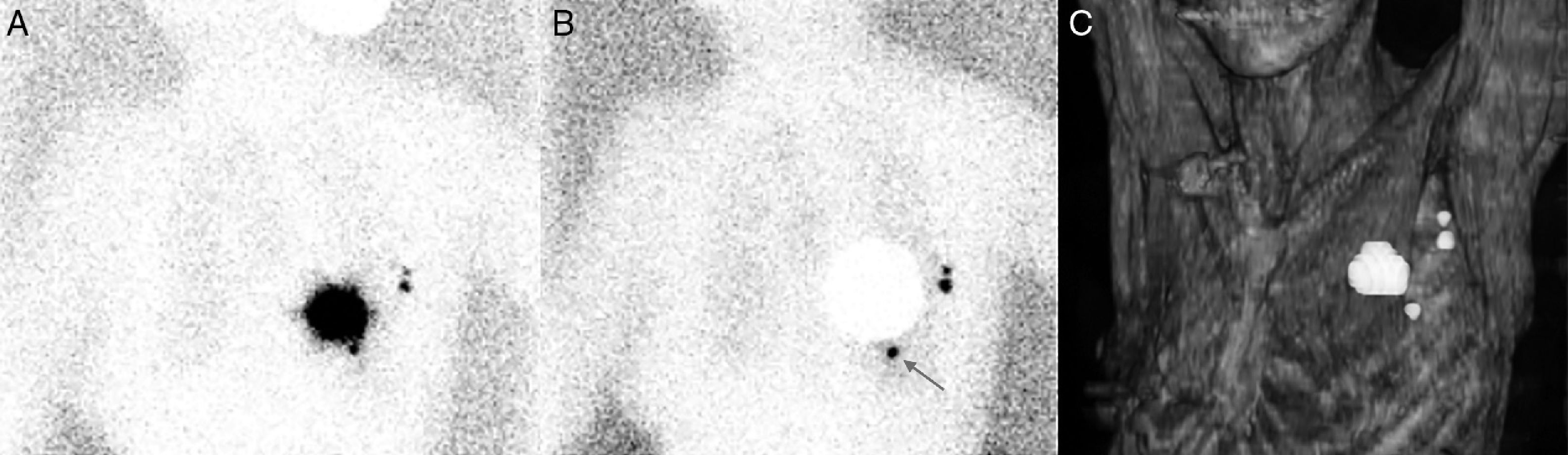
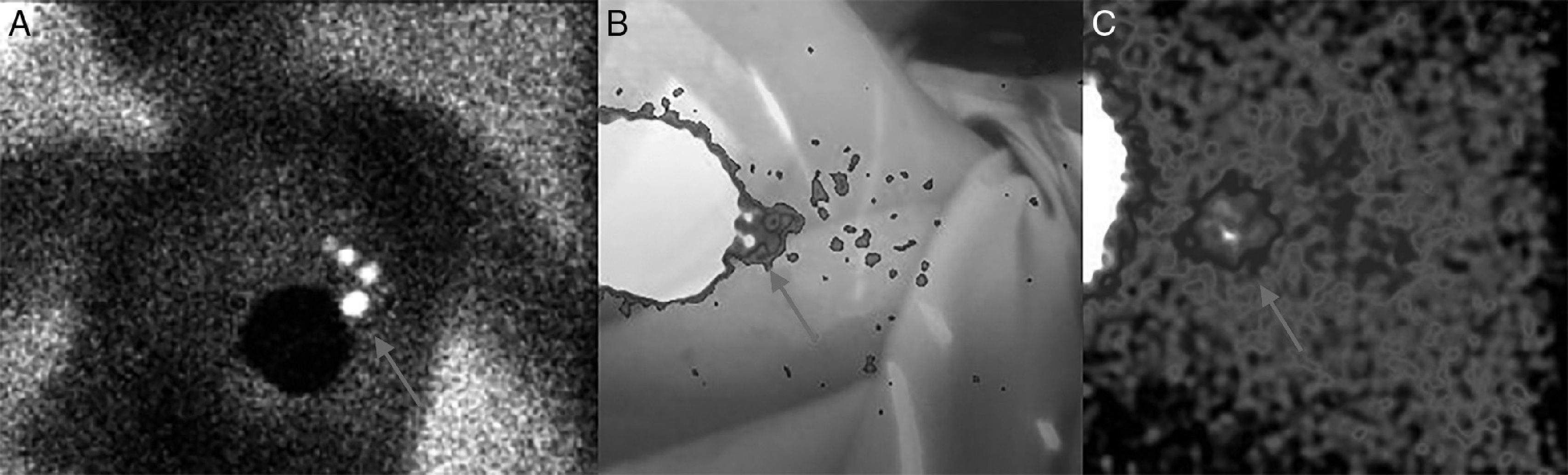
The routes of lymphatic drainage from a breast cancer are the axilla (the most frequent) and the extra axillary regions. Among the latter, there are the so-called intrammamary lymph nodes (IMLN). This study has aimed to assess the incidence of IMLNs in our patients and study the evolution of these cases with IMLN in the lymphoscintigraphy.
Material and methodsThirty-eight patients (out of 1725) with IMLN in the pre-operative lymphoscintigraphy were assessed. During the surgical procedure, using a gamma probe, IMLNs were located and excised. After their harvesting, a meticulous surgical field scan was performed. When the axillary sentinel node was positive for metastasis, a complete axillary lymphadenectomy was performed. In those where the axillary sentinel node was negative and IMLN was positive (IMLN+), axillary lymphadenectomy was also performed, except for one case.
