To characterize blood coagulation index in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome (OAPS) and its subtypes, analyzing correlations with immunological indices and diagnostic value.
MethodsA retrospective analysis was performed on OAPS patients treated at the Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, from September 2023 to March 2024. Healthy women of the same age range were matched for comparison.
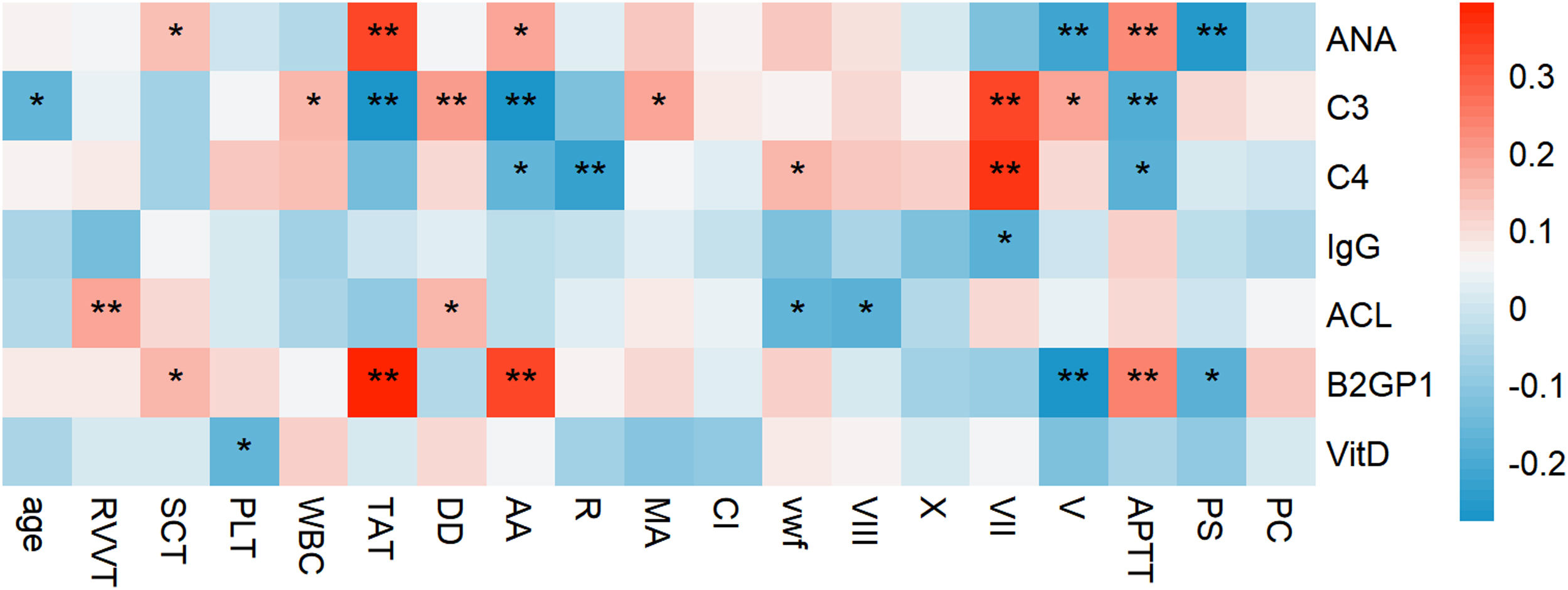
ResultsA total of 102 OAPS patients and 80 matched healthy controls were included. OAPS patients exhibited significantly lower levels of complement factors C3 and C4, coagulation factors V and VII activities, and protein S activity (p<0.05). Conversely, they had elevated levels of anti-β2 glycoprotein I antibodies, platelets, thrombin–antithrombin complex (TAT), thromboelastographic reaction time (R), maximum amplitude (MA), clot formation index (CI), von Willebrand factor activity, coagulation factor VIII activity, and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) (p<0.05). Among OAPS patients, criteria OAPS cases showed significantly higher anti-β2-GPI antibodies and anticardiolipin antibody levels (p<0.01), with more spontaneous abortions and fetal deaths in this group (p<0.01).
