The aim of this study was to evaluate the utility of radiomics based on [18F]FDG PET/CT imaging for the prediction of histological differentiation grade in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) of either adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma subtype.
Materials and methodsA single-center retrospective observational study was conducted, including 150 patients with histologically confirmed NSCLC who underwent [18F]FDG PET/CT imaging prior to complete surgical resection of the tumor. Patients were excluded if they showed no significant FDG uptake, lacked differentiation data, or had insufficient tumor volume. Image segmentation and feature extraction were performed using LIFEx software, obtaining both textural and morphological features. Predictive variables were selected using classical statistical techniques and LASSO regression, and model performance was evaluated using ROC curve analysis.
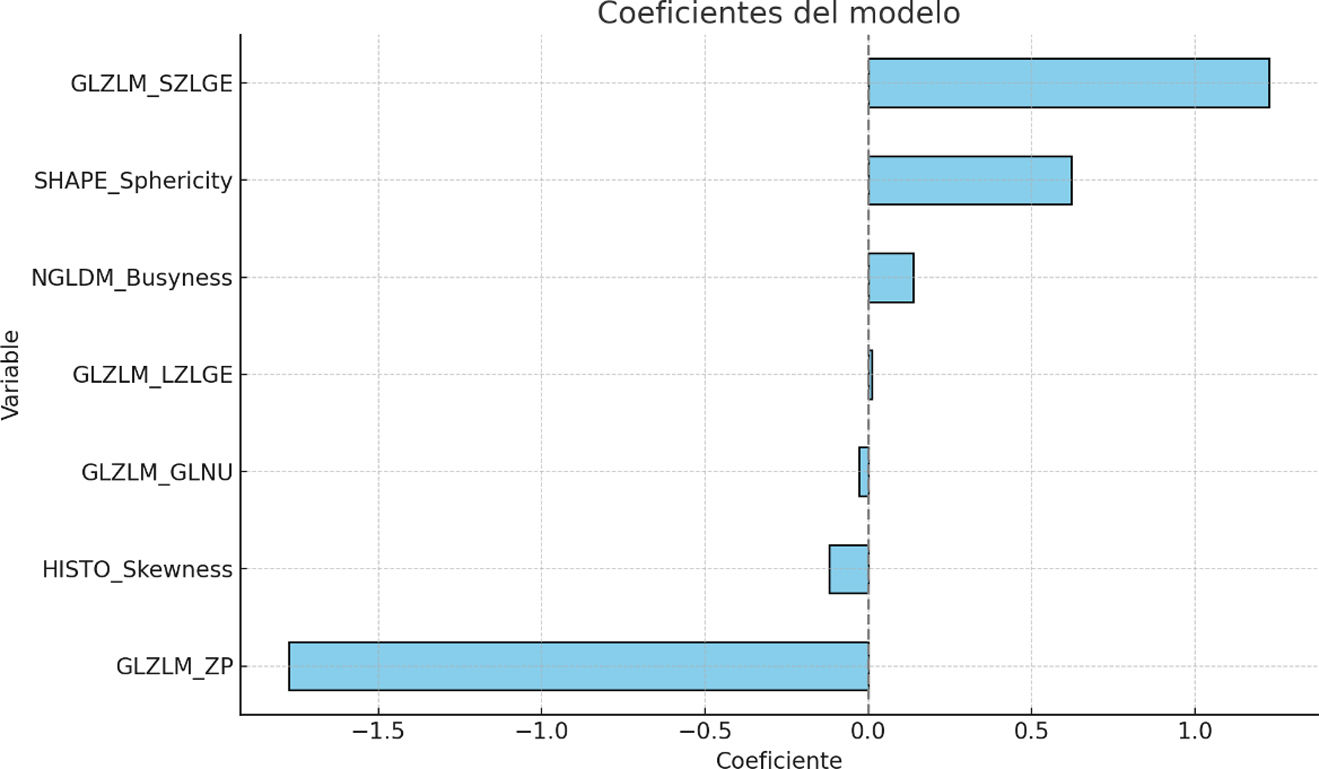
