Es necesario conocer la tasa de flebitis asociada a su uso y los factores de riesgo asociados al manejo del catéter vascular periférico que influye directamente sobre la presencia de flebitis.
MetodologíaEstudio descriptivo observacional, realizado tras la implementación del Proyecto Flebitis Zero en un hospital terciario urbano de gran capacidad (> 1.000 camas) y de referencia de Navarra. La implantación del Proyecto Flebitis Zero se realizó de forma progresiva incorporando 4 unidades (2 médicas y 2 quirúrgicas) por año, finalizando en el mes de febrero del 2023. Seguidamente, se inició la recogida de datos para el presente estudio, en el mes de mayo del 2023.
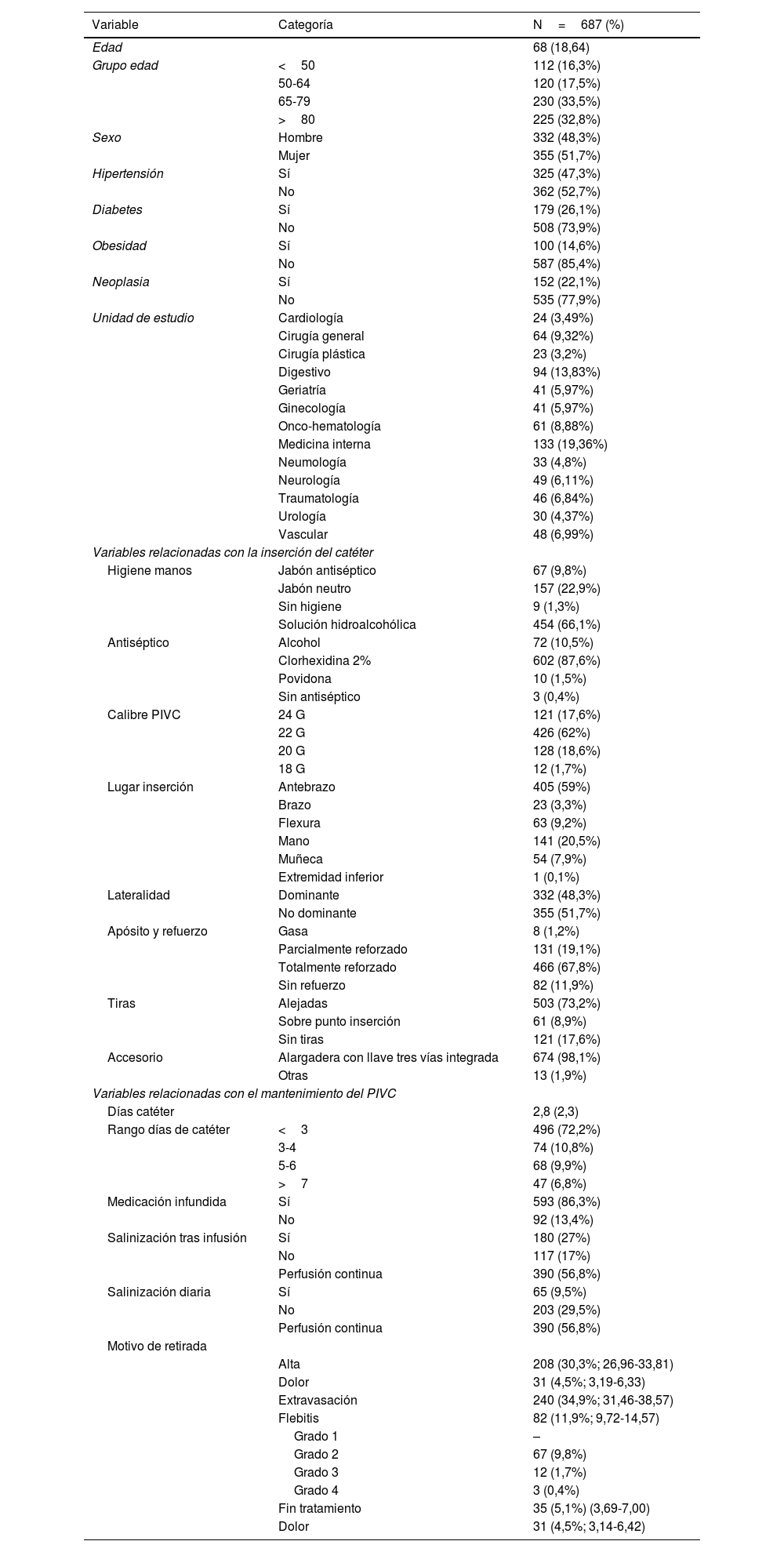
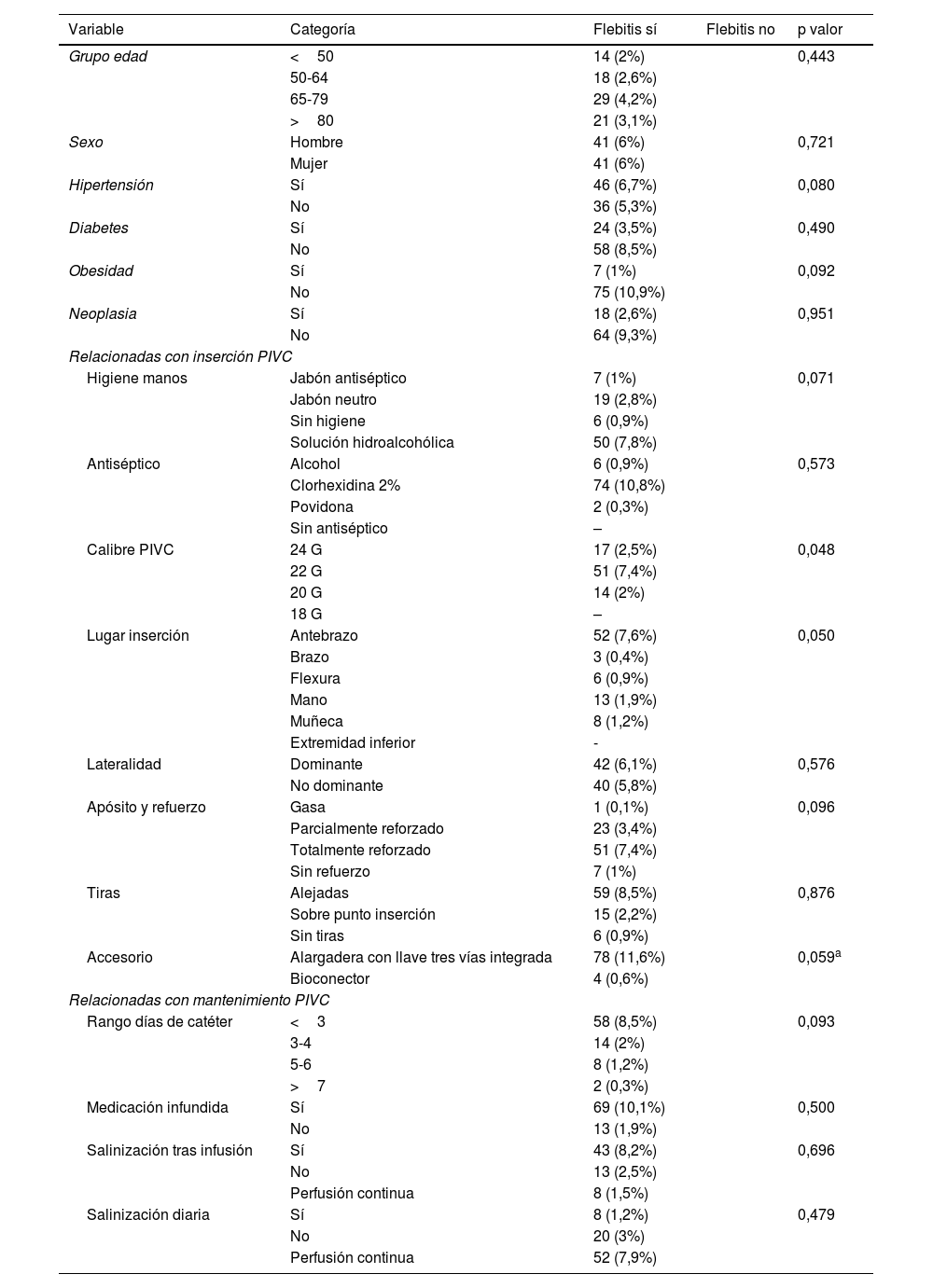
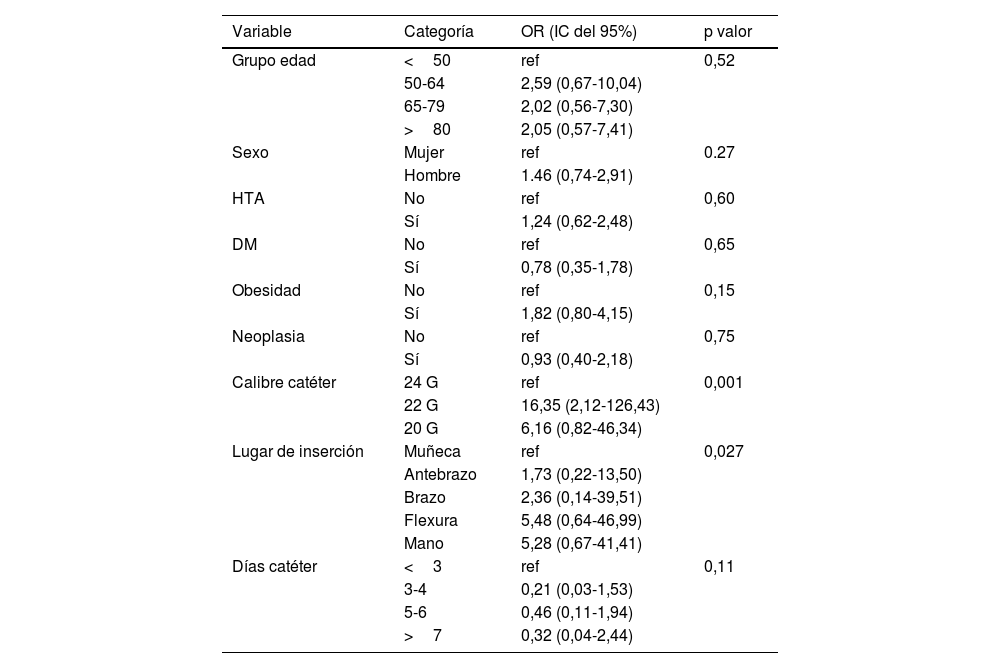
