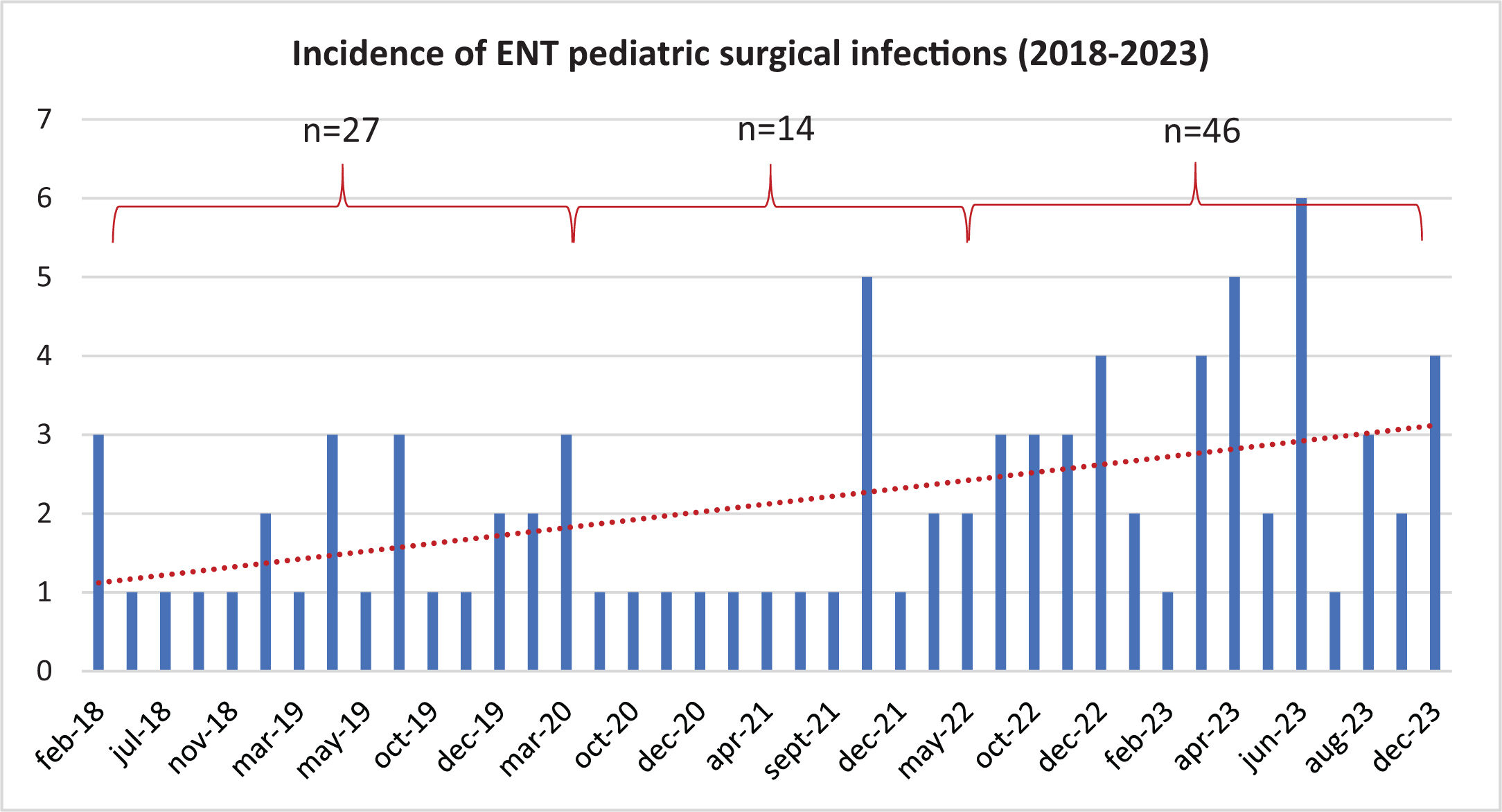
During the COVID-19 pandemic, ENT infections decreased but became more severe when combined with COVID-19. Post-pandemic, there has been a notable rise in ENT infections globally, particularly ear infections. In our region, we observed an increase in complicated pediatric ENT infections requiring urgent surgical intervention after the end of preventive measures. This study investigates the changes in ENT infection profiles in Madrid, Spain, following the pandemic.
Material and methodsWe analyzed data from children who underwent urgent ENT surgical interventions at a Spanish tertiary hospital between January 2018 and December 2023. The data was divided into three groups: pre-pandemic (1st group), during the pandemic with preventive measures (2nd group), and post-pandemic after the removal of these measures (3rd group). Variables included demographics, clinical data, imaging, treatment, and hospitalization duration.
