Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) using holmium-166 (¹⁶⁶Ho) microspheres is a treatment for unresectable primary and secondary liver malignancies. The pre-therapeutic simulation procedure using a scout dose is critical to predict microsphere distribution and exclude extrahepatic leakage. This single-center observational study aimed to evaluate the dosimetric agreement between ¹⁶⁶Ho-scout and ¹⁶⁶Ho-therapy, and to correlate tumor-absorbed dose with treatment response at both tumor and patient levels.
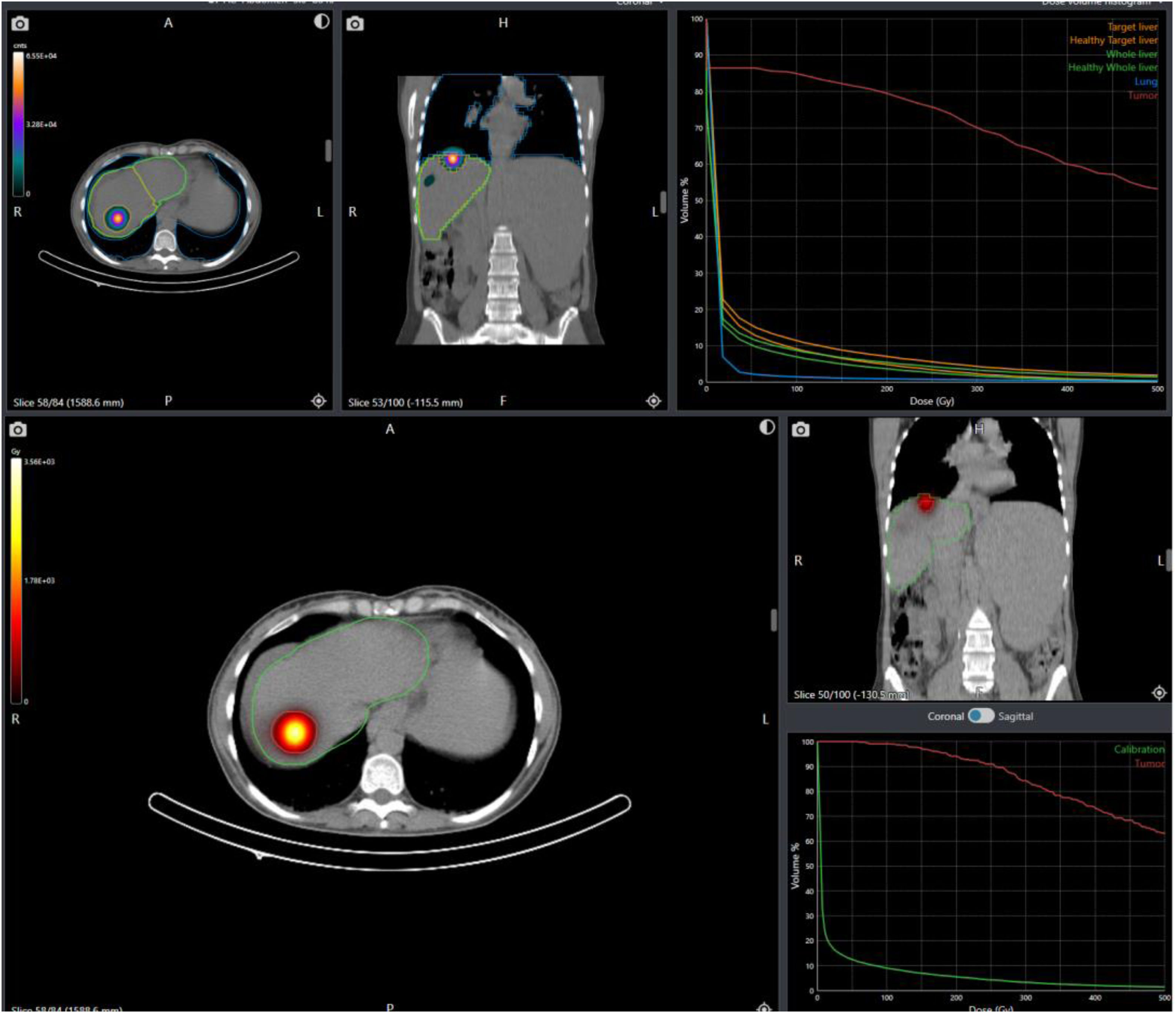
MethodsProspective, observational study included patients with BCLC 2022 stage A/B hepatocellular carcinoma or oligometastatic liver disease undergoing ¹⁶⁶Ho-TARE were included. Voxel-based dosimetry was performed using Q-suite. Contrast-enhanced CT was acquired 3 months post-treatment. Treatment response was assessed by RECIST/mRECIST criteria.
