Child maltreatment is a risk factor for psychopathology in adulthood, and it is important to elucidate avenues for intervention. Social support and emotion dysregulation are two psychosocial factors which mediate the relationship between child maltreatment and psychopathology; however, few studies have examined both simultaneously in an Asian clinical context. This study aimed to investigate the dual roles of social support and emotion dysregulation in the pathway from child maltreatment to depressive symptoms in adulthood by testing three competing pathway models.
MethodsA total of 200 participants (Mean age = 36.53; 78 % Chinese ethnicity) with a primary diagnosis of affective disorder were recruited from a tertiary psychiatric hospital in Singapore. Respondents completed self-report measures of child maltreatment exposure, depressive symptoms, perceived social support, and emotion dysregulation. Pathway analyses based on ordinary least squares regressions were conducted using the PROCESS 4.1 tool.
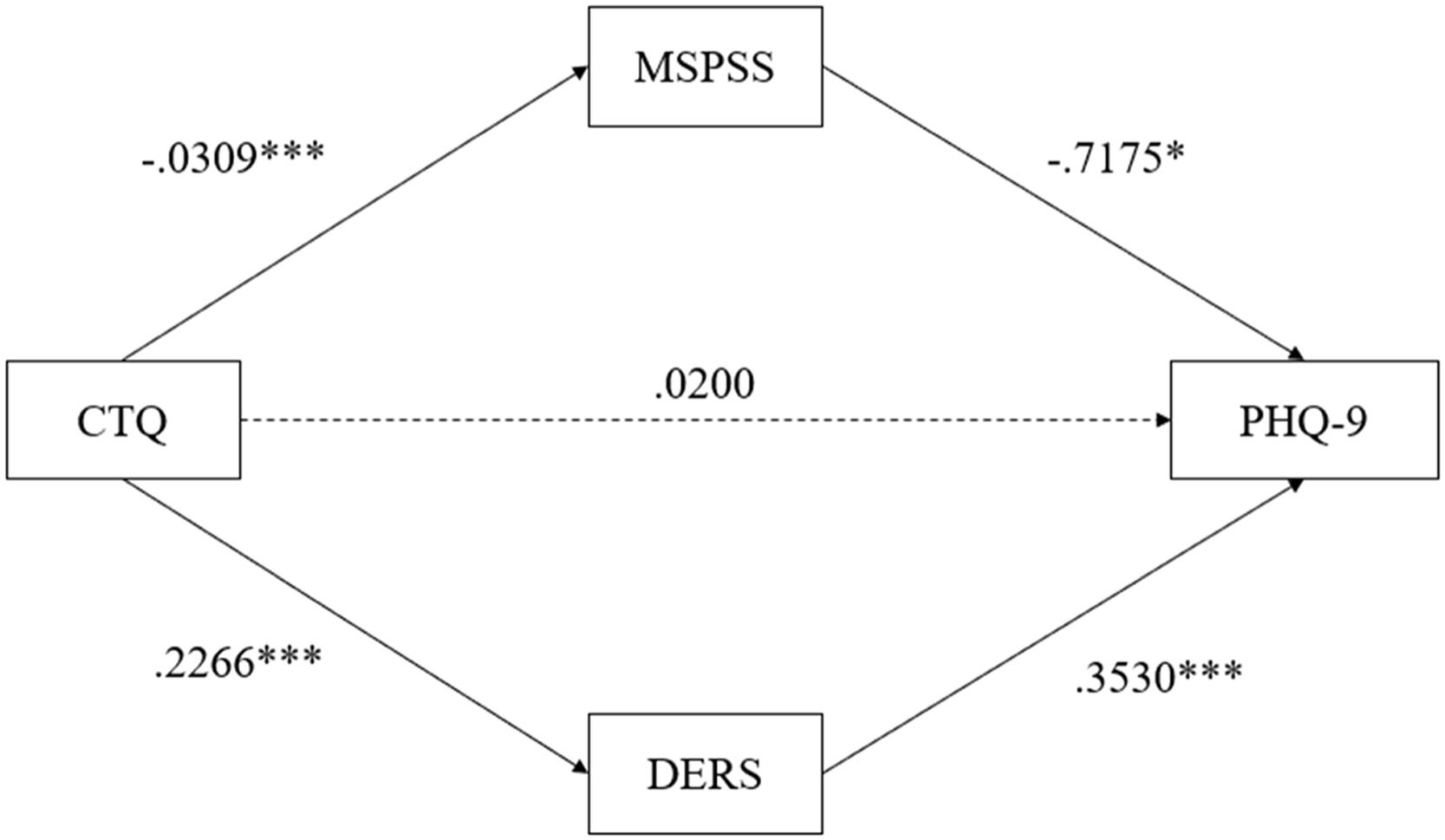
Results and conclusionsHigher exposure to child maltreatment was associated with lower perceived social support, greater emotion dysregulation, and more depressive symptoms. Pathway analyses revealed a significant indirect effect of child maltreatment on depressive symptoms via perceived social support and emotion dysregulation (b = 0.0172). This indirect effect was significant for emotional neglect while controlling for other forms of maltreatment (b = 0.0914). Findings provide conceptual support for the serial pathway involving social support and emotion dysregulation in the relationship between child maltreatment and depressive symptoms, highlighting the need to target both interpersonal and intrapersonal factors in treating clinical populations with child maltreatment exposure.