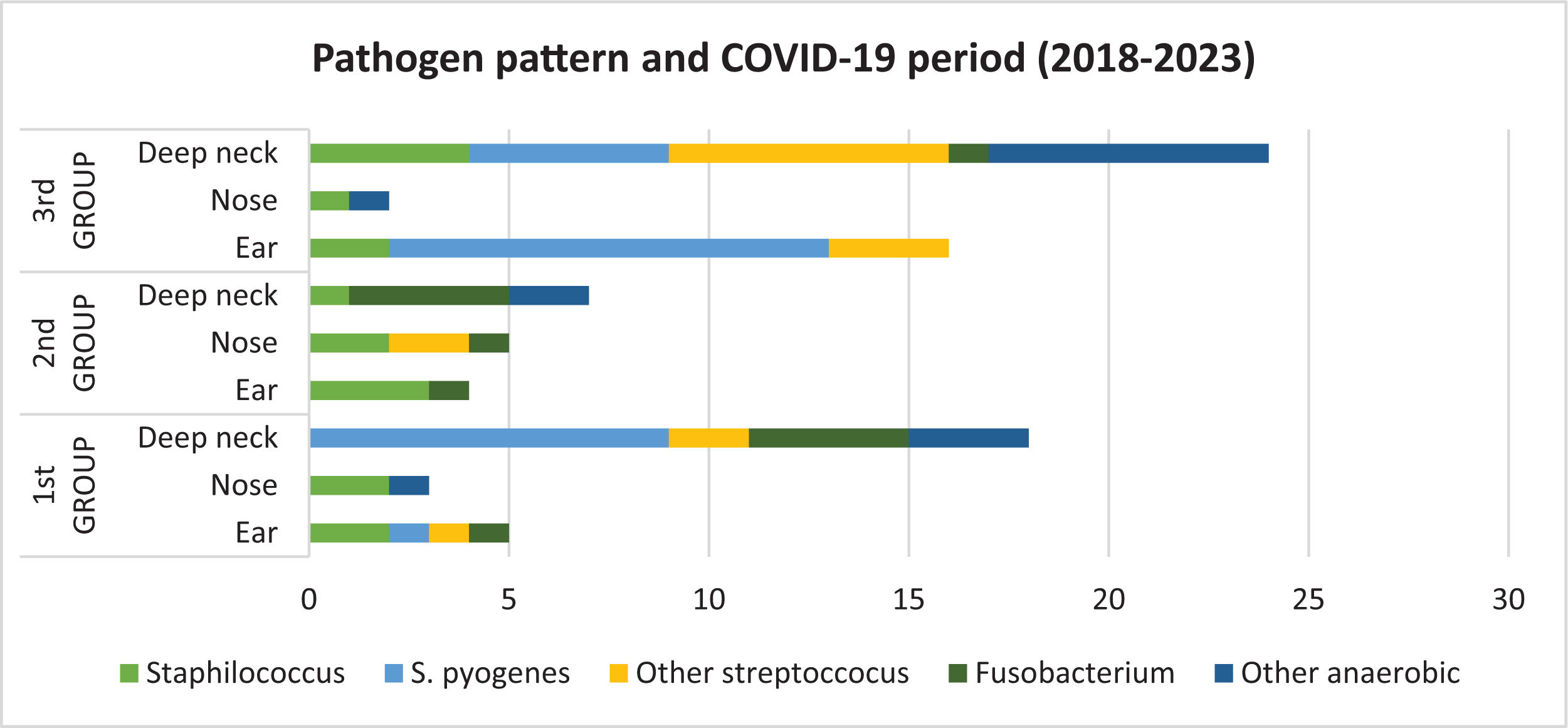
ResultsThe study involved 87 children (58.6% male) with a mean age of 6.4 years. There was a significant overall increase in ENT infections in the 3rd group compared to the 1st and 2nd groups (p = 0.036). Specifically, ear infections increased significantly after the removal of social measures (p = 0.033). In the 3rd group, Streptococcus pyogenes infections increased (p = 0.028), with Amoxicillin becoming the predominant treatment (p = 0.047), as opposed to Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid used for Fusobacterium in earlier periods (p = 0.00).
Discussion and conclusionThe pandemic has shifted the ENT infection profile, with increased ear infections and a rise in Group A streptococcus post-pandemic. This underscores the need for updated treatment strategies for pediatric ENT infections.
Durante la pandemia COVID-19, las infecciones ORL disminuyeron, pero se volvieron más graves cuando se combinaban con COVID-19. Tras la pandemia, ha habido un aumento notable en las infecciones ORL a nivel global, particularmente en infecciones otológicas. En nuestra región, hemos observado un incremento en las infecciones ORL pediátricas complicadas que requirieron intervención quirúrgica urgente tras la eliminación de las medidas preventivas sociales. El objetivo de este estudio es investigar el cambio en el perfil de infecciones ORL en Madrid (España) tras la pandemia.
Material y métodosAnalizamos los datos de aquellos niños que se sometieron a intervenciones quirúrgicas urgentes por infecciones ORL en un hospital terciario español entre enero de 2018 y diciembre de 2023. Los datos se dividieron en tres grupos: pre-pandemia (1º grupo), durante la pandemia con medidas preventivas (2º grupo) y post-pandemia tras la eliminación de estas medidas (3º grupo). Las variables analizadas incluyeron datos demográficos, clínicos, pruebas de imagen, tratamiento utilizado y tiempo de hospitalización.
ResultadosEl estudio involucró a 87 niños (58,6% varones) con una edad media de 6,4 años. Hubo un aumento significativo en las infecciones ORL en el 3º grupo en comparación con los grupos 1º y 2º (p = 0.036). Específicamente, las infecciones otológicas aumentaron significativamente después de la