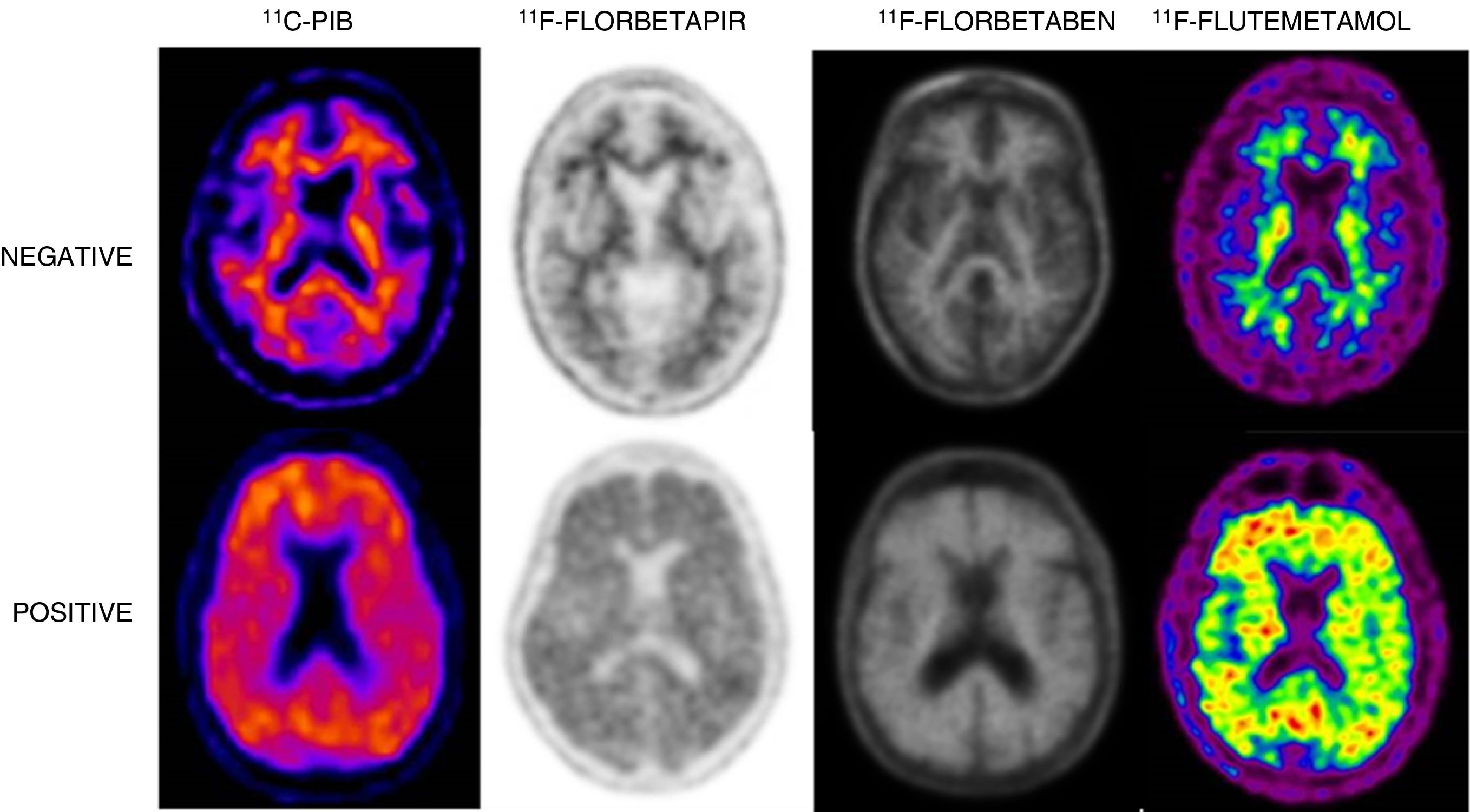
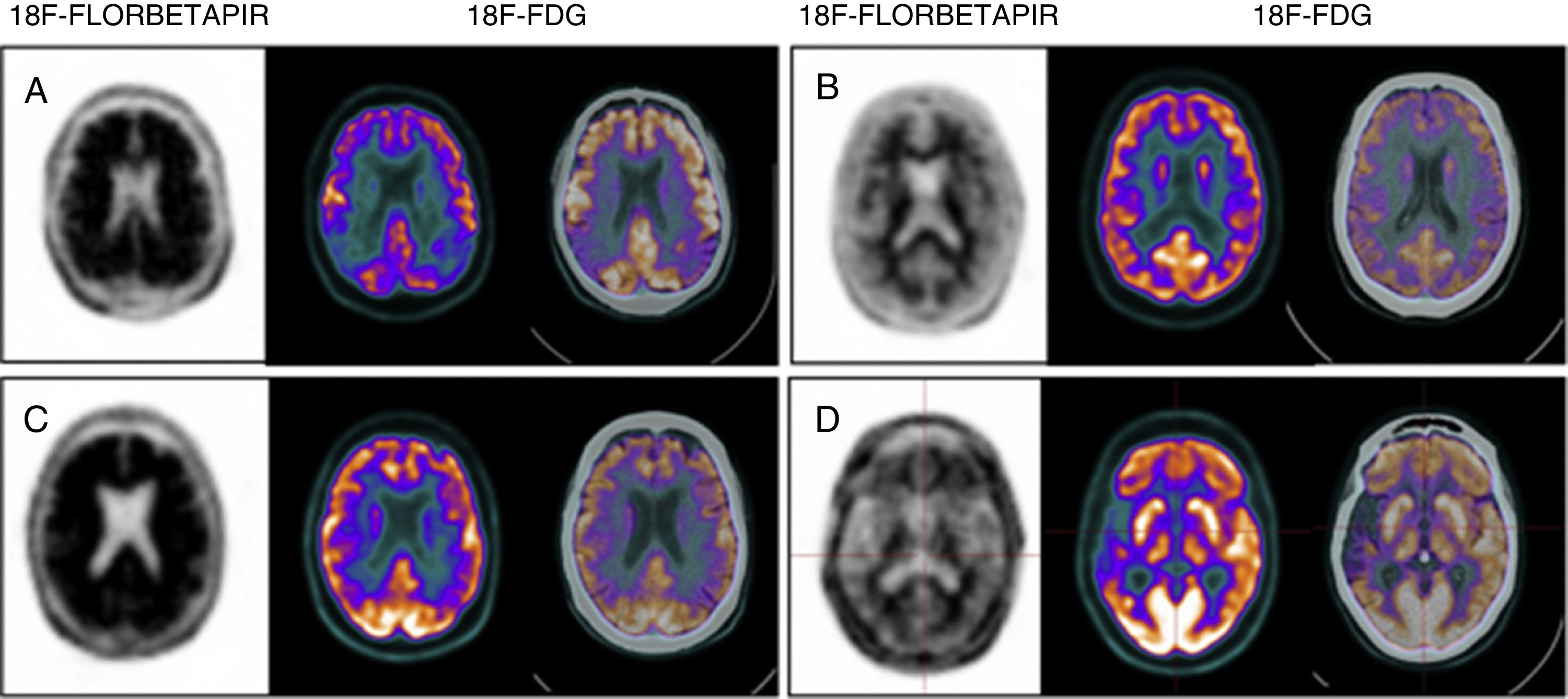
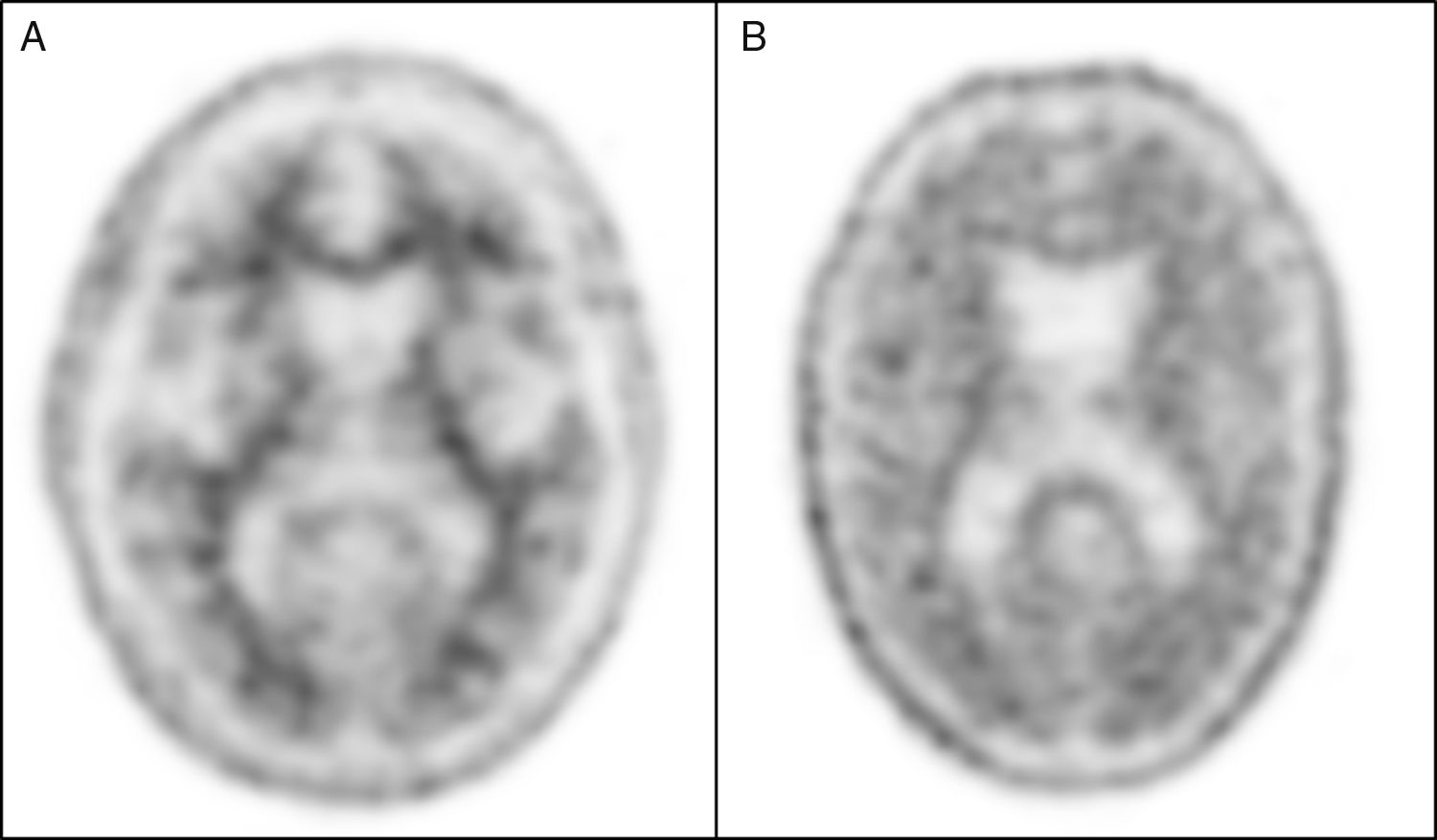
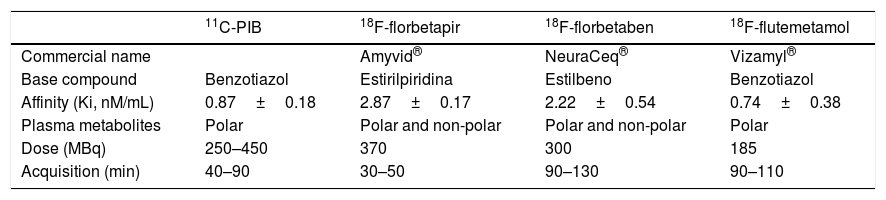
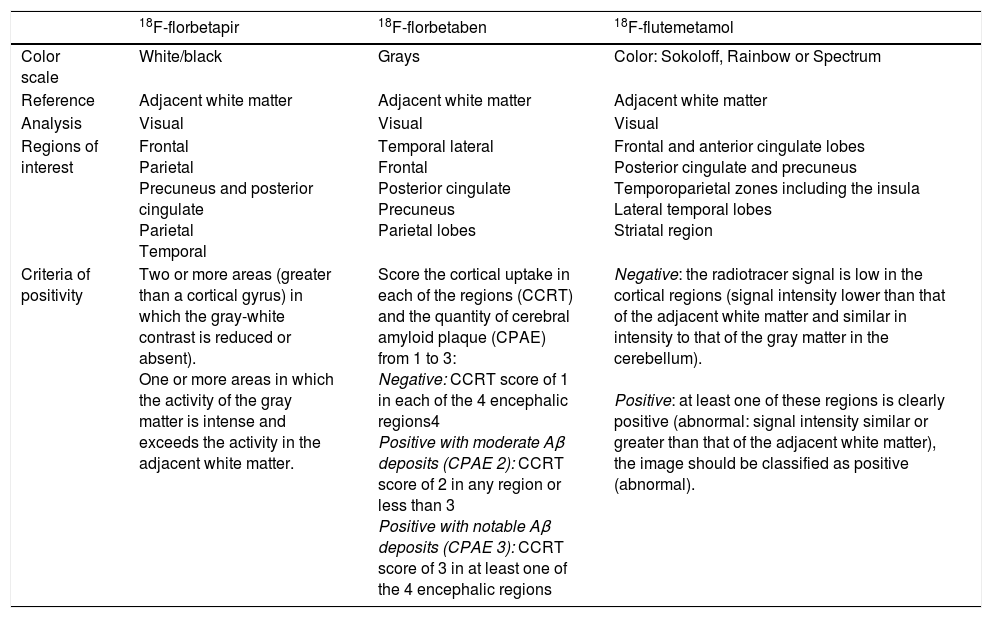
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative condition characterized by progressive cognitive decline and memory loss, and is the most common form of dementia. Amyloid plaques with neurofibrillary tangles are a neuropathological hallmark of AD that produces synaptic dysfunction and culminates later in neuronal loss. Amyloid PET is a useful, available and non-invasive technique that provides in vivo information about the cortical amyloid burden. In the latest revised criteria for the diagnosis of AD biomarkers were defined and integrated: pathological and diagnostic biomarkers (increased retention on fibrillar amyloid PET or decreased Aβ1-42 and increased T-Tau or P-Tau in