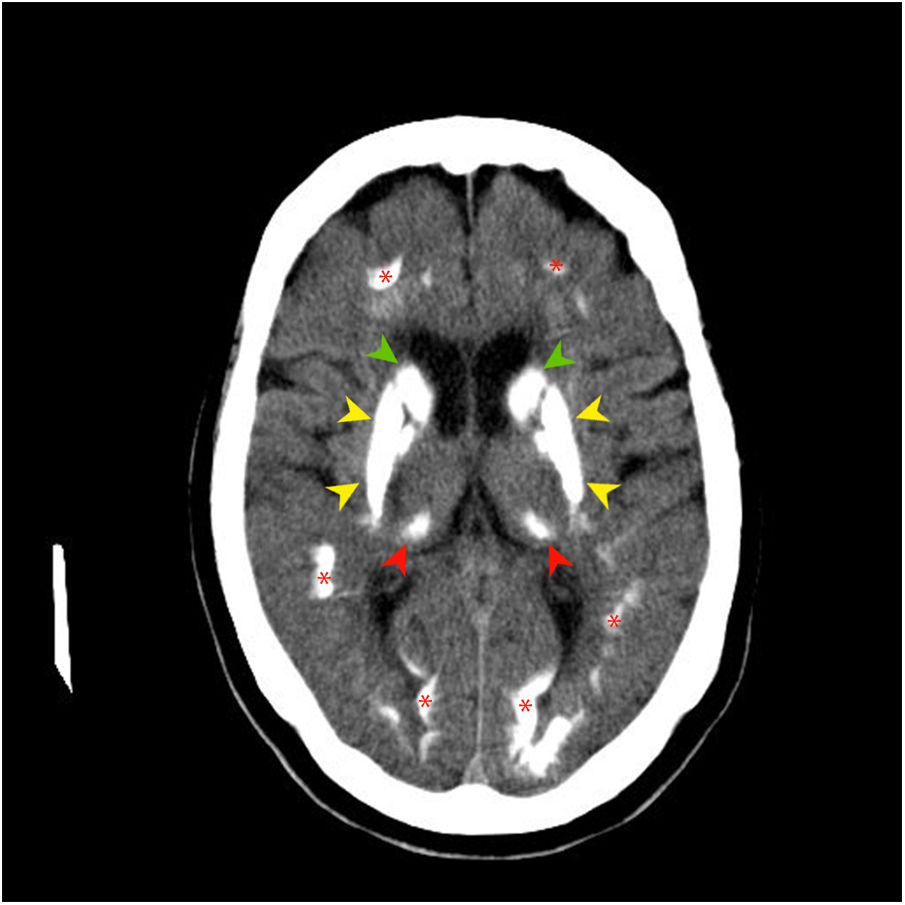
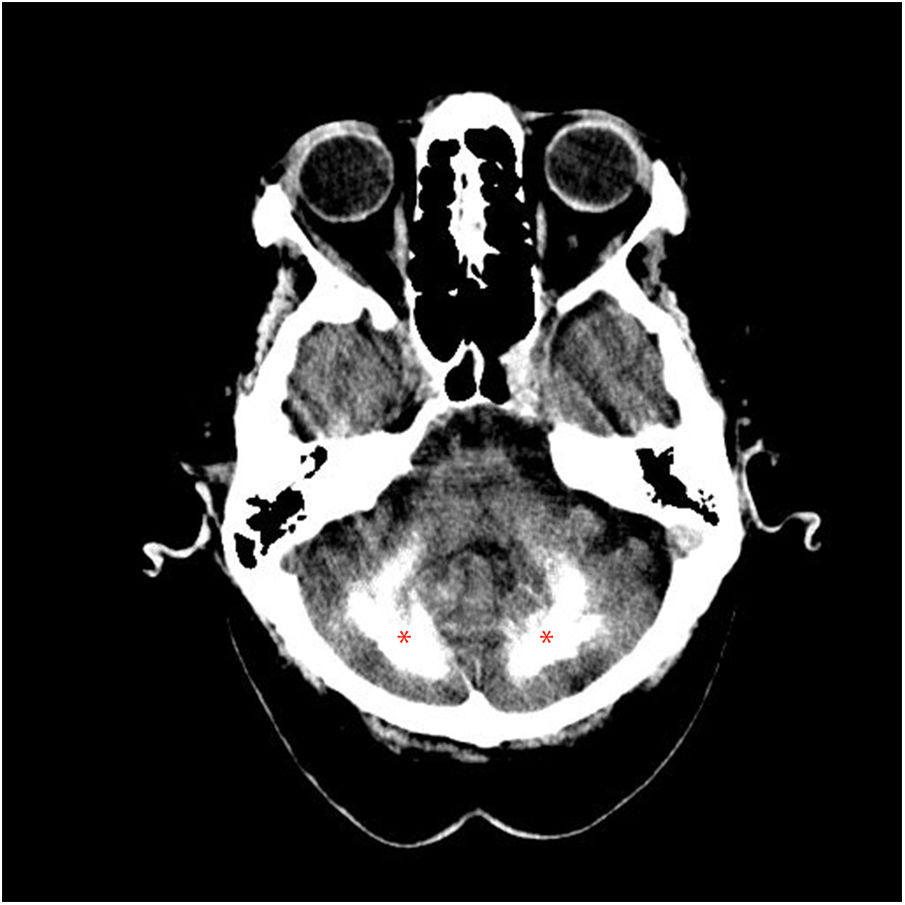
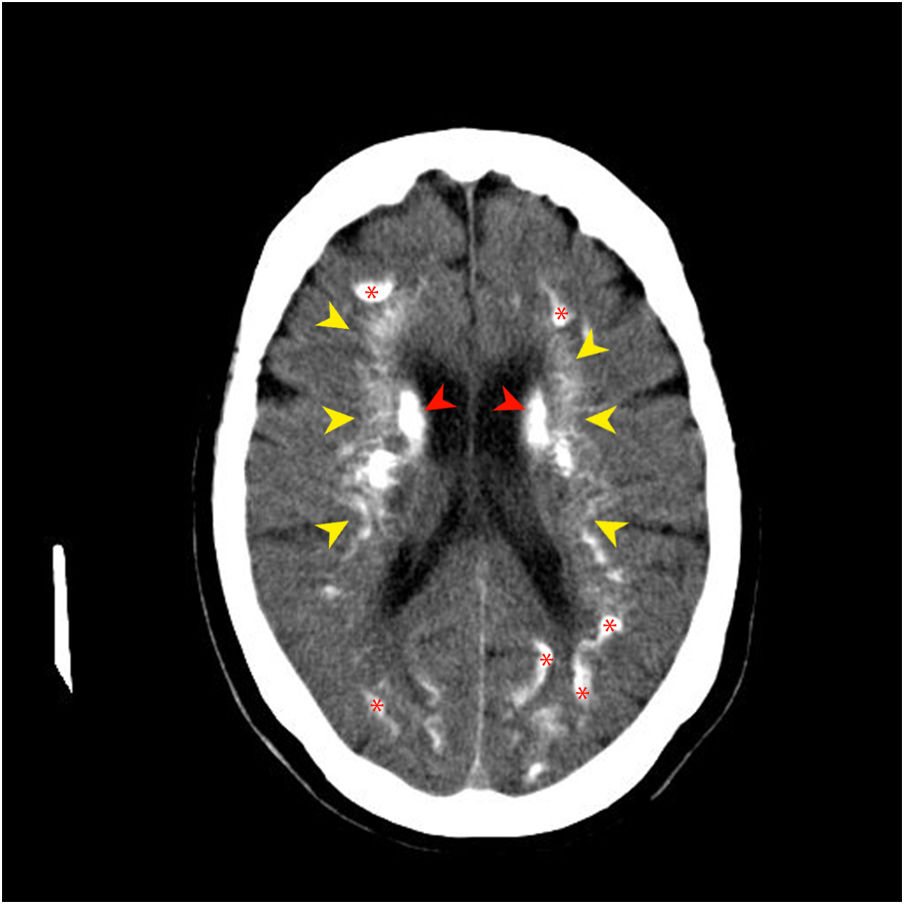
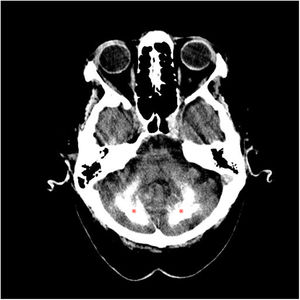
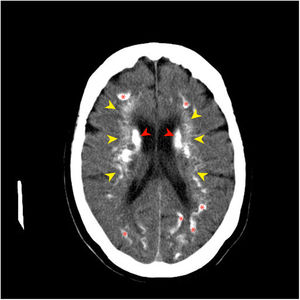
Idiopathic basal ganglia calcification or Fahr's syndrome is a rare neurological disease characterized by the presence of deposits of calcium in the basal ganglia and other areas of the brain that control movements including the thalamus, dentate nucleus, cerebral cortex, cerebellum, subcortical white matter, and hippocampus.1
We report a case of a 78-year-old woman with history of arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia and major depressive disorder. A computed tomography of the brain was performed and shows extensive coarse calcifications involving the infra and supratentorial white matter and the basal ganglia. Other causes of brain calcification were excluded and the diagnosis of Fahr's syndrome was made.
The images are characteristic of Fahr's syndrome. We observe extensive and relatively typical distribution of calcification in basal ganglia and thalami (Fig. 1) and symmetrical dense calcific foci in the dentate nuclei (Fig. 2). Calcification can also be found in corona radiata and subcortical white matter (Fig. 3).
Clinical manifestations typically include movement disorders or neuropsychiatric manifestations.1 However, the presence of calcifications in asymptomatic individuals is possible. In the clinical case presented, the only manifestation is depression, an infrequent presentation.2