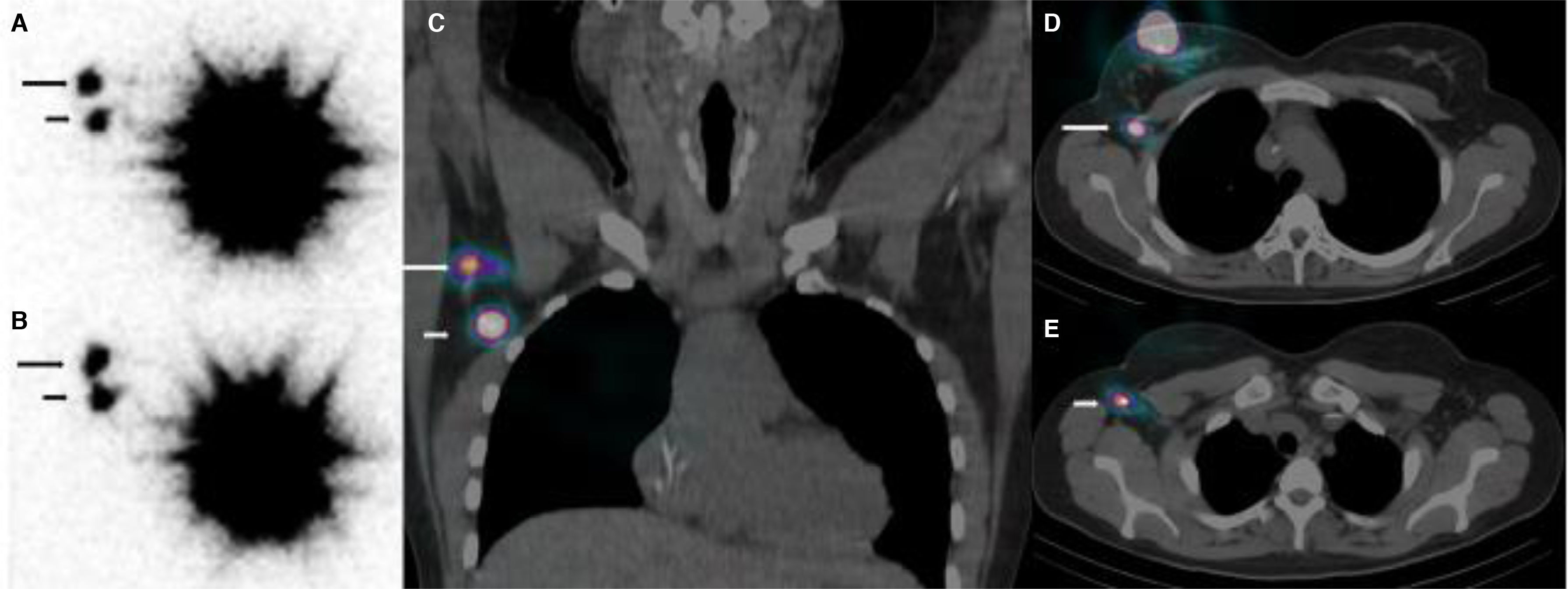
To evaluate the contribution of sentinel node biopsy using lymphoscintigraphy in breast cancer (BC) with clip-marked lymph node involvement and neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) in axillary staging and reduction of potential false negatives from exclusively radiological localization.
Material and methodsA retrospective study of 20 women with BC and nodal involvement marked with clip and NACT. Lymphoscintigraphy was complemented with SPECT/CT in 12 patients. The correlation between lymphoscintigraphic sentinel lymph node (SLN) and the clip-marked node was analyzed.
