Reducir ingresos por insuficiencia cardiaca (IC) es uno de los principales objetivos en el control de la enfermedad, por su impacto en el pronóstico y en el gasto sanitario. Los modelos transicionales al alta se imponen como una estrategia capaz de reducirlos, la mayoría basados en unidades hospitalarias específicas. Tratamos de valorar el impacto del seguimiento post-alta realizado desde atención primaria (AP).
Material y métodosEstudio ecológico observacional retrospectivo en el área de referencia de un hospital terciario. Se efectúa un análisis de regresión lineal entre la tasa de seguimiento precoz desde el centro de salud tras un ingreso por IC y las tasas de reingreso a 30días por todas las causas a lo largo de 2021.
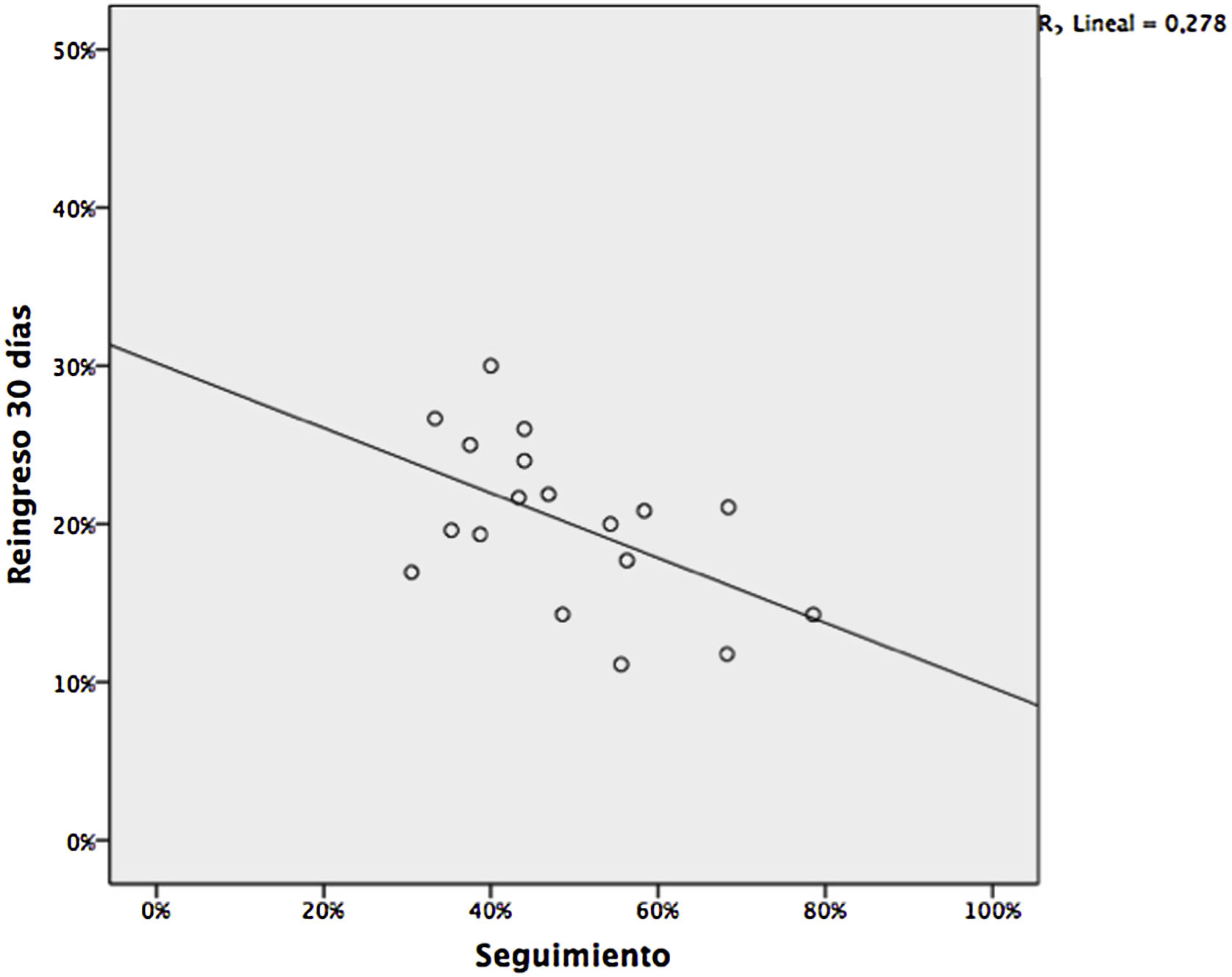
ResultadosEl grado de seguimiento desde AP tras un alta hospitalaria por insuficiencia cardiaca se asocia con un menor reingreso a 30días por todas las causas (R de Pearson=0,53; p=0,02), con un descenso del 20%, similar al observado cuando se realiza desde otros dispositivos asistenciales y que se mantiene cuando se ajusta por complejidad de los pacientes.
