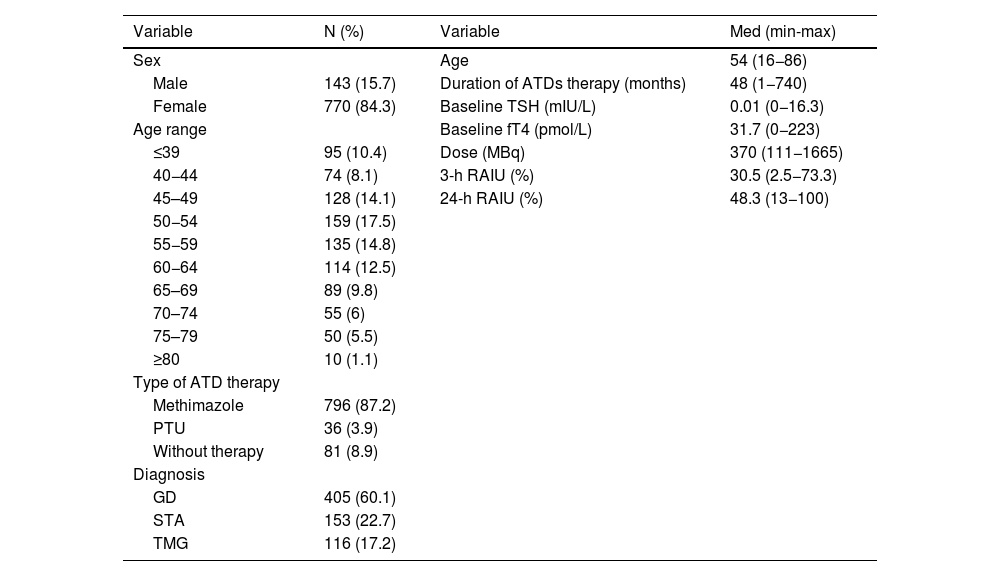
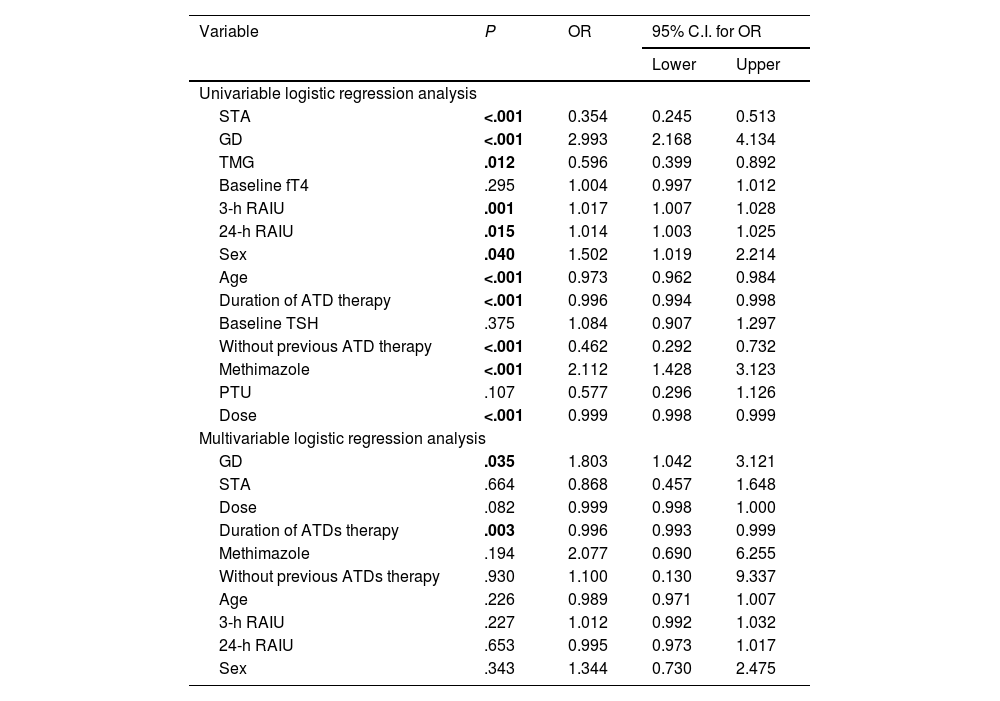
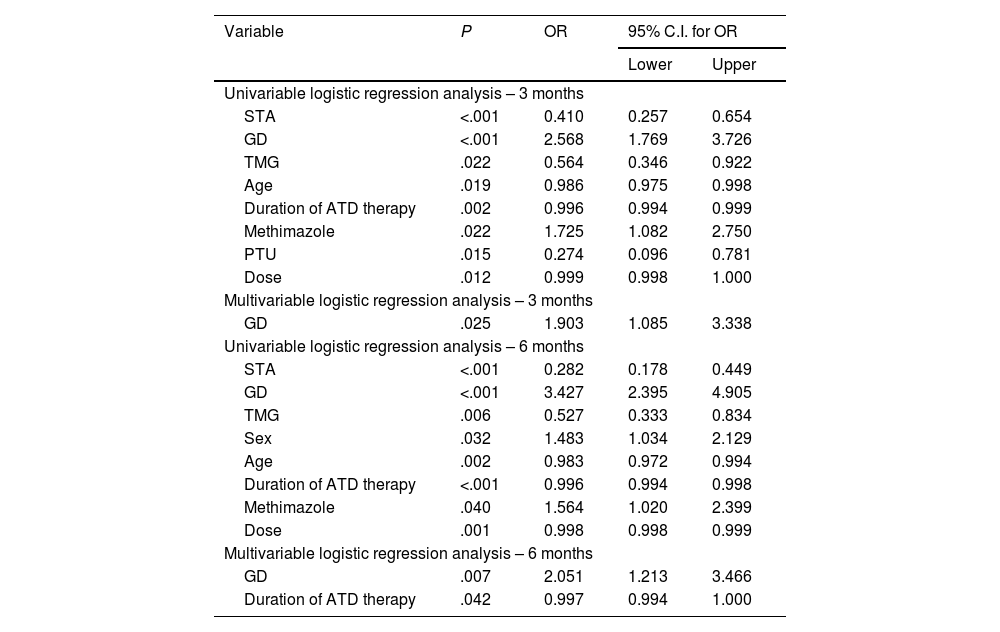
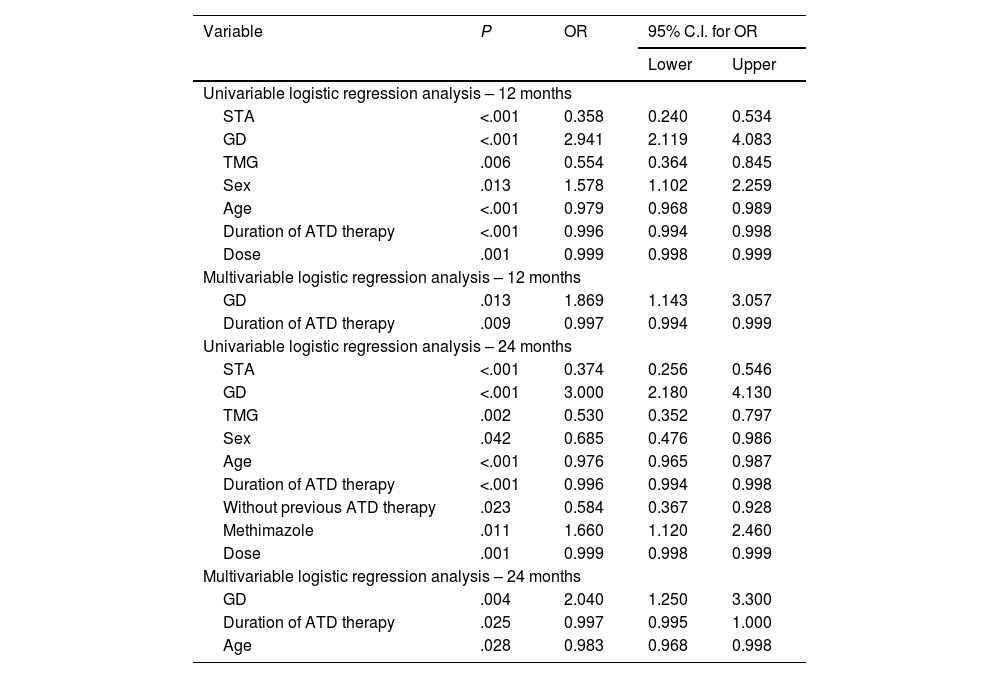
ResultsHypothyroidism was ultimately achieved in 62.9% of the patients. Multiple variables are possible predictors in univariable logistic regression analysis. However, only shorter duration of ATD therapy (odds ratio 0.996; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.093–0.999; P = .003, multivariable logistic regression analysis) and a diagnosis of Graves’ disease (GD) (odds ratio 1.803; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.042–3.141; P = .035, multivariable logistic regression analysis) are the independent predictors of post-treatment hypothyroidism, with decreasing age also being a late-response independent predictor of hypothyroidism 24 months after the treatment (odds ratio 0.983; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.968–0.998; P = .028, multivariable logistic regression analysis). The median time to hypothyroidism was 10.0 ± 0.7 months (Kaplan-Meier method), with a statistically significant difference in hypothyroidism-free survival (HFS) between patients with GD on one side and solitary toxic adenoma (STA) and toxic multinodular goiter (TMG) on the other (P < .001, log-rank test).
