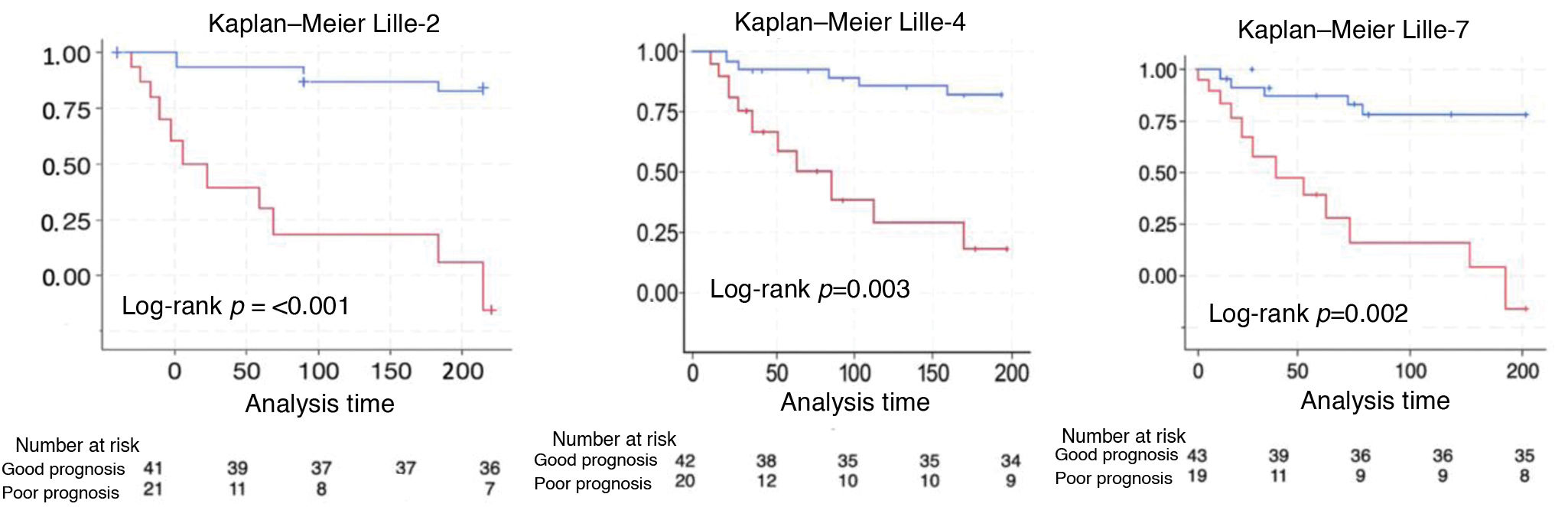
To evaluate the effectiveness of the Lille Index (LI) on day 2 (LI2) and day 4 (LI4) in predicting short-term mortality in patients with severe alcohol-associated hepatitis (SAH) and to assess its concordance compared to the Lille Index on day 7 (LI7).