ResultadosSe incluyeron 687 catéteres, 48,3% (332) catéteres fueron implantados en hombres frente a 51,7% (355) en mujeres con una edad media de 68 (DE 18,64). Se detectó una tasa de flebitis del 11,93%, siendo los factores de calibre de catéter y el lugar de inserción los directamente relacionados con la presencia de flebitis.
ConclusionesLa presencia de flebitis está marcada tanto por factores modificables, siendo recomendable el uso de dispositivos de pequeño calibre y la zona de antebrazo los indicados para disminuir la tasa de flebitis.
It is necessary to know the rate of phlebitis associated with its use and the risk factors associated with peripheral vascular catheter management that directly influence the presence of phlebitis.
Methodologyobservational descriptive study, carried out after the implementation of the Zero Phlebitis Project in a large-capacity (>1,000 beds) urban tertiary hospital of reference in Navarra. The implementation of the Zero Phlebitis Project was carried out progressively, incorporating 4 units (2 medical and 2 surgical) per year, ending in February 2023. Subsequently, data collection for the present study began in May 2023.
Results687 catheters were included, 48.3% (332) catheters were implanted in men versus 51.7% (355) in women with a mean age of 68 (SD 18.64). A phlebitis rate of 11.93% was detected, with catheter caliber and insertion site factors being directly related to the presence of phlebitis.
ConclusionsThe presence of phlebitis is marked by both modifiable factors, being recommended the use of small caliber devices and the forearm area the indicated ones to decrease the rate of phlebitis.