ConclusionsGD and a shorter duration of previous ATD therapy are independent predictors of post-therapeutic hypothyroidism in patients treated for hyperthyroidism with RAI, with younger age also being an independent predictor of a late response.
Las tres modalidades de tratamiento para pacientes con hipertiroidismo son los fármacos antitiroideos (FAT), la cirugía y la terapia con yodo radiactivo (YRA). El estudio busca determinar los predictores de la respuesta al YRA en pacientes con hipertiroidismo.
Materiales y métodosEvaluamos retrospectivamente a 914 pacientes que recibieron YRA para el tratamiento del hipertiroidismo entre enero de 2000 y diciembre de 2023, con un seguimiento de al menos 6 meses después de la primera dosis.
ResultadosEl hipotiroidismo se logró en el 62,9% de los pacientes. Múltiples variables son posibles predictores en el análisis de regresión logística univariable. Sin embargo, solo una duración más corta de la terapia con ATD (odds ratio 0,996; intervalo de confianza del 95% [IC], 0,093–0,999; P = ,003, análisis de regresión logística multivariable) y un diagnóstico de enfermedad de Graves (EG) (odds ratio 1,803; intervalo de confianza del 95% [IC], 1,042–3,141; P = ,035, análisis de regresión logística multivariable) son los predictores independientes de hipotiroidismo posterior al tratamiento, siendo la disminución de la edad también un predictor independiente de respuesta tardía de hipotiroidismo 24 meses después del tratamiento (odds ratio 0,983; intervalo de confianza del 95% [IC], 0,968–0,998; P = ,028, análisis de regresión logística multivariable). La mediana de tiempo hasta el hipotiroidismo fue de 10,0 ± 0,7 meses (método de Kaplan-Meier), con una diferencia estadísticamente significativa en la supervivencia libre de hipotiroidismo (SLI) entre pacientes con EG por un lado y adenoma tóxico solitario (ATS) y bocio multinodular tóxico (BMT) por el otro (P < ,001, prueba de log-rank).
ConclusionesLa EG y una menor duración del tratamiento previo con ATD son predictores independientes de hipotiroidismo posterapéutico en pacientes tratados con yodo radiactivo (RAI) para hipertiroidismo, siendo la edad más joven también un predictor independiente de una respuesta tardía.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)