It is very important to diagnose Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) early through appropriate screening and preventive treatment of a patient and their affected family members. This study aimed to report on a case of a Chinese family with heterozygous ENG-related HHT.
MethodsGene mutations were identified by whole-exome sequencing and physical examination were conducted to reveal the clinical symptoms.
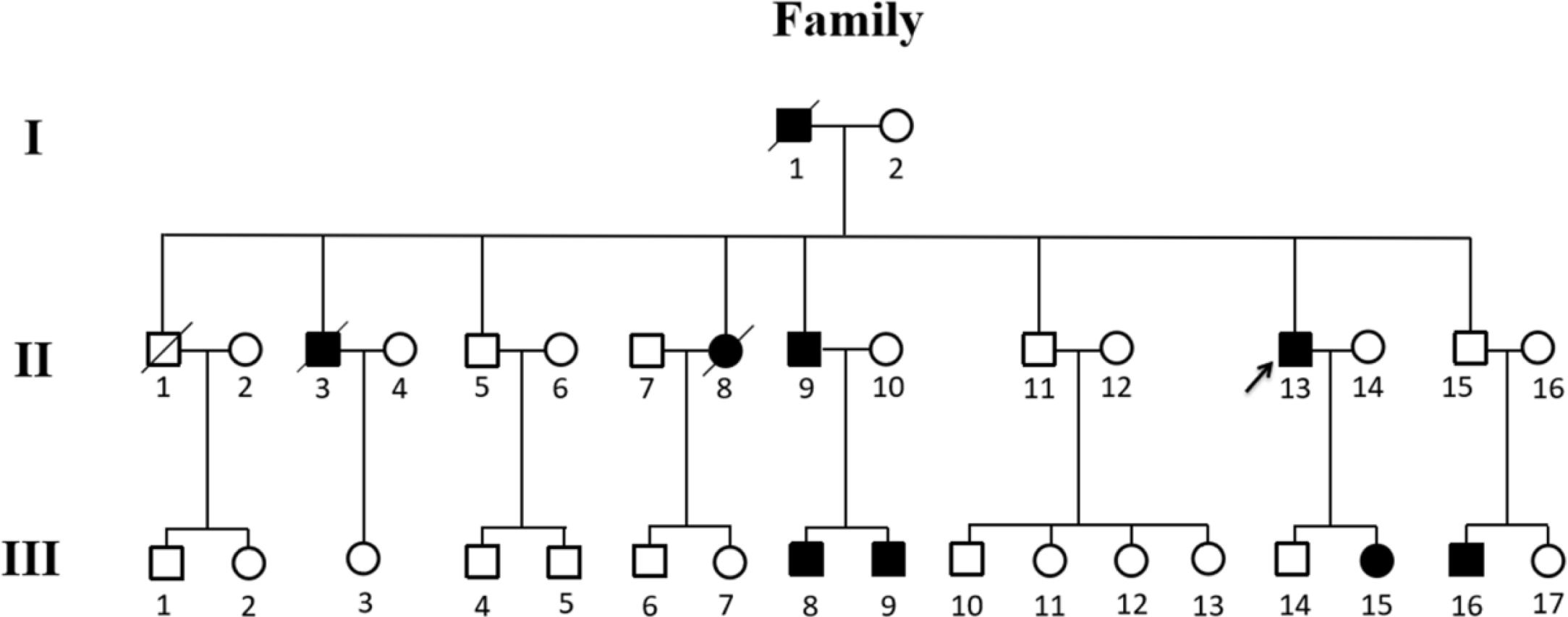
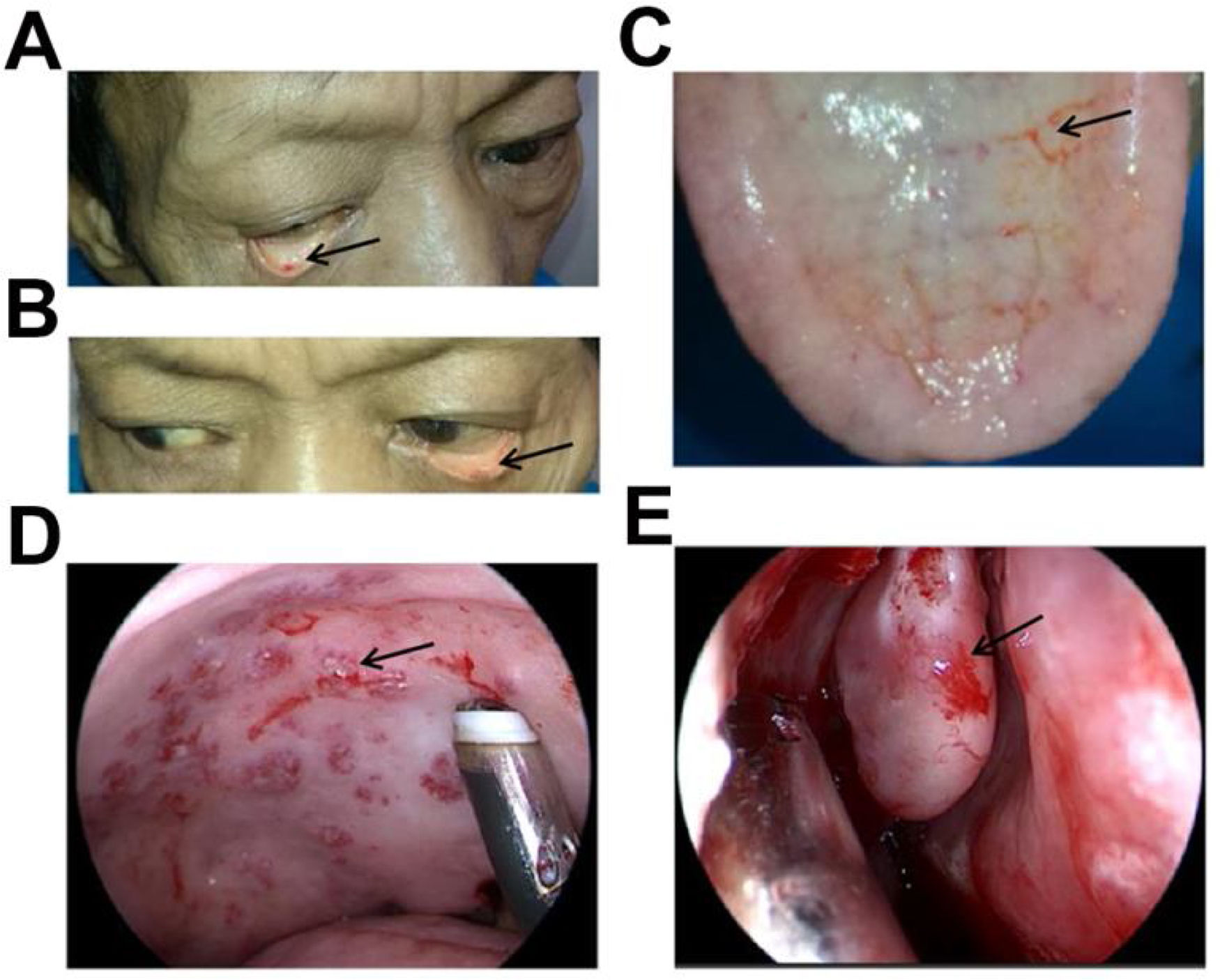
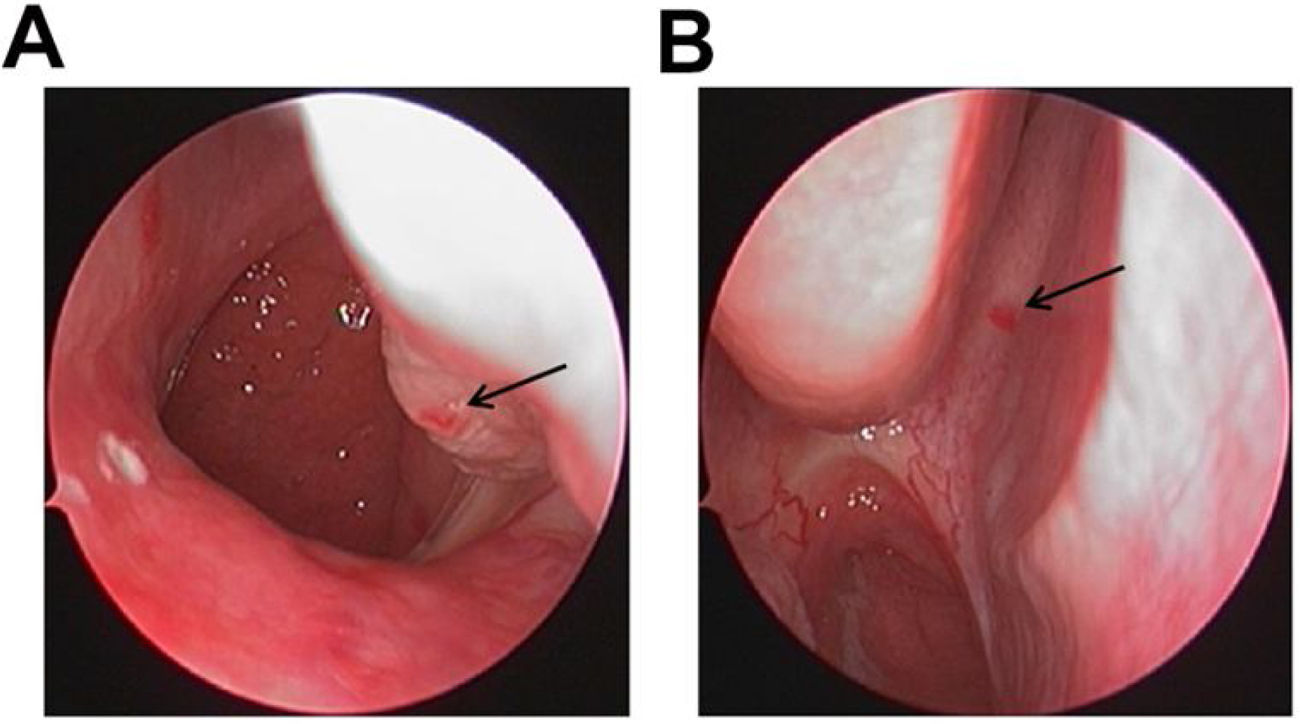
ResultsPhysical examination revealed symptomatic anaemia, coagulation system disorder and multiple red or pink spots reflecting telangiectases on the eyelids, tongue, palate and nasal cavity. Nine other affected relatives were identified in examining his family tree, among which three family members had died