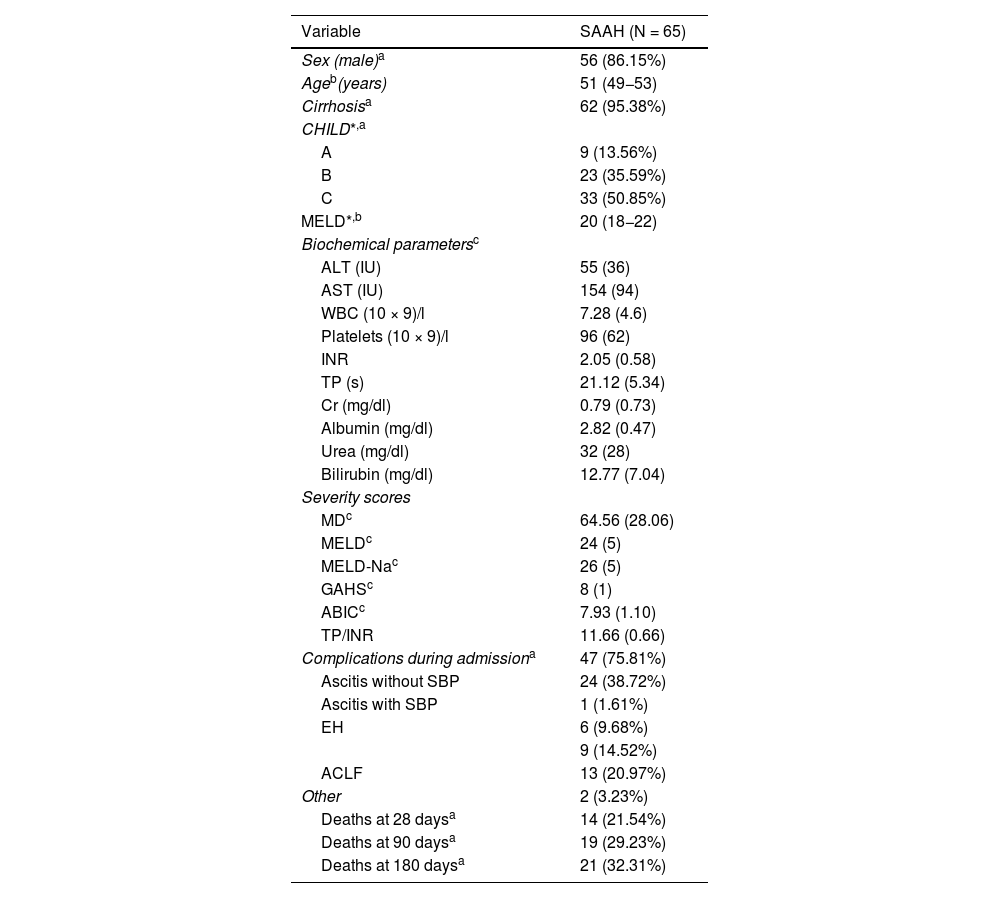
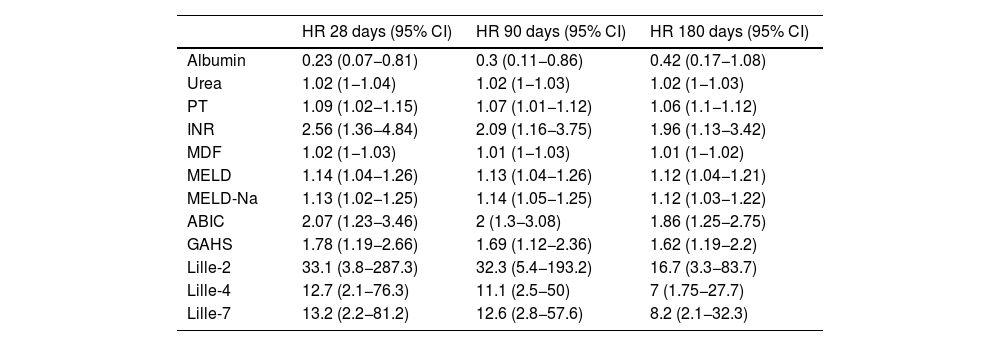
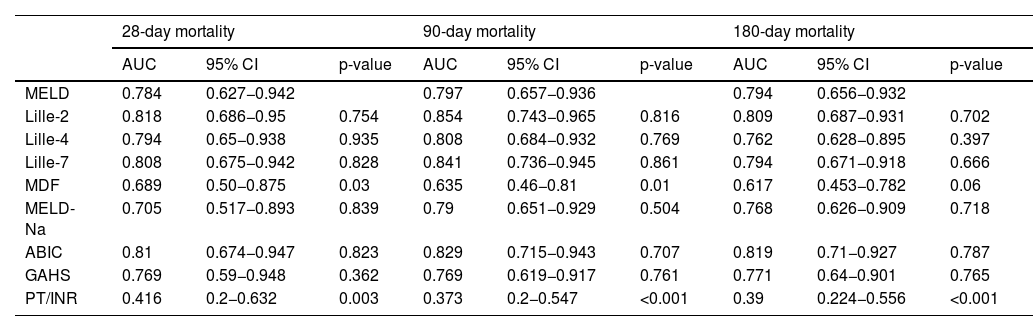
Patients and methodsThis retrospective, observational, single-center study included SAH patients admitted between 2016 and 2023. SAH was defined as a Maddrey score ≥32 and/or a MELD score ≥21. The predictive ability of LI2, LI4, and LI7 for 28-, 90-, and 180-day mortality was analyzed using AUC, Cox regression (Hazar Ratio (HR)), and Kaplan-Meier curves. Results: Among 65 SAH patients, 62 received corticosteroids. Median follow-up was 722 days. LI2 was associated with a 28-day mortality HR of 33.1 (95% CI: 3.8–287.3), similar to LI7 (HR: 13.2; 95% CI: 2.2–81.2). AUCs for 28-day mortality were 0.818 for LI2, 0.794 for LI4, and 0.809 for LI7 (p > 0.05). The proportion of patients classified by prognosis was similar for LI2 vs. LI7 (68.33% vs. 70.97%, p = 0.752) and LI4 vs. LI7 (73.33% vs. 70.97%, p = 0.771). Concordance between LI2 and LI7 was 85%, and between LI4 and LI7 was 93.33%.
ResultsAmong 65 SAH patients, 62 received corticosteroids. The median follow-up was 722 days. LI2 was associated with a 28-day mortality HR of 33.1 (95% CI: 3.8–287.3), similar to LI7 (HR: 13.2; 95% CI: 2.2–81.2). AUCs for 28-day mortality were 0.818 for LI2, 0.794 for LI4, and 0.809 for LI7 (p > 0.05). The proportion of patients classified by prognosis was similar for LI2 vs. LI7 (p = 0.752) and LI4 vs. LI7 (p = 0.771). Concordance between LI2 and LI7 was 85%, and between LI4 and LI7, 93.33%.