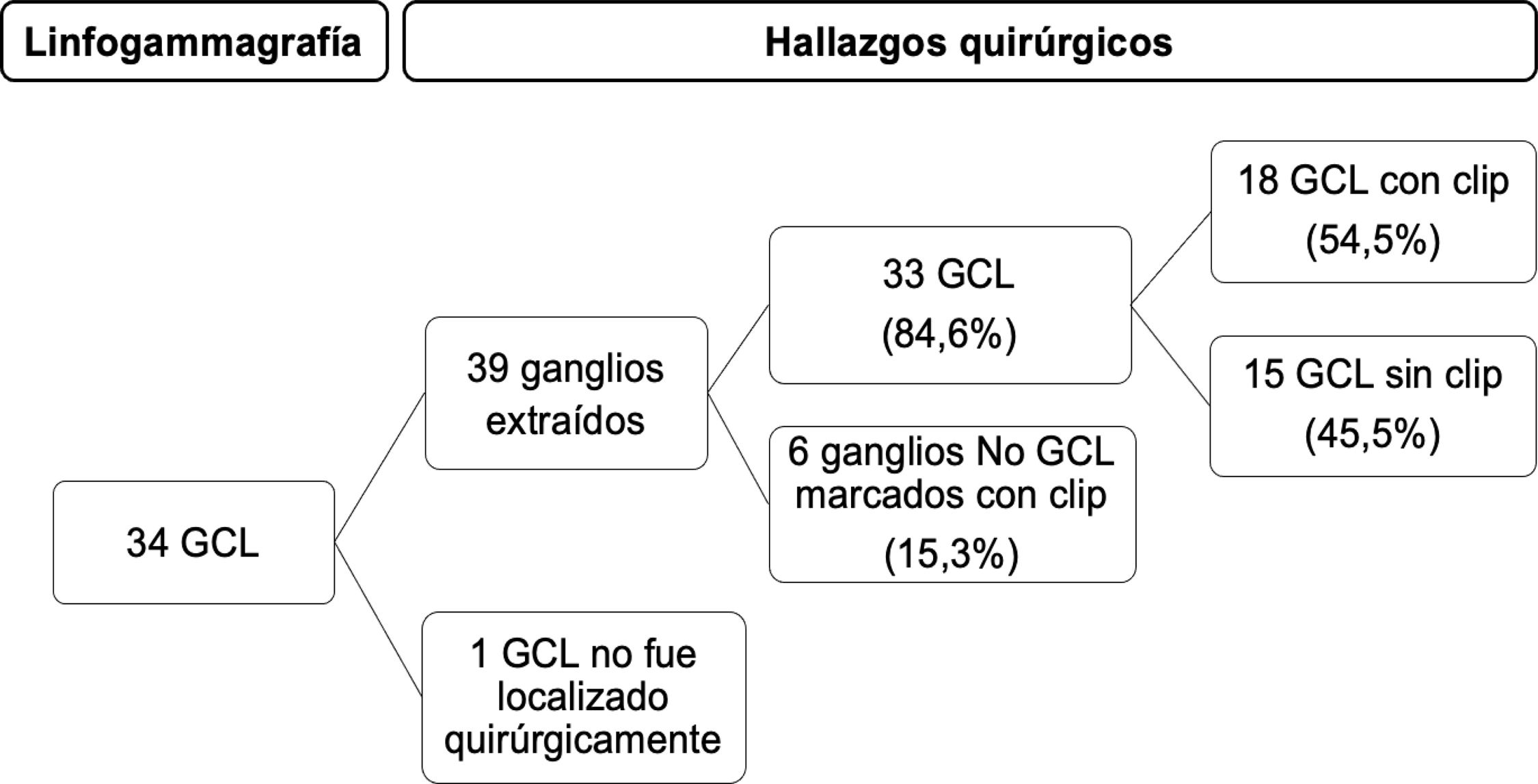
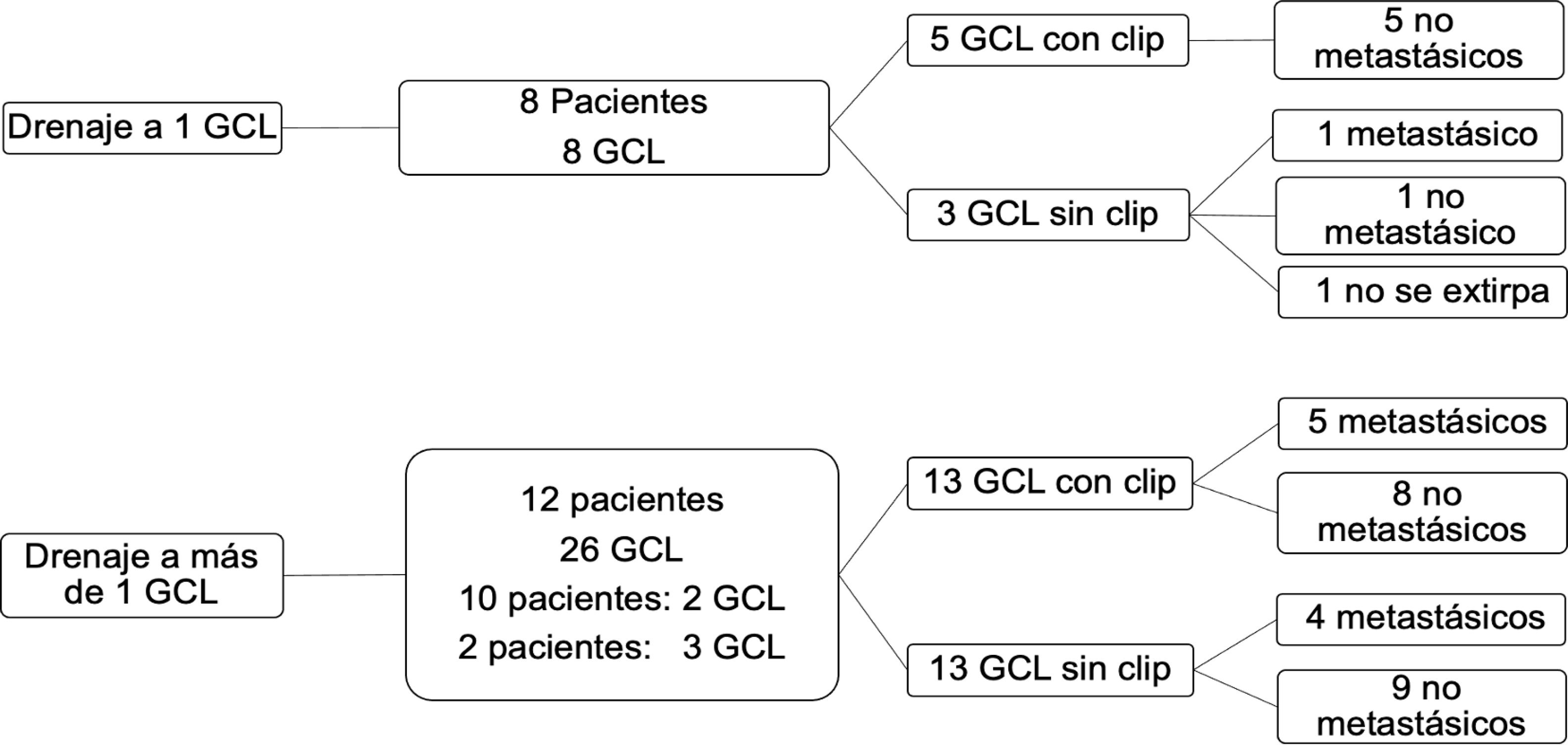
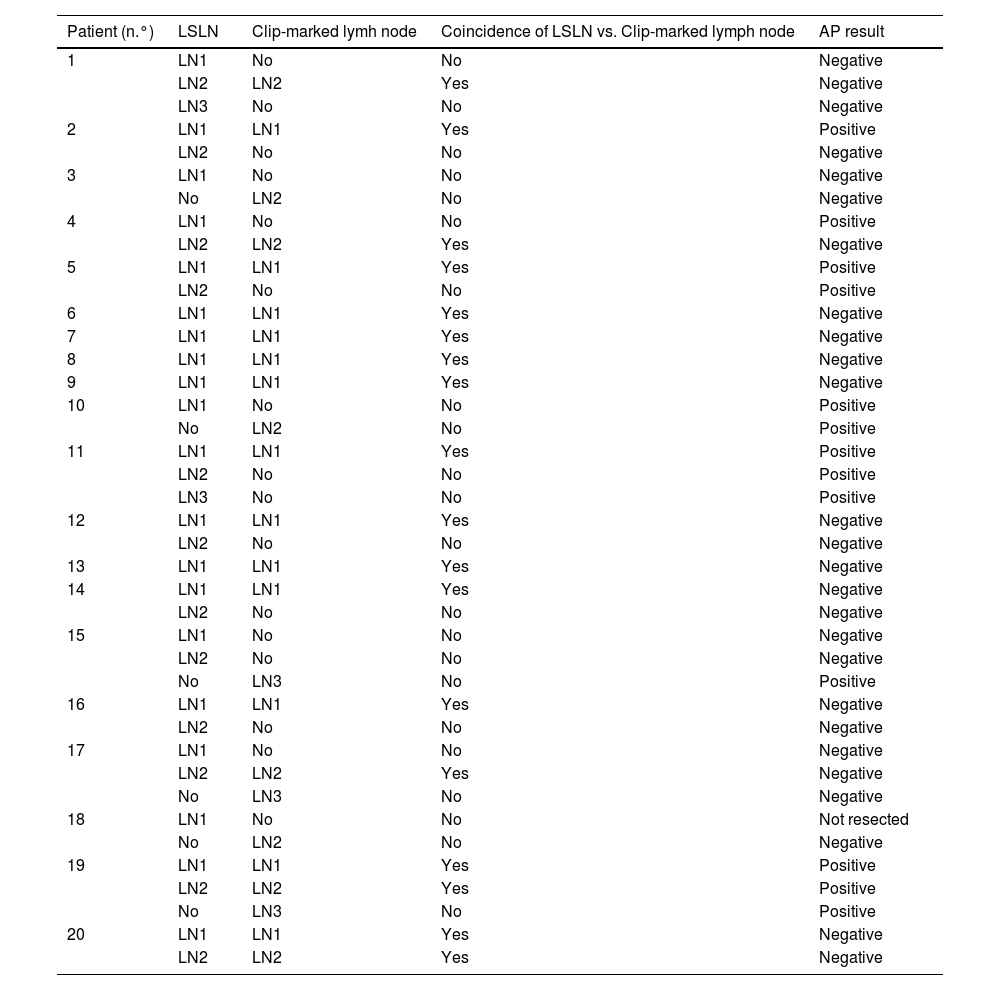
ResultsLymphoscintigraphy detected 34 axillary SLNs. SPECT/CT showed uptake in 10 of 16 clip-marked nodes (62.5%). During surgery, 39 nodes were removed; 33 (84.6%) were SLNs, 18 with clip, and 15 without clip. One SLN was not located surgically. Six clip-marked nodes (15.3%) showed no uptake. In 8 of 20 patients (40%), drainage to a single SLN was detected; this corresponded to the clip-marked node in 5 cases (non-metastatic) and non-clip-marked nodes in 3 cases (1 metastatic). In 12 of 20 patients (60%), lymphoscintigraphy showed drainage to more than one SLN. A total of 26 SLNs were detected: 13 SLNs with clip (5 metastatic) and 13 without clip (4 metastatic). Lymphoscintigraphy detected 5 SLNs in 4 of 20 patients (20%) that did not match the clip-marked node and were metastatic.
The detection and removal rate of GCL was 97% and false negative rate was 16,67%.