ConclusionesTras un ingreso por IC, el seguimiento post-alta desde AP puede ser eficaz, reduciendo ingresos evitables y complementario al realizado por las unidades hospitalarias.
Reducing heart failure (HF) admissions is one of the main objectives in disease control, due to its impact on prognosis and costs. The transitional models at discharge are imposed as a strategy capable of reducing hospitalizations, most of them based on specific hospital units. We analyzed the impact of the primary care (PC) post-discharge follow-up.
Material and methodsRetrospective observational study at the referral area of a tertiary hospital. Linear regression analysis was performed between early follow-up from the PC center after HF admission rate and the 30-day all-cause readmission rate throughout 2021.
ResultsThe degree of follow-up from PC after hospital discharge for heart failure is associated with fewer 30-day readmissions for all causes (Pearson's R=0.53, P=.02); with a decrease of 20%, similar to that observed when it is performed from other care facilities and which is maintained when adjusting for the complexity of the patients.
ConclusionsPC heart failure post-discharge follow-up could be effective in reducing hospitalizations, and is complementary to that carried out by hospital units.
La insuficiencia cardiaca (IC) es una patología con un alto impacto sanitario y económico, estando este muy asociado a los ingresos repetidos, que suponen casi el 40% total de los costes directos e indirectos1. Los recientes avances en el tratamiento han mejorado significativamente el pronóstico de la enfermedad; sin embargo, el control de los reingresos continúa siendo un reto2. Este problema afecta especialmente al denominado «periodo vulnerable», los primeros 30-60días tras el alta hospitalaria, en la que se concentran la mayor parte de los ingresos evitables. Para ello se han desarrollado distintas estrategias de transición al alta3 centradas en su mayoría en el nivel hospitalario, y que han demostrado ser capaces de reducir estos eventos4,5. En algunos de los más exitosos se incluye la coordinación entre niveles asistenciales como pilar de la intervención6, por lo que esta surge como acción fundamental a desarrollar en distintos documentos de consenso7. Sin embargo, es escasa la bibliografía que mida el impacto que tienen acciones específicamente realizadas desde atención primaria (AP) en esta transición al alta de la hospitalización por IC.
Nuestro objetivo es medir la efectividad de dicha intervención post-alta desde AP en cuanto a su impacto en la reducción de reingresos precoces, independientemente de las acciones que se realicen desde el nivel hospitalario/unidades de IC. La comparación en vida real entre pacientes sobre los que se realiza o no una intervención que debería ser universal es compleja, por la imposibilidad de aleatorizar y la posible presencia de múltiples sesgos sistemáticos que pueden llevar a sobrestimar o subestimar el efecto. Es probable que ante la imposibilidad de atender a todos los pacientes se dé prioridad a aquellos de mayor riesgo o complejidad; o viceversa, la atención podría centrarse en aquellos con más seguimiento previo. Buscamos responder a esta pregunta analizando los resultados poblacionales de reingreso precoz en los distintos centros de salud, dentro de una misma área sanitaria, con distinto grado de implantación de dicho seguimiento.
Material y métodosRealizamos un estudio ecológico observacional y retrospectivo en el que valoramos la relación entre el grado de seguimiento de los pacientes dados de alta del Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre pertenecientes a cada uno de los 18 centros de salud de su área sanitaria y su tasa de reingreso a 30días por todas las causas durante un año completo.
Tras el alta hospitalaria por IC, se genera una alerta automática en la historia clínica de atención primaria (programa APMadrid) y una cita en la agenda de enfermería comunitaria. El paciente recibe una llamada de su enfermera en las 24-48h desde el alta, en la que se realiza una intervención estructurada que revisa datos de alarma clínica, verifica que la transición de cuidados en correcta (se ha conciliado medicación, se han explicado los cambios y los nuevos fármacos están dispensables en prescripción electrónica) y que el paciente y los cuidadores han sido educados sobre la enfermedad y saben reconocer los signos de alarma. Si identifica algún problema clínico, enfermería genera una cita presencial con el profesional adecuado del centro de salud. Esta estrategia presenta un grado de implantación variable según el centro de salud por ser de reciente introducción, y esta variabilidad es monitorizable, pues enfermería debe dejar registro electrónico de su realización.
