El fenómeno de Raynaud (FR) es una condición vasoespástica que conlleva una carga significativa de dolor y discapacidad. Cuando las terapias habituales no son suficientemente efectivas, surge la necesidad de buscar otras alternativas terapéuticas, como la toxina botulínica (TB) interdigital.
ObjetivoDeterminar la mejoría clínica de los pacientes con FR (número de episodios diarios, EVA durante episodios, duración de los episodios y el Raynaud Condition Score).
Materiales y métodosEstudio observacional, descriptivo, retrospectivo, de los pacientes con FR a quienes se les realizó una infiltración ecoguiada interdigital de TB tipoA. Se obtuvieron los datos de los controles posprocedimiento (meses1, 3 y6) y se realizó el análisis mediante la prueba de Wilcoxon, para lo cual se empleó el programa StatPlus.
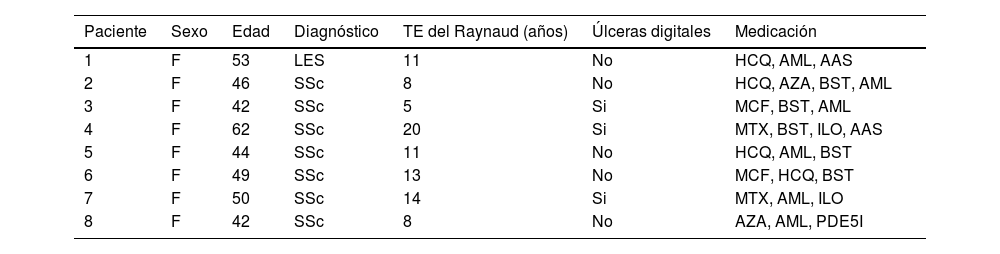
ResultadosSe realizó el estudio en ocho pacientes (100% mujeres) con una media de edad 48,5años, todas con FR secundario a una enfermedad sistémica (87,5% esclerosis sistémica). Se evidenciaron diferencias significativas (mediana y rango intercuantílico) en el número de los episodios de FR en el primer mes (p=0,043). La EVA de dolor de cada episodio se redujo el primer mes (p=0,027) y en el tercer mes (p=0,043). Se encontraron diferencias en el Raynaud Condition Score al primer mes (p=0,027) y al tercer mes (p=0,043).
ConclusionesLa TB tipoA infiltrada de forma ecoguiada interdigital podría ser un tratamiento adyuvante para los pacientes con FR.
Raynaud's phenomenon (RP) is a vasospastic condition that carries a significant burden of pain and disability. When conventional therapies are not sufficiently effective, the need arises to explore other therapeutic alternatives such as interdigital botulinum toxin (BT) injection.
ObjectiveTo determine clinical improvement in patients with RP (number of daily episodes, Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) during episodes, duration of episodes, and Raynaud Condition Score).
Materials and methodsObservational, descriptive, retrospective study of patients with RP who received ultrasound-guided interdigital injection of typeA BT. Data from post-procedure controls (months1, 3, and6) were obtained, and analysis was performed using the Wilcoxon test through the StatPlus programme.
ResultsThe study was conducted on 8 patients (100% female) with a mean age of 48.5years, all of whom had RP secondary to a systemic disease (87.5% systemic sclerosis). Significant differences were observed (median and interquartile range) in the number of RP episodes in the first month (P=.043). The pain VAS for each episode decreased in the first month (P=.027) and in the third month (P=.043). Differences were found in the Raynaud condition score in the first month (P=.027) and the third month (P=.043).
ConclusionsUltrasound-guided interdigital injection of typeA BT could be an adjuvant treatment for patients with RP.