CSF) and neurodegeneration or topographical biomarkers (temporoparietal hypometabolism on 18F-FDG PET and temporal atrophy on MRI). Recently specific recommendations have been created as a consensus statement on the appropriate use of the imaging biomarkers, including amyloid PET: early-onset cognitive impairment/dementia, atypical forms of AD, mild cognitive impairment with early age of onset, and to differentiate between AD and other neurodegenerative diseases that occur with dementia. Amyloid PET is also contributing to the development of new therapies for AD, as well as in research studies for the study of other neurodegenerative diseases that occur with dementia where the deposition of Aβ amyloid is involved in its pathogenesis. In this paper, we review some general concepts and study the use of amyloid PET in depth and its relationship with neurodegenerative diseases and other diagnostic techniques.
La enfermedad de Alzheimer (EA) es una enfermedad neurodegenerativa que se caracteriza por un deterioro cognitivo progresivo y pérdida de memoria, siendo la causa más común de demencia. Los hallazgos anatomopatológicos de la EA son los depósitos de Aβ amiloide y proteína Tau, que producen disfunción sináptica y muerte neuronal. La PET amiloide es una técnica útil, disponible y no invasiva que nos proporciona información in vivo del depósito amiloide. En las últimas revisiones de los criterios diagnósticos de la EA se definen e incorporan los biomarcadores, que se clasifican en biomarcadores fisiopatológicos o de diagnóstico (aumento de la retención fibrilar amiloide observada por PET o disminución del péptido Aβ1-42 y elevación de las proteínas T-Tau y F-Tau en el LCR) y biomarcadores de neurodegeneración o topográficos (disminución del metabolismo temporoparietal en la PET con 18F-FDG y atrofia temporal medial en la RM). Recientemente se han creado unas recomendaciones específicas para la correcta utilización de los biomarcadores, donde se incluye la PET amiloide: deterioro cognitivo persistente/progresivo, deterioro cognitivo atípico, deterioro cognitivo de inicio precoz y diagnóstico diferencial entre EA y otras enfermedades neurodegenerativas que cursan con demencia. Nuevos estudios de investigación y ensayos clínicos están utilizando la PET amiloide en la evaluación y el desarrollo de nuevas terapias para la EA, así como para el estudio de otras enfermedades neurodegenerativas que cursan con demencia. En este trabajo revisamos algunos conceptos generales y profundizamos en el uso de esta nueva técnica y su relación con las enfermedades neurodegenerativas y el resto de las técnicas diagnósticas.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)