due to nose bleeding and one member presented symptomatic anaemia requiring blood transfusions. A novel heterozygous variation c.1550_1551dupTG (p.S518*) in ENG gene was identified.
ConclusionsThe patient and his daughter were confirmed to have heterozygous ENG-related HHT and the novel ENG heterozygous variant may play an important role on the severe symptoms of HHT. However, further case follow-up and functional studies should be conducted to confirm these mechanismal hypotheses.
El diagnóstico temprano de telangiectasia hemorrágica hereditaria (HHT) es muy relevante tanto para el propio paciente como para sus familiares afectados ya que permite un tratamiento preventivo. El objetivo de este estudio es presentar una familia china con HHT heterocigótica relacionada con una mutación en el gen ENG.
MétodosSe llevó a cabo un estudio clínico y se identificaron mutaciones genéticas mediante secuenciación del exoma completo.
ResultadosSe detectaron anemia sintomática, trastornos de la coagulación y múltiples telangiectasias en párpados, lengua, paladar y cavidad nasal. Al examinar el árbol genealógico, se detectaron otros nueve familiares afectados, tres de los cuales habían fallecido por hemorragia nasal y uno presentaba anemia sintomática que había requerido transfusiones de sangre. Se identificó una nueva variación heterocigótica c.1550_1551dupTG (p.S518 *) en el gen ENG.
ConclusionesSe confirmó que el paciente y su hija tenían HHT heterocigótica relacionada con el gen ENG. La nueva variante heterocigótica ENG puede desempeñar un papel relevante en la gravedad de los síntomas de la HHT, aunque se precisan nuevos estudios funcionales y de seguimiento de casos para confirmar dicha hipótesis.