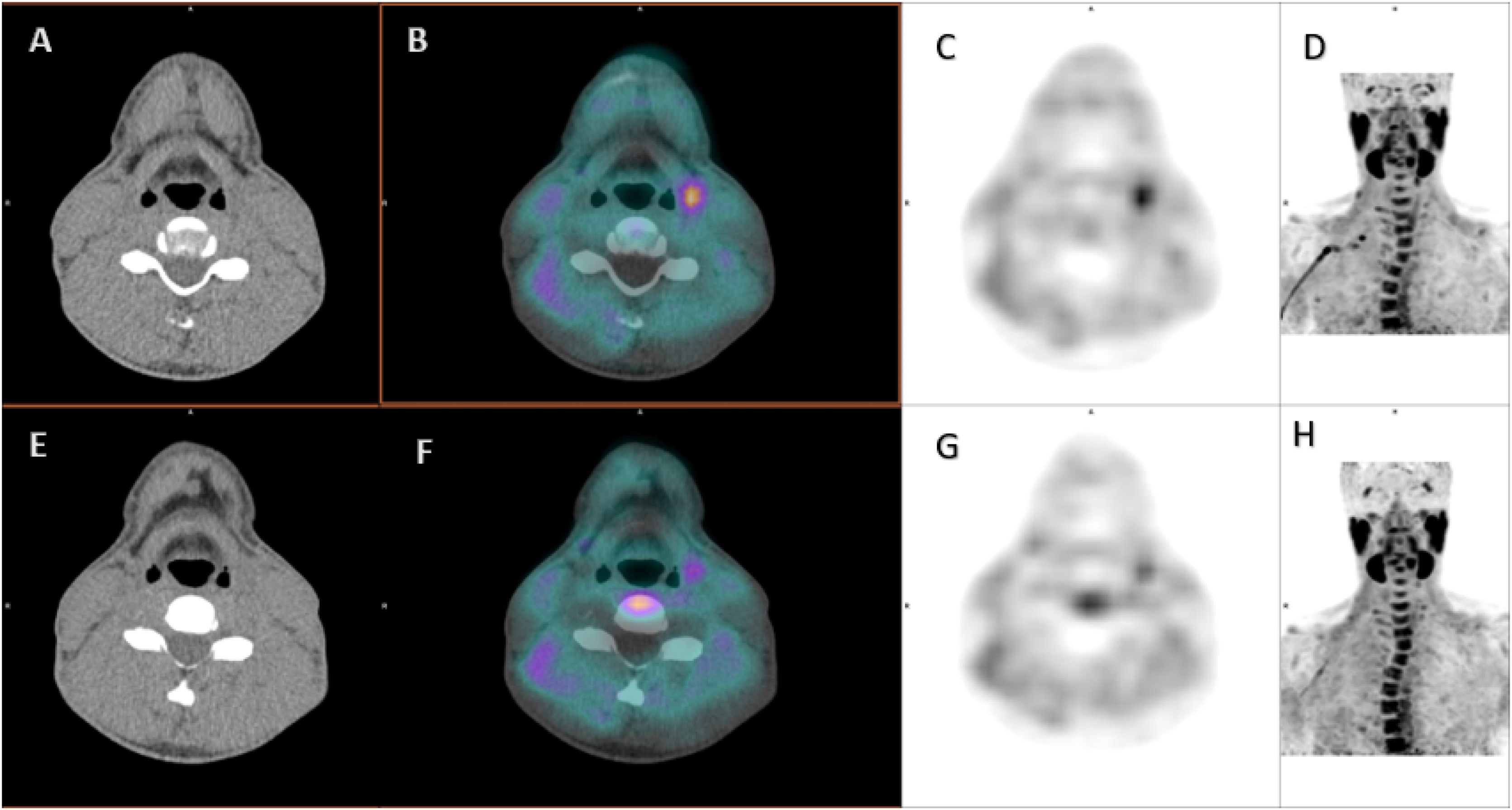
To assess the usefulness of performing a dual-time-point protocol in the acquisition of 18F-choline (18F-FCH) PET/CT in the pre-surgical localization of PHPT, and to demonstrate the impact of this imaging technique on the management and outcome-based surgical decision making, compared to other imaging techniques. To evaluate the diagnostic performance of the test to discriminate between pathological parathyroid gland and cervical lymph node, as well as to establish its correlation with other imaging techniques (scintigraphy, ultrasound, CT and MRI).