ConclusionLymphoscintigraphy in BC with positive axilla before NACT detected metastases in a significant percentage of patients not identified with clip, being an essential tool for accurate axillary staging.
Evaluar la contribución de la biopsia del ganglio centinela mediante linfogammagrafía en cáncer de mama (CM) con afectación ganglionar marcada con clip y quimioterapia neoadyuvante (QTNA) en la estadificación axilar y reducción de los potenciales falsos negativos de la localización exclusivamente radiológica.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de 20 mujeres con CM y afectación ganglionar marcada con clip y QTNA. La linfogammagrafía se complementó con SPECT/TC en 12. Se analizó la correlación entre el ganglio centinela linfogammagráfico (GCL) y el marcado con clip.
ResultadosLa linfogammagrafía detectó 34 GCL axilares. La SPECT/TC mostró captación en 10/16 ganglios con clip (62,5%). En la cirugía se extirparon 39 ganglios, 33 (84,6%) eran GCL, 18 con clip y 15 sin clip. Uno de los GCL no fue localizado quirúrgicamente. Seis ganglios con clip (15,3%) no mostraron captación.
En 8/20 pacientes (40%) se detectó drenaje a un GCL que se correspondió con clip en 5 (todos no metastásicos) y sin clip en 3 (1 metastásico). En los otros 12 pacientes (60%) la linfogammagrafía mostró drenaje a más de un GCL. Se detectaron 26 GCL, 13 con clip (5 metastásicos) y 13 sin clip (4 metastásicos).
La linfogammagrafía detectó 5 GCL metastásicos en 4 de 20 pacientes (20%), los cuales no coincidieron con los ganglios marcados con clip.
La tasa de detección y extirpación de GCL fue del 97% y la de falsos negativos del 16,67%.
ConclusiónLa linfogammagrafía en CM con axila positiva previa a QTNA detectó metástasis ganglionares en un porcentaje significativo de pacientes no identificados con clip, siendo una herramienta indispensable para la correcta estadificación axilar.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)