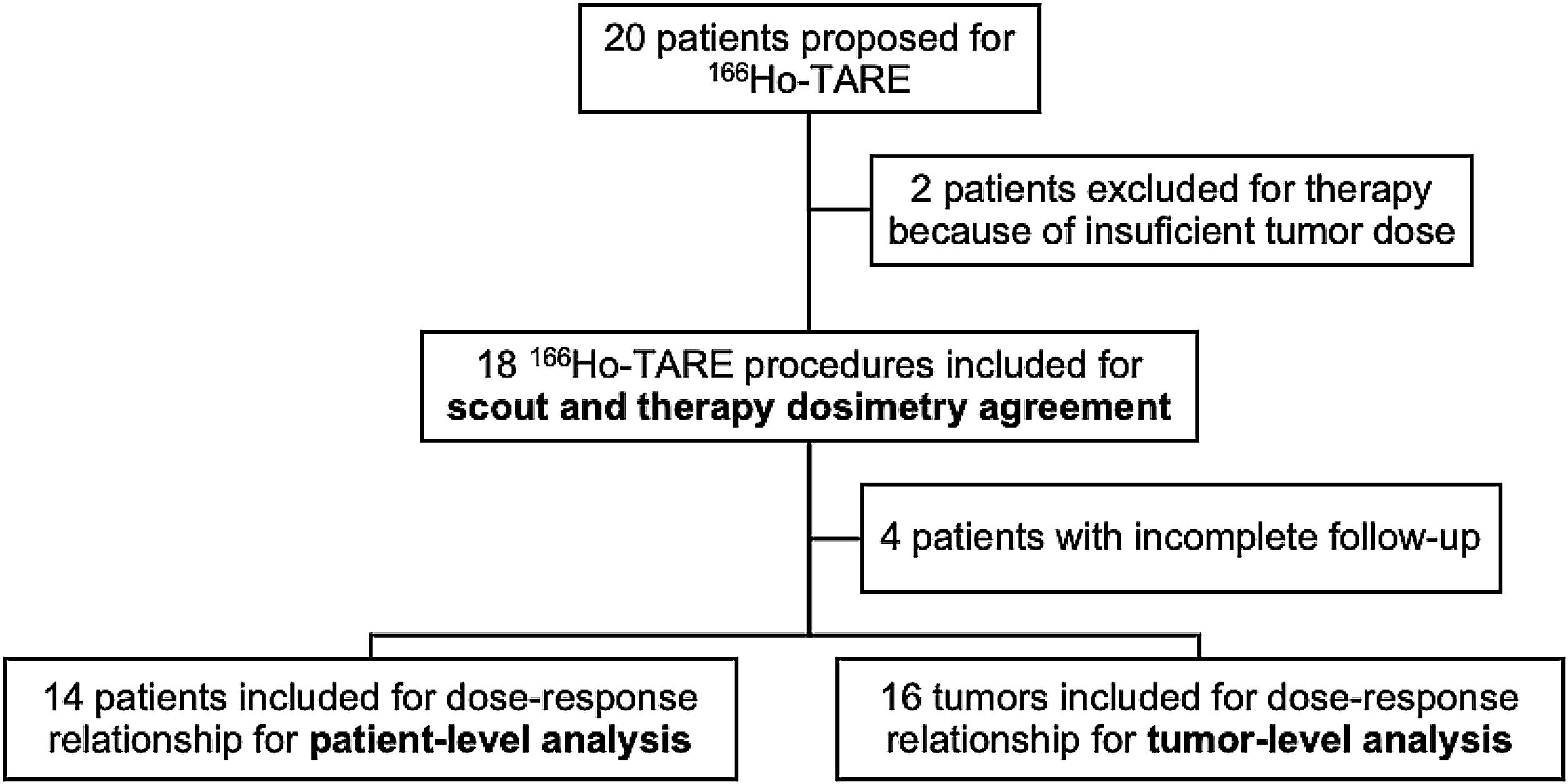
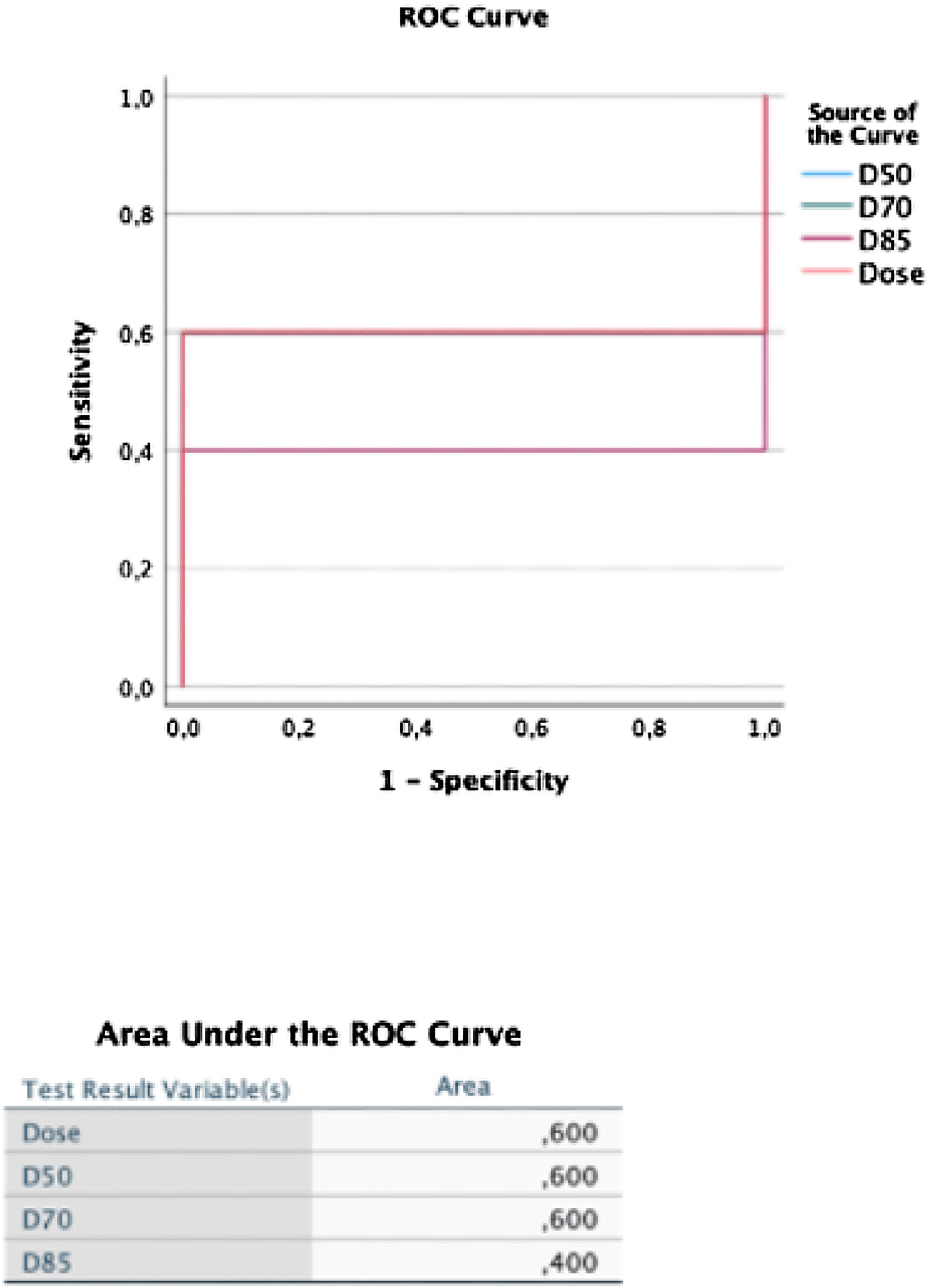
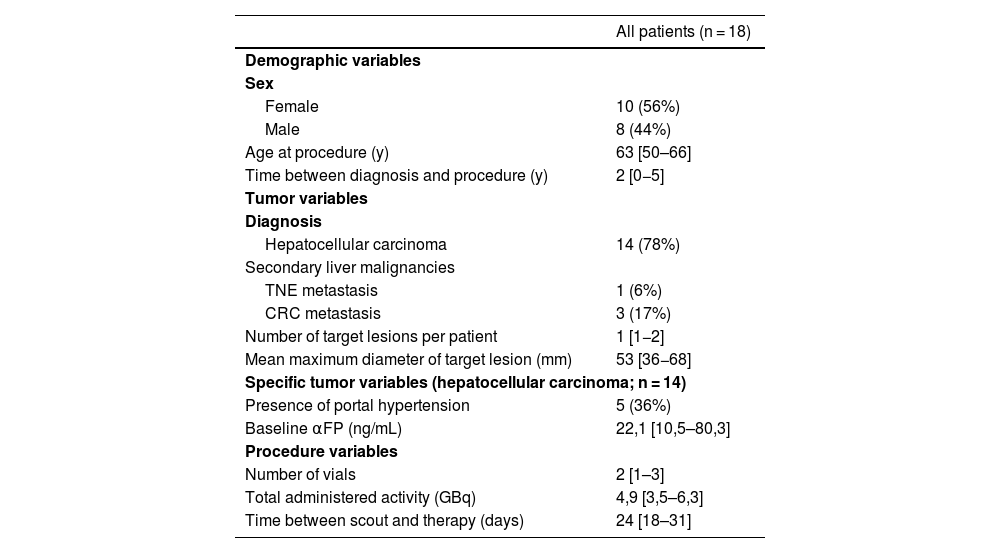
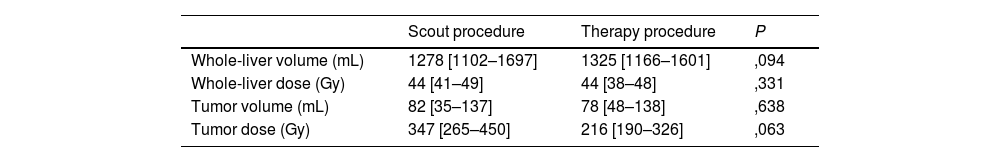
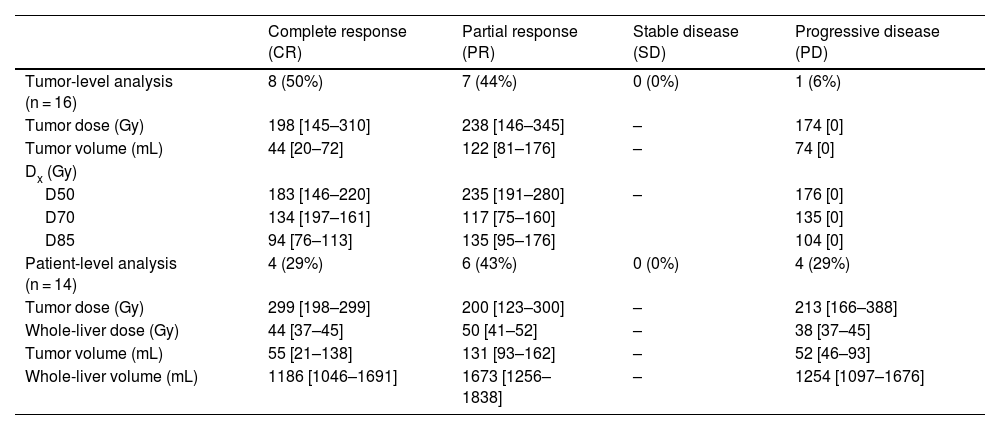
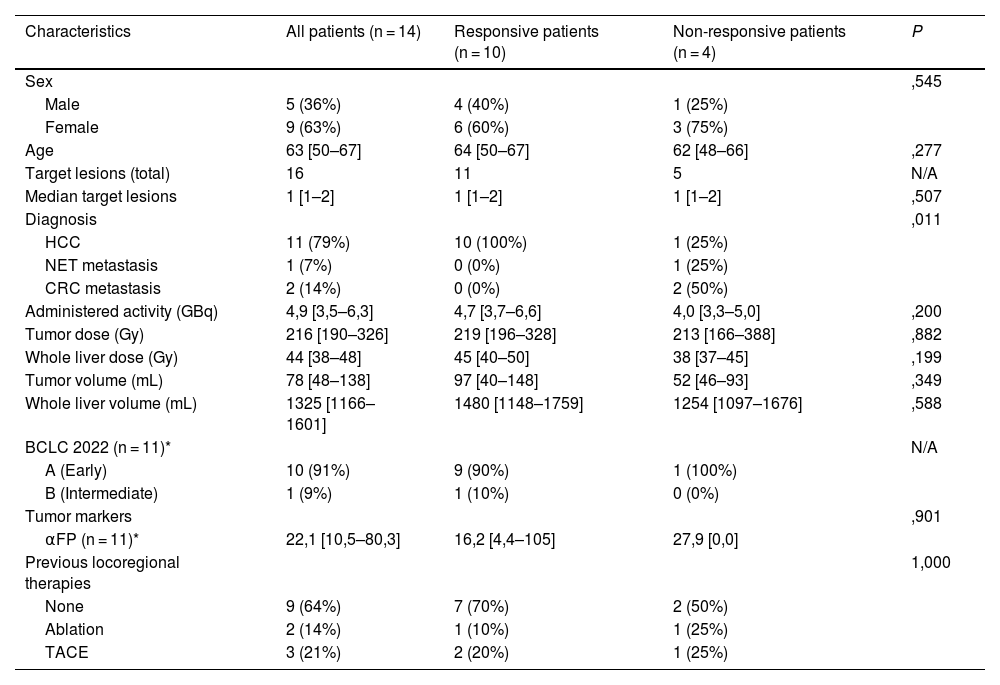
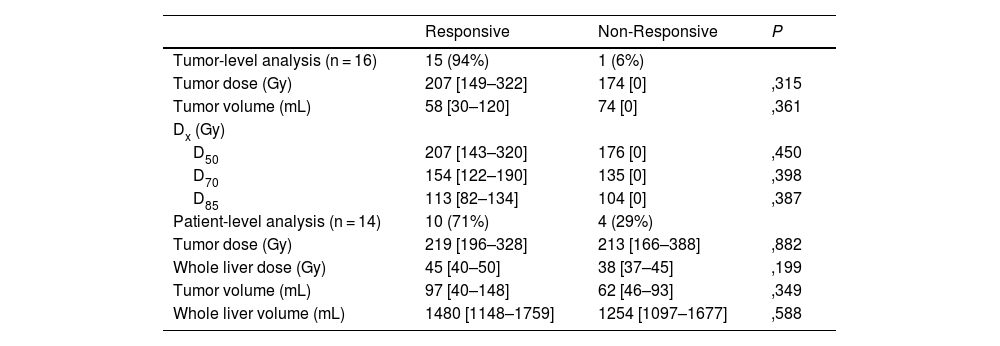
ResultsTwenty patients underwent the pre-treatment procedure; 18 proceeded to therapy. No significant differences were observed between scout and therapy procedures in whole-liver (P = .331) and tumor doses (P = .063), indicating reliable pre-therapeutic evaluation. Fourteen patients with 16 treated lesions were included in the dose-response analysis (median volume: 22,1 [10,5–80,3] mL; dose: 22,1 [10,5–80,3] Gy). The objective tumor response rate at 3 months was 94%. However, no significant differences were found in absorbed dose metrics (P = .315) or dose-volume histogram values (D50, D70, D85) between responsive and non-responsive (NR) lesions. Patient-level analysis showed a 29% progression rate, with NR patients more likely to have secondary liver tumors (P = .011).
