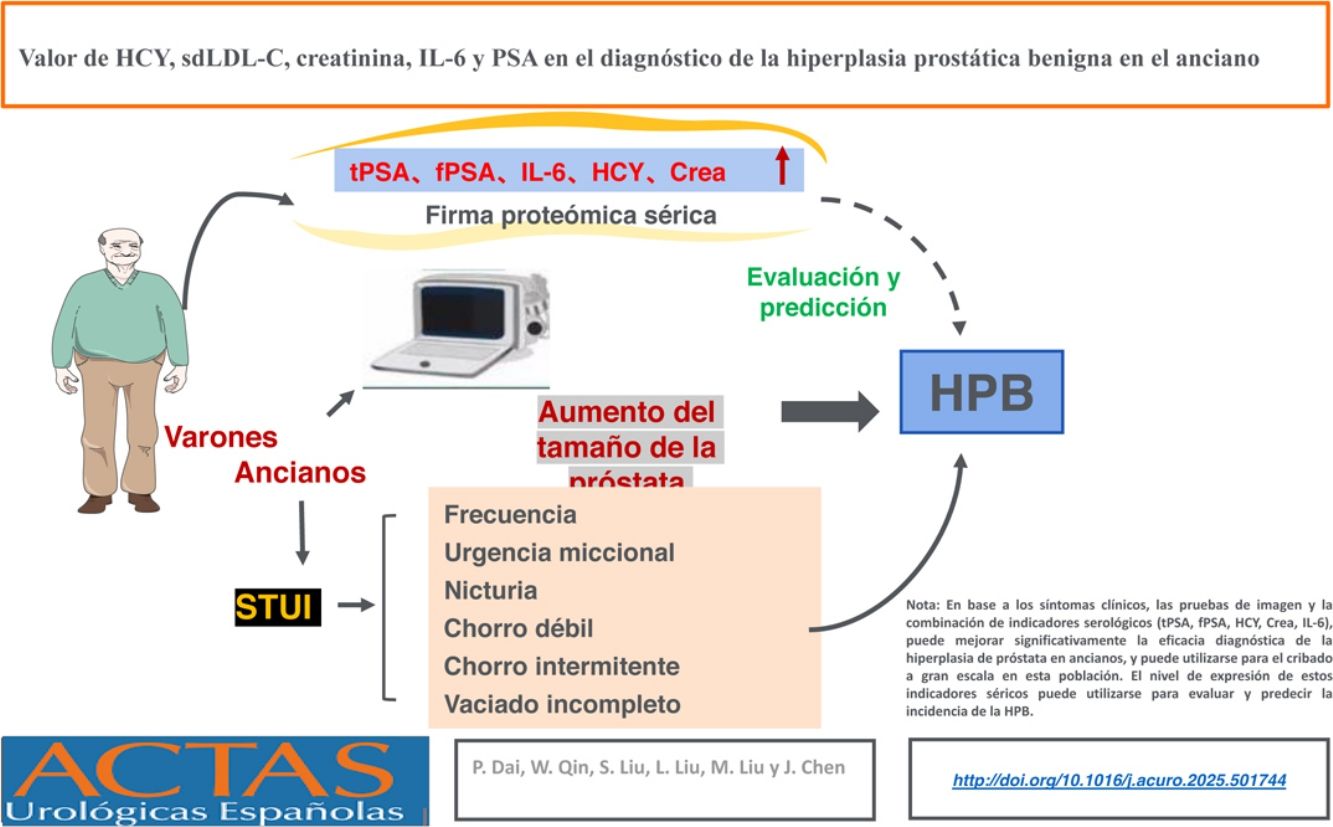
Investigar el valor diagnóstico de marcadores metabólicos séricos como la homocisteína (HCY), el colesterol en lipoproteínas pequeñas y densas (c-sdLDL), la creatinina (Crea), la interleucina 6 (IL-6) como factor inflamatorio y el antígeno prostático específico (PSA) en pacientes ancianos con hiperplasia prostática benigna (HPB).