A través de la base de datos de Continuidad Asistencial de la Comunidad de Madrid se extraen los datos de reingreso a 30días por todas las causas y seguimiento al alta desde AP. Se dispone de los datos agregados, estratificados por centro de salud, seguimiento realizado y nivel de intervención de los pacientes, definiendo este como el asignado por su médico de familia dentro de la estrategia de atención a pacientes crónicos del Servicio de Salud de la Comunidad de Madrid, basada en la pirámide de Kaiser Permanente8. Dado que la intervención referida está coordinada solo entre el Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre y los centros de salud correspondientes al área de AP de referencia, se excluyen del análisis aquellos casos que tras el alta tuvieron seguimiento en AP de otras áreas o los pacientes procedentes de otras comunidades autónomas. No se consideran como ingresos hospitalarios las visitas a urgencias ni la derivación a hospital de día.
Se realizó un análisis de regresión lineal para valorar la relación entre la tasa de reingreso y de seguimiento en cada centro de salud. Posteriormente, se realiza un análisis multivariable con los otros valores disponibles de cada centro de salud para identificar posibles factores modificadores y de confusión: población total atendida y población mayor de 75años, incidencia de ingreso por IC total y ajustada por mayores de 75años, y estratificación de los pacientes por nivel de intervención asignado. Utilizamos el paquete estadístico SPSS 22.
ResultadosDurante 2021 se produjeron en el Hospital 12 de Octubre 1.304 ingresos por IC. Se excluyeron 483 pacientes por no pertenecer al área sanitaria (361 de otras comunidades autónomas y 122 de centros de salud pertenecientes a otras áreas de la Comunidad de Madrid), por lo que se valoraron 813 ingresos asignados a 18 centros de salud. De ellos, se produjo la intervención en 401 (49,3%) y reingresaron 159 (19,6%). Las tasas de seguimiento, reingreso a 30días y resto de características de cada centro se recogen en la tabla 1.
Características basales analizadas por centro de salud
| C. de salud | Ingresos | Población asignada | Ingresos por IC/10.000 hab. | Seguimiento | Reingreso 30 días |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 96 | 34.675 | 27,69 | 56,25% | 17,71% |
| 2 | 85 | 40.043 | 21,23 | 68,24% | 11,77% |
| 3 | 64 | 26.078 | 24,54 | 37,50% | 25,00% |
| 4 | 64 | 37.023 | 17,29 | 46,88% | 21,88% |
| 5 | 60 | 22.259 | 26,96 | 43,33% | 21,67% |
| 6 | 59 | 31.595 | 18,67 | 30,51% | 16,95% |
| 7 | 51 | 28.295 | 17,63 | 35,28% | 19,61% |
| 8 | 50 | 27.236 | 18,36 | 44,00% | 24,00% |
| 9 | 50 | 12.732 | 39,27 | 44,00% | 26,00% |
| 10 | 38 | 12.719 | 29,88 | 68,42% | 21,05% |
| 11 | 35 | 28.173 | 12,42 | 48,57% | 14,29% |
| 12 | 35 | 21.506 | 16,27 | 54,29% | 20,00% |
| 13 | 31 | 25.343 | 12,23 | 38,71% | 19,35% |
| 14 | 28 | 17.878 | 15,66 | 78,57% | 14,28% |
| 15 | 24 | 21.500 | 11,16 | 58,33% | 20,83% |
| 16 | 18 | 20.170 | 8,92 | 55,56% | 11,11% |
| 17 | 15 | 9.271 | 16,18 | 33,33% | 26,67% |
| 18 | 10 | 15.582 | 6,42 | 40,00% | 30,00% |
Al valorar el efecto del seguimiento post-alta en la tasa de reingresos de manera bruta, se observó una tendencia a la reducción no estadísticamente significativa (17,9% vs 20,8%; OR: 0,86; p=0,29), que no se modificó al ajustar por nivel de intervención asignado. Sí observamos un efecto estadísticamente significativo cuando se valoró la correlación entre el grado de seguimiento realizado por cada centro de salud y su tasa de reingreso (R=0,53; p=0,02; fig. 1).
La correlación se mantiene tras ajustar el resultado por tamaño del cupo, la incidencia de ingresos por IC bruta y ajustada a mayores de 75años y el nivel de intervención de los pacientes. El tamaño del cupo se asocia con mejores resultados (−1% por cada 3.550 habitantes, p=0,05), pero sin presentar interacción con el grado de seguimiento en el análisis multivariable (tabla 2).
