Lyell Syndrome is a rare and severe mucocutaneus adverse reaction mostly common induced by medication. It is related to Stevens-Johnson syndrome and both are collectively known as epidermal necrolysis. Classification is based on the affected total body area, with Lyell syndrome skin detachment affecting more than 30% of the total body area, and therefore is a more severe condition.
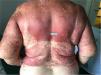
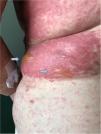
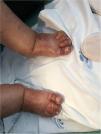
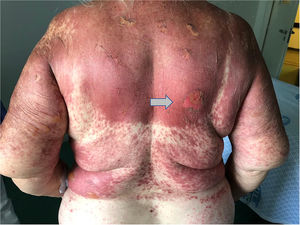
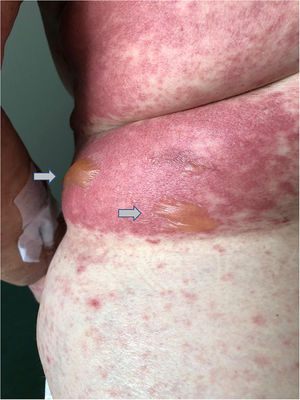
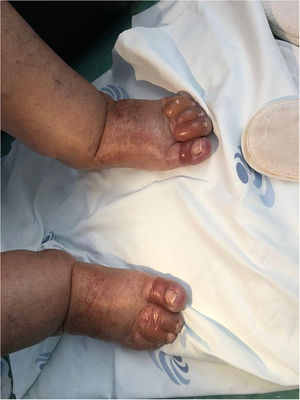
This case reports a 75 year-old woman whom was prescribed diclofenac after having fallen at home. One day after starting diclofenac, the patient showed up to the emergency department complaining of multiple skin lesions (that started in the right arm). Clinical examination revealed a generalized disseminated mucocutaneous reaction, characterized by confluent macular erythematous skin lesions (Fig. 1), associated with blisters, namely in the arms, posterior trunk and feet (Fig. 2 and 3). The patient started immunoglobulin associated with corticosteroid and anti-histamines, along with skin care. Over time, more and more blisters appeared, affecting more that 30% of total body area, becoming very difficult to control patient pain.
Medical team decided to transfer the patient to a Burn Unit, so that the best wound care could be provided. Later, the patient developed a respiratory complication, namely pneumonia with severe ARDS and sadly died.