Patients and methodsWe included 39 patients who underwent surgery for PHPT, in whom dual-time-point 18F-FCH PET/CT was performed. Metabolic index of parathyroid (P-SUVmax; P-SUVpeak), lymph node (N-SUVpeak), thyroid (T-SUVpeak) and mediastinum (M-SUVpeak) uptake were analyzed visually and semiquantitatively in both images. PET/CT results were correlated with 99mTc-MIBI scintigraphy, ultrasound, MRI and CT.
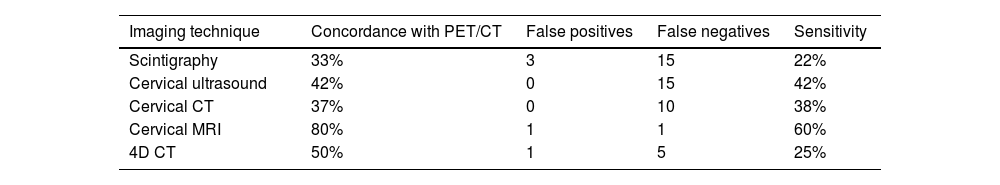
ResultsIn 36 patients (92%), PET/CT was positive, localizing 38 pathological glands. The sensitivity (S) of PET/CT was 97% and positive predictive value (PPV) 94%. In the visual analysis, dual-time-point protocol was necessary in 61% of the cases. Correlation between PET/CT with MRI was 80%, with 4D-CT 50%, and with the other techniques <50%. P-SUVmax shows correlation with adenoma weight and size, and with presurgical PTH. The best cutoff point for SUVpeak to differentiate parathyroid vs. lymph node was 2.6 in early images (S = 70%; specificity = 75%; p = 0.007) and 0.86 for SUVpeak/T-SUVpeak index (S = 73%; specificity = 69%; p = 0.001).
Conclusion18F-FCH PET/CT is an excellent preoperative localization technique in patients with HPTP with negative, doubtful or inconclusive imaging techniques, being of vital importance in guiding minimally invasive surgery. The dual-time-point protocol was necessary in more than half of the cases (61%). The SUVpeak cut-off points to discriminate between parathyroid gland and lymph nodes were statistically significant.
Valorar la utilidad del "dual-time-point" en la adquisición de la PET/TC con 18F-colina (18F-FCH) en la localización prequirúrgica del HPTP, y demostrar el impacto de esta técnica de imagen en el manejo y toma de decisiones quirúrgicas basadas en su resultado, en comparación con otras técnicas de imagen. Evaluar el rendimiento diagnóstico de la prueba para discriminar entre glándula paratiroides patológica y ganglio linfático, así como establecer su correlación con otras técnicas de imagen (gammagrafía, ecografía, TC y RM).
Material y métodosSe incluyeron 39 pacientes intervenidos quirúrgicamente por HPTP, a los que se realizó una PET/TC con 18F-FCH con el protocolo "dual-time-point". Se analizó visualmente y semicuatitativamente la captación y comportamiento de la paratiroides (P-SUVmax; P-SUVpico), ganglios linfaticos (N-SUVpico), tiroides (T-SUVpico) y mediastino (M-SUVpico) en ambas imágenes. Se correlacionaron los resultados de la PET/CT con los de la gammagrafía con 99mTc-MIBI, ecografía, RM y CT.
ResultadosEn 36 pacientes (92%), la PET/TC fue positiva, localizando 38 glándulas patológicas. La sensibilidad (S) de la PET/TC fue del 97% y el valor predictivo positivo (VPP) del 94%. En el análisis visual, el protocolo "dual-time-point" fue necesario en el 61% de los casos. La correlación entre PET/TC y RM fue del 80%, con 4D-TC del 50%, y con las demás técnicas <50%. P-SUVmax muestra correlación con el peso y tamaño del adenoma, y con la PTH prequirúrgica. El mejor punto de corte de SUVpico para diferenciar paratiroides vs ganglio linfático fue 2,6 en imágenes precoces (S = 70%; especificidad = 75%; p = 0,007) y 0,86 para el índice SUVpico/T-SUVpico (S = 73%; especificidad = 69%; p = 0,001).
ConclusiónLa PET/TC con 18F-FCH es una excelente técnica de localización prequirúrgica en pacientes con HPTP con técnicas de imagen negativas, dudosas o no concluyentes, siendo de vital importancia para guiar la cirugía mínimamente invasiva. El protocolo "dual-time-point", fue necesario en más de la mitad de los casos (61%). Los puntos de corte de SUVpico para discriminar entre glándula paratiroides y ganglios linfáticos fueron estadísticamente significativos.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)