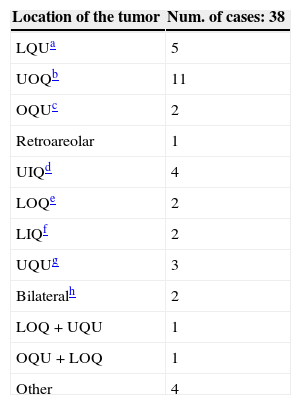
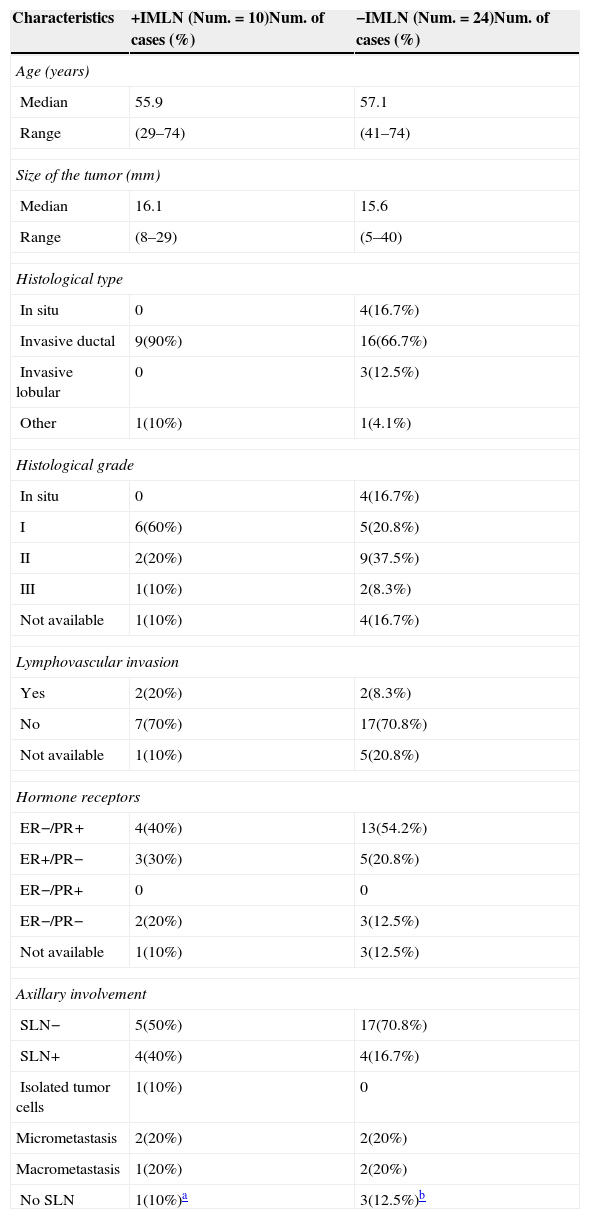
ResultsThirty-four out of the 38 IMLN were obtained (89.5%), because no lymphatic tissue was found in pathology analysis in three cases (8%) and in one patient (3%) IMLN was not found during surgery. Ten (26%) metastatic IMLN were located and the remaining 24 IMLN cases (63%) were metastasis-free. During the clinical follow-up, one patient with IMLN+ developed hepatic metastases. The remaining 33 patients did not present any recurrence. No follow-up data were available for three patients.
ConclusionsIMLN and axillary sentinel node biopsy are recommended when both are depicted in preoperative lymphoscintigraphy. The axilla treatment will only depend on the axillary sentinel node status. Based on the data from other authors and our own experience, avoiding the axillary lymphadenectomy when a metastatic IMLN without axillary involvement seems reasonable.
Entre las vías de drenaje linfático de un tumor mamario se encuentran las de la cadena axilar (la más frecuente) y a las regiones extraaxilares. Dentro de éstas últimas existen los denominados ganglios intramamarios (GIM). El objetivo de este estudio fue valorar la incidencia de GIM en nuestra casuística y estudiar la evolución de las pacientes que presentaron GIM en la linfogammagrafía.
Material y métodosSe han evaluado 38 pacientes (de un total de 1725) que presentaron un GIM en la linfogammagrafía preoperatoria. Durante el acto quirúrgico, utilizando una sonda detectora, se procedió a su localización y exéresis. Posteriormente a su resección y meticuloso rastreo del lecho quirúrgico, se realizó linfadenectomía axilar en los casos en los que el GC axilar fue positivo para metástasis. En aquellas pacientes con GC axilar negativo y GIM positivo (GIM+) se realizó también, con excepción de un caso, linfadenectomía axilar.
ResultadosSe obtuvo el GIM en 34/38 pacientes estudiadas (89,5%), porque en tres (8%) no se encontró tejido linfoide en el análisis antomopatológico y en una (3%) no se detectó el GIM en la cirugía. Se localizaron 10 GIM metastáticos (26%) y los 24 casos restantes (63%) resultaron libres de metástasis. Durante el seguimiento clínico una de las pacientes con GIM+ desarrolló metástasis hepáticas. Las 33 pacientes restantes no presentaron recidiva. No disponemos del seguimiento de tres pacientes.
ConclusionesRecomendamos realizar biopsia del GIM y del GC axilar cuando ambos se detecten mediante linfogammagrafía y, que el manejo axilar dependa únicamente del estatus del GC axilar. Según los datos de diversos autores y nuestra experiencia, parece razonable omitir la linfadenectomía axilar cuando nos encontremos ante un GIM+ sin afectación axilar asociada.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)