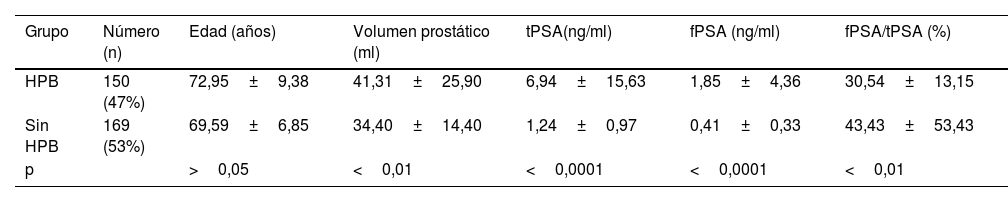
MétodosSe seleccionaron 150 pacientes ancianos con hiperplasia de próstata como grupo de observación, y 169 pacientes ancianos sanos como grupo de control. Se recogieron los datos de tPSA, fPSA, fPSA/tPSA y tamaño de la próstata en los dos grupos, y se tomaron muestras de suero de los sujetos para la detección de HCY, sdLDL, Crea, IL-6 y otros marcadores. Se realizó un análisis univariante, un análisis de correlación y un análisis de regresión logística para estudiar la relación entre indicadores y la hiperplasia prostática senil. La eficacia diagnóstica de cada metabolito sérico se analizó mediante curvas ROC.
ResultadosLos niveles séricos de tPSA, fPSA, Crea, HCY, c-sdLDL e IL-6 aumentaron significativamente, la ratio fPSA/tPSA y las HDL disminuyeron significativamente, y los niveles de colesterol total (CT), triglicéridos (TG) y LDL no tuvieron significación estadística. Los niveles séricos de tPSA y fPSA se correlacionaron positivamente con el tamaño de la próstata, los niveles séricos de IL-6, Crea y HCY se correlacionaron positivamente con los niveles de tPSA y fPSA, y los niveles séricos de c-sdLDL se correlacionaron negativamente con los niveles de fPSA. Según el análisis de regresión logística, el tPSA, el fPSA, el tamaño de la próstata, la HCY, la Crea y la IL-6 son factores de riesgo de hiperplasia prostática. Las HDL y la relación fPSA/tPSA son factores protectores de la hiperplasia benigna de próstata. El análisis de la curva ROC mostró que la sensibilidad y la especificidad de fPSA/tPSA e IL-6 fueron del 82,7% y del 72%, y del 83,4% y del 80,5%, respectivamente; el área bajo la curva ROC fue de 0,840 y 0,825, respectivamente. La combinación de tPSA y fPSA con HCY, IL-6 y Crea presentó la mejor eficacia diagnóstica, con un área bajo la curva ROC de 0,881 y una especificidad y una sensibilidad del 84% y del 77,3%, respectivamente.
ConclusiónLa medición combinada del antígeno prostático específico, HCY, Crea e IL-6 puede mejorar significativamente la eficacia diagnóstica de la hiperplasia prostática senil y optimizar el esquema de diagnóstico y tratamiento, e incluso puede utilizarse como un importante índice de cribado para evaluar y predecir la incidencia de HPB en la población mayor.
To investigate the diagnostic value of serum metabolic markers such as HCY, sdLDL-C, Crea, inflammatory factor IL-6 and prostate-specific antigen in elderly patients with prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Methods150 senile patients with hyperplasia of prostate were selected as observation group and 169 healthy senile patients were selected as control group. The tPSA, fPSA, fPSA/tPSA and prostate size data of the two groups were collected, and serum samples of the subjects were collected for the detection of HCY, sdLDL, Crea, IL-6 and other indicators. Univariate analysis, correlation analysis and logistic regression analysis were conducted to analyze the relationship between each index and senility prostatic hyperplasia. The diagnostic efficiency of each serum metabolite was analyzed by receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC).
ResultsSerum levels of tPSA, fPSA, Crea, HCY, sdLDL-C and IL-6 were significantly increased, fPSA/tPSA ratio and HDL were significantly decreased, and TCHO, TG and LDL had no statistical significance. Serum tPSA and fPSA levels were positively correlated with prostate size, serum IL-6, Crea and HCY levels were positively correlated with tPSA and fPSA levels, and serum sdLDL-C levels were negatively correlated with fPSA levels. Logistic regression analysis showed that tPSA, fPSA, prostate size, HCY, Crea and IL-6 were risk factors for prostate hyperplasia. HDL and fPSA/tPSA are protective factors for benign prostatic hyperplasia. ROC curve analysis showed that the sensitivity and specificity of fPSA/tPSA and IL-6 were 82.7% and 72%, 83.4% and 80.5%, and the area under ROC curve were 0.840 and 0.825, respectively. tPSA and fPSA combined with HCY, IL-6 and Crea had the best diagnostic efficiency, with the area under ROC curve reaching 0.881, specificity and sensitivity reaching 84% and 77.3%, respectively.
ConclusionThe combined detection of prostate-specific antigen, HCY, Crea and IL-6 can significantly improve the diagnostic efficiency of senile prostatic hyperplasia, and optimize the diagnosis and treatment scheme can even be used as a major screening index to evaluate and predict the incidence of BPH in senile prostatic hyperplasia.