DiscusiónLas estrategias transicionales al alta en IC se han establecido como estándar de práctica clínica tras múltiples estudios que muestran su eficacia en la mejora del pronóstico y la reducción de ingresos evitables. Sin embargo, no encontramos evidencia de acciones desarrolladas desde AP, siendo la IC una patología con varias características que la hacen idónea para este nivel asistencial: su altísima prevalencia, la cronicidad que exige longitudinalidad, el valor de las acciones preventivas y la presencia de múltiples enfermedades extracardiacas con capacidad para descompensar al paciente. Nuestro trabajo intenta contribuir al conocimiento en esta área a través de un estudio ecológico, que nos permite responder si un seguimiento más amplio se corresponde con una reducción de ingresos.
El resultado obtenido sugiere un impacto en la reducción de reingresos en torno al 20%, similar al mostrado en intervenciones similares realizadas desde otros niveles asistenciales4,6. Que del resto de variables analizadas la única que sea significativa sea el tamaño de la población atendida, en nuestra opinión apoya el valor del seguimiento, pues nos podría estar mostrando la existencia de una curva de aprendizaje más fácil de alcanzar en centros con mayor casuística. El beneficio es independiente de la complejidad o nivel de intervención, probablemente porque muchos de los factores que pueden llevar al reingreso evitable (falta de adherencia, déficits de cuidados o conocimiento de la enfermedad, efectos secundarios de nuevos fármacos, complicaciones nosocomiales, etc.) no son exclusivos de los pacientes más complejos.
La principal limitación del estudio es su diseño observacional, con las limitaciones que ello conlleva, si bien es difícil, y éticamente cuestionable, diseñar un ensayo clínico donde un grupo se viese privado de la intervención por su equipo de AP. Por otro lado, una de las bondades del diseño ecológico es que permite limitar sesgos asociados a la selección de pacientes, y que el efecto tenga un gradiente dosis-respuesta cuantitativamente similar al descrito en estudios cuando la transición al alta se realiza desde unidades hospitalarias. Otra limitación es que es probable que el seguimiento descrito no vaya aislado sino asociado a otras intervenciones, por lo que el mayor porcentaje de revisiones post-alta sería una variable intermedia asociada a mayor seguimiento global desde el centro de AP a los pacientes con IC, ya sea por menor sobrecarga, por mayor conciencia sobre la enfermedad o por otras causas. En todo caso, esto no cambiaría la conclusión: un mayor seguimiento desde AP tras un alta por IC se asocia con mejores resultados.
Por último, el análisis corresponde a una única área sanitaria. Esto nos permite controlar otros sesgos, como puede ser la accesibilidad del territorio, la situación socioeconómica o la disponibilidad o no de una unidad de IC, que serán similares para todos los pacientes. Sin embargo, deja sin responder si la intervención es eficaz en sí misma o es dependiente de un contexto adecuado. En el Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre existe un Programa Transversal de IC que implica a todos los niveles desde la hospitalización hasta el seguimiento crónico, compartido entre cardiología, medicina interna y AP. Existe igualmente un programa de formación continuada, compartido entre ambos niveles asistenciales desde hace 5años y que ha implicado la rotación de más de 300 profesionales sanitarios, tanto facultativos como enfermería, por la unidad hospitalaria. Todo ello favorece el trabajo en equipo, la existencia de vías rápidas de comunicación y atención precoz a la descompensación en el hospital de día. Es plausible que las intervenciones en uno u otro nivel asistencial sean más potentes cuando se complementan por un adecuado funcionamiento de ambas, o mejor aún se coordinan a través de protocolos compartidos y comunicación eficaz.
ConclusionesEl seguimiento desde AP, tras un alta hospitalaria por IC, es eficaz en la reducción de ingresos precoces evitables por todas las causas. Esta actuación se añade al resto de acciones que se desarrollan desde las unidades de IC hospitalarias. El impacto parece independiente de la complejidad o del nivel de intervención, pudiendo beneficiar a todos los pacientes.
FinanciaciónEste trabajo no ha recibido ningún tipo de financiación.
Conflicto de interesesLos autores declaran no tener ningún conflicto de intereses.
Consideraciones éticasLos autores declaran que para esta investigación no se han realizado experimentos en seres humanos ni animales y se han seguido los protocolos de los centros de trabajo sobre tratamiento de la información de los pacientes.