ConclusionsLI2 and LI4 were comparable to LI7 in predicting short-term mortality in SAH. Earlier calculation, particularly LI2, could anticipate clinical decisions in poor prognosis patients, such as corticosteroid discontinuation or evaluation for liver transplantation in selected cases.
Evaluar la eficacia deI índice de Lille (IL) al día 2 (IL2) y al día 4 (IL4) para predecir mortalidad a corto plazo en pacientes con hepatitis asociada al alcohol grave (HAG) y su concordancia con el IL en el día 7 (IL7).
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional, retrospectivo y unicéntrico que incluyó pacientes con HAG ingresados entre 2016 y 2023. Se definió HAG si Maddrey≥32 y/o MELD ≥ 21. Analizamos la capacidad de IL2, IL4 e IL7 para predecir mortalidad a 28, 90 y 180 días y su concordancia mediante AUC, regresión de Cox (Hazar Ratio (HR)) y curvas de Kaplan-Meier.
ResultadosDe 65 pacientes con HAG, 62 recibieron tratamiento con corticoides. El seguimiento mediano fue de 722 días. IL2 se asoció con un HR de 33.1 (IC95%: 3.8–287.3) para mortalidad a 28 días, comparable a IL7 (HR: 13.2; IC95%: 2.2–81.2). Las AUC para mortalidad a 28 días fueron 0.818 para IL2, 0.794 para IL4 y 0.809 para IL7 (p > 0.05). La proporción de pacientes clasificados según el pronóstico fue similar en IL2 y IL7 (p = 0.752) y en IL4 y IL7 (p = 0.771). La concordancia entre IL2 e IL7 fue 85% y entre IL4 e IL7 93,33%.
ConclusionesIL2 e IL4 fueron comparables a IL7 en predecir mortalidad a corto plazo en pacientes con HAG. Adelantar el cálculo de estos índices, especialmente IL2, permitiría anticipar decisiones clínicas en pacientes de mal pronóstico, como la suspensión de corticoides o la evaluación para trasplante hepático en casos seleccionados.