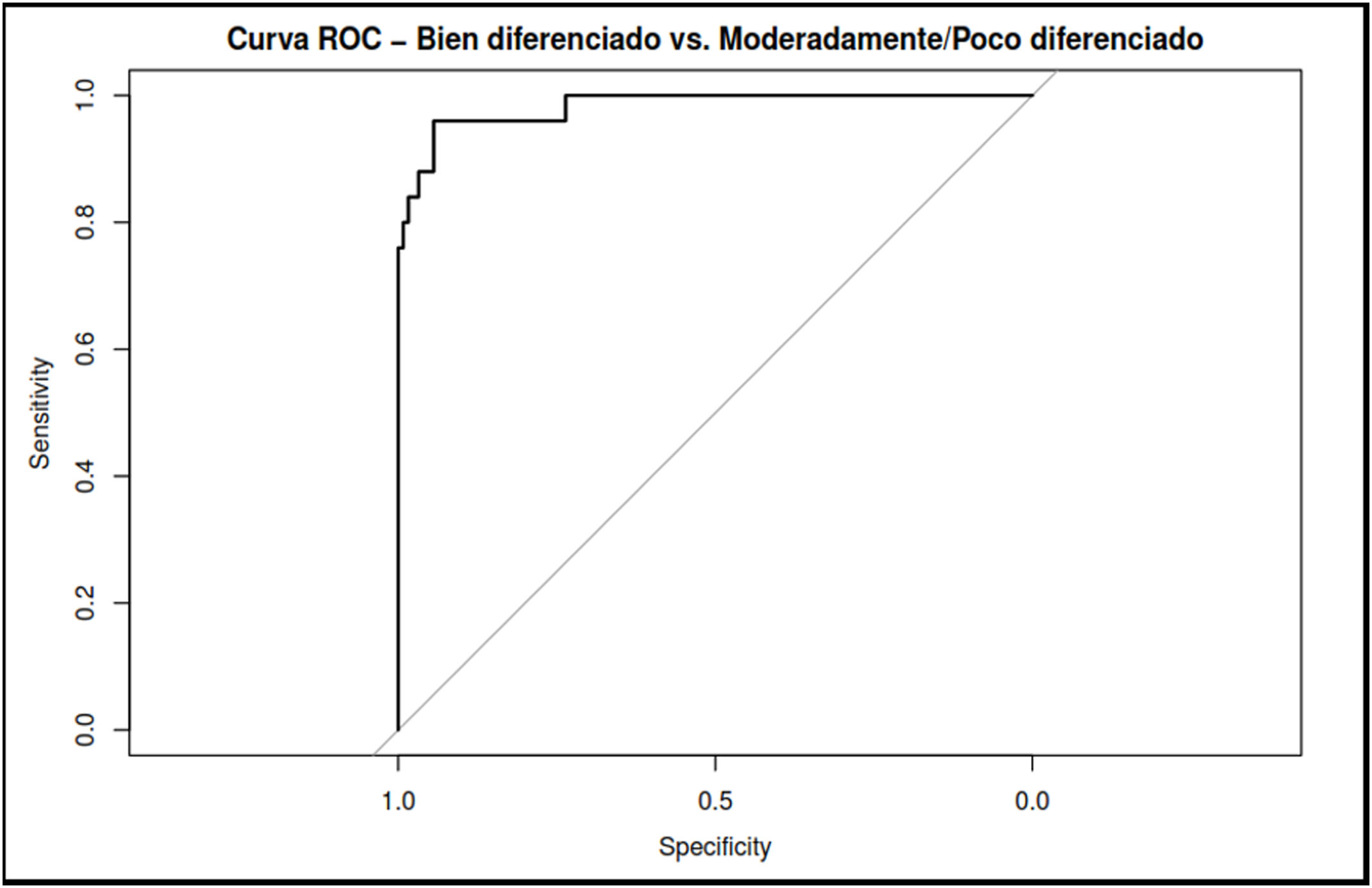
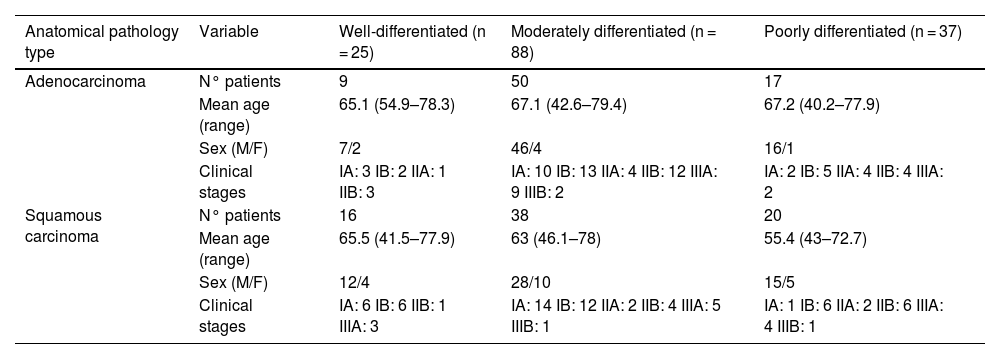
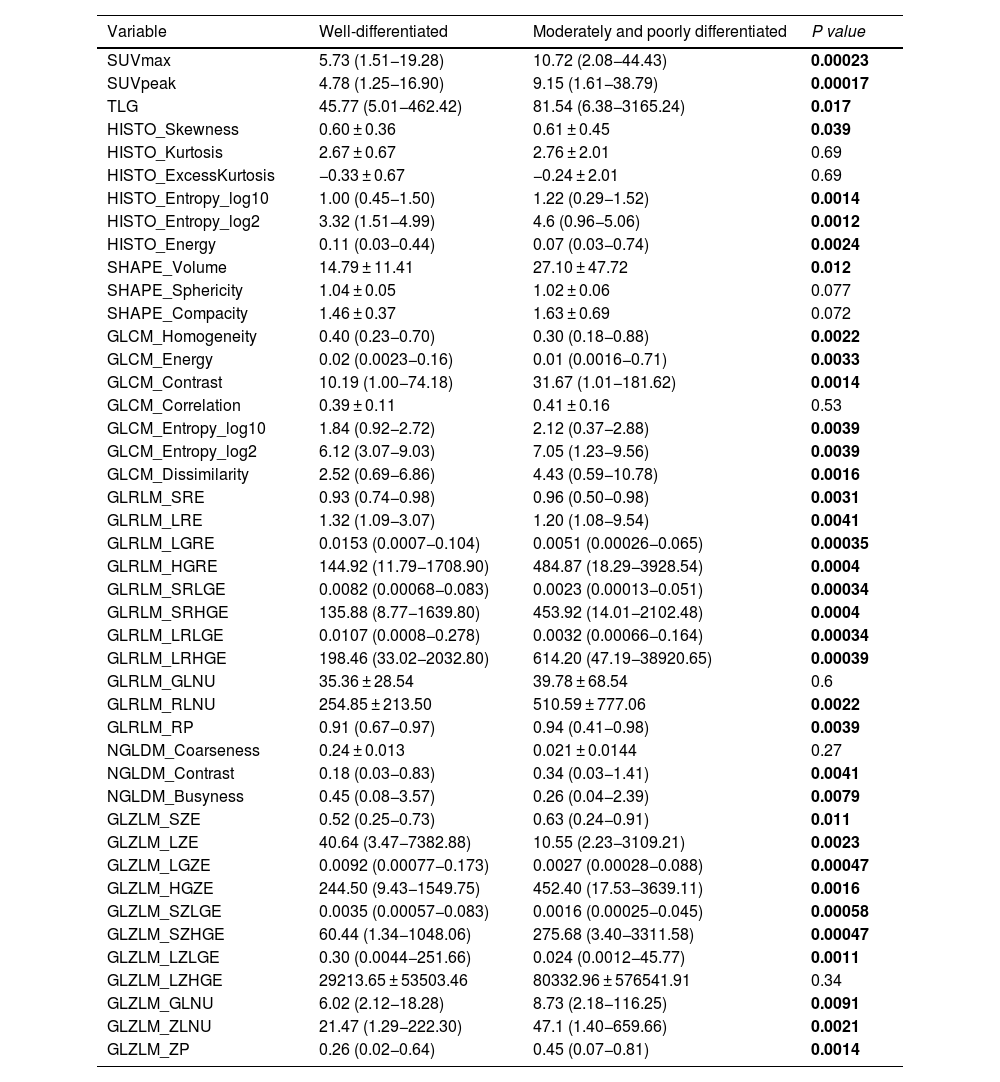
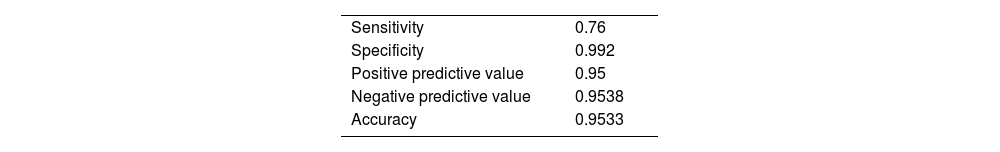
ResultsAmong the 150 patients included, 25 had well-differentiated tumors, 88 moderately differentiated, and 37 had poorly differentiated. Comparison between well-differentiated tumors and those with moderate or poor differentiation revealed statistically significant differences in several radiomic features. The LASSO model identified seven variables with high discriminative power. The model achieved a sensitivity of 76%, specificity of 99.2%, positive predictive value of 95%, negative predictive value of 95.4%, and an overall accuracy of 95.3%.
ConclusionsRadiomic features extracted from [18F]FDG PET/CT images can predict tumor differentiation grade in NSCLC with high specificity. This non-invasive approach may serve as a valuable adjunct to histopathological evaluation, potentially aiding clinical decision-making.