ConclusionThis study including a Portuguese cohort treated with ¹⁶⁶Ho-TARE showed a high tumor response rate. However, the limited sample size reduces the robustness of the conclusions. Further data from ongoing follow-up are awaited.
La radioembolización transarterial (TARE) con microesferas de holmio-166 (¹⁶⁶Ho) es un tratamiento para las neoplasias hepáticas primarias y secundarias no resecables. El procedimiento de simulación preterapéutica mediante una dosis de exploración (“scout dose”) es fundamental para predecir la distribución de las microesferas y excluir fugas extrahepáticas. Este estudio observacional unicéntrico tuvo como objetivo evaluar la concordancia dosimétrica entre el procedimiento de exploración con ¹⁶⁶Ho y la terapia con ¹⁶⁶Ho, así como correlacionar la dosis absorbida por el tumor con la respuesta al tratamiento, tanto a nivel tumoral como del paciente.
MétodosSe incluyeron pacientes con carcinoma hepatocelular en estadio A/B según la clasificación BCLC 2022 o con enfermedad hepática oligometastásica sometidos a TARE con ¹⁶⁶Ho. Se realizó dosimetría basada en vóxeles utilizando el software Q-suite. A los tres meses postratamiento se adquirió una tomografía computarizada con contraste. La respuesta terapéutica se evaluó de acuerdo con los criterios RECIST/mRECIST.
ResultadosVeinte pacientes se sometieron al procedimiento preterapéutico; dieciocho continuaron con la terapia. No se observaron diferencias significativas entre los procedimientos de exploración y de tratamiento en la dosis absorbida por el hígado completo (P = ,331) ni por el tumor (P = ,063), lo que indica una evaluación preterapéutica fiable. Catorce pacientes con dieciséis lesiones tratadas fueron incluidos en el análisis dosis-respuesta (volumen mediano: 22,1 [10,5–80,3] mL; dosis: 22,1 [10,5–80,3] Gy). La tasa de respuesta tumoral objetiva a los tres meses fue del 94%. Sin embargo, no se encontraron diferencias significativas en las métricas de dosis absorbida (P = ,315) ni en los valores de los histogramas dosis-volumen (D50, D70, D85) entre las lesiones respondedores y no respondedores (NR). El análisis a nivel de paciente mostró una tasa de progresión del 29%, siendo más frecuente la falta de respuesta en pacientes con tumores hepáticos secundarios (P = ,011).
ConclusiónEste estudio, que incluye una cohorte portuguesa tratada con TARE con ¹⁶⁶Ho, mostró una alta tasa de respuesta tumoral. No obstante, el tamaño limitado de la muestra reduce la solidez de las conclusiones. Se esperan nuevos datos procedentes del seguimiento en curso.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)