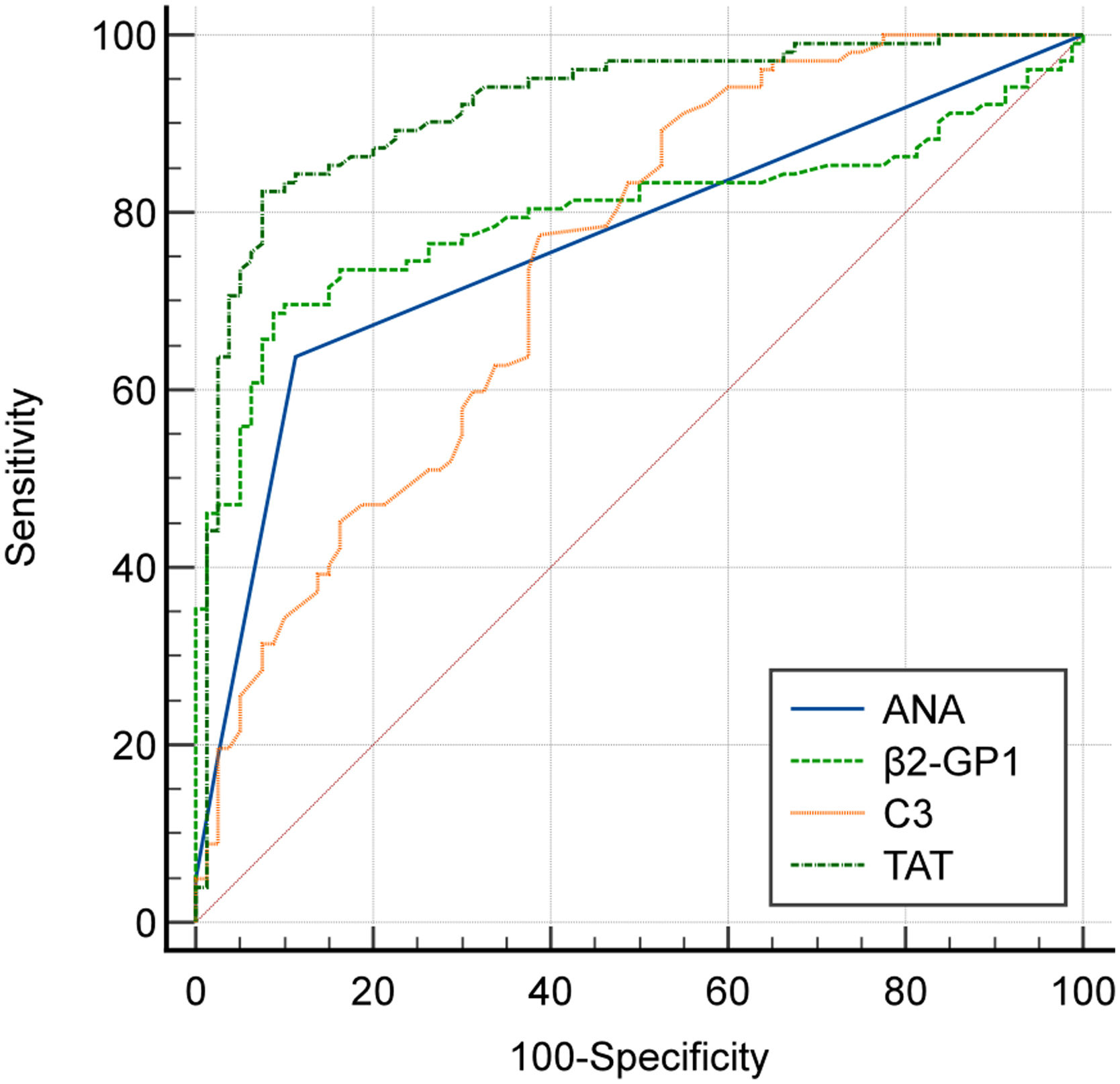
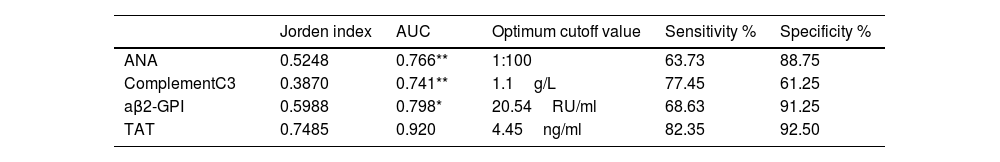
ConclusionCorrelations were found between immunological indices (ANA, complement C3, anti-β2-GPI) and coagulation indices (TAT, APTT). ANA, complement C3, anti-β2-GPI antibodies, and TAT were identified as risk factors for predicting OAPS. Blood coagulation and immune indices correlate in OAPS. Detecting these indices may provide diagnostic value for OAPS and its subtypes.
Caracterizar el índice de coagsanguínea en el síndrome antifosfolípido obstétrico (sof) y sus subtipos, analizando correlaciones con índices inmuny valor diagnóstico.
MétodosSe realizó un análisis retrospectivo de pacientes con APS atendidos en el departamento de reumatología e inmunología, segundo Hospital de la universidad médica de Hebei, de septiembre de 2023 A marzo de 2024. Se emparea a mujeres sanas del mismo rango de edad para su comparación.
ResultadosSe incluyó un total de 102 pacientes con APS y 80 controles sanos empare. Los pacientes con APS presentaron niveles significativamente más bajos de los factores del complemento C3 y C4, actividad de los factores de coagv y VII y actividad de la proteína S (p<0.05). Por el contrario, tenían niveles elevados de anticuerpos anti-glicoproteína I ≥ 2, plaquetas, complejo trombinantitrombina (TAT), tiempo de reacción tromboelastográfico (R), amplitud máxima (MA), índice de formación de coágulos (IC), actividad del factor de von Willebrand, actividad del factor de coagulación VIII y tiempo parcial de tromboplastina activado (ttpa) (p<0.05). Entre los pacientes con APS, los casos con criterios de APS mostraron niveles significativamente más altos de anticuerpos anti-≥2-GP β y niveles de anticuerpos anticardiolipina (p<0,01), con más abortos espontáy muertes fetales en este grupo (p<0,01).
ConclusiónSe encontraron correlaciones entre los índices inmunológicos (ANA, complemento C3, anti-−2-GP β) y los índices de coag(TAT, ttpa). ANA, complemento C3, anticuerpos anti-−2-GP β y TAT fueron identificados como factores de riesgo para la predicción de APS. La coagulación sanguínea y los índices inmunse correlacionan en la APS. La detección de estos índices puede proporcionar un valor diagnóstico para los EPA y sus subtipos.