Evaluar la utilidad de la radiómica usando imágenes PET-TC con [18F]FDG para predecir de forma no invasiva el grado de diferenciación histológica en pacientes con cáncer de pulmón no microcítico (CPNM) de tipo adenocarcinoma o carcinoma escamoso.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio observacional retrospectivo en un único centro, incluyendo 150 pacientes con CPNM confirmados histológicamente, que se sometieron a una PET-TC con [18F]FDG previa a la resección quirúrgica completa del tumor. Se excluyeron pacientes sin captación significativa de [18F]FDG, sin datos de diferenciación o con volumen tumoral insuficiente. Las imágenes fueron segmentadas y analizadas con el software LIFEx, extrayendo características radiómicas texturales y morfológicas. Se emplearon métodos estadísticos clásicos y regresión LASSO para la selección de variables predictoras, evaluando el rendimiento diagnóstico mediante curvas ROC.
ResultadosDe los 150 pacientes analizados, 25 presentaban tumores bien diferenciados, 88 moderadamente diferenciados y 37 pobremente diferenciados. La comparación entre tumores bien diferenciados frente a los moderada o pobremente diferenciados mostró diferencias estadísticamente significativas en múltiples variables radiómicas. El modelo LASSO identificó siete variables predictivas con alto valor discriminativo. La curva ROC del modelo alcanzó una sensibilidad del 76%, especificidad del 99,2%, valor predictivo positivo del 95%, valor predictivo negativo del 95,4% y una exactitud global del 95,3%.
ConclusionesLas características radiómicas obtenidas de imágenes [18F]FDG PET-TC permiten predecir con alta especificidad el grado de diferenciación tumoral en el CPNM, ofreciendo una alternativa no invasiva y potencialmente útil para complementar la evaluación histopatológica en la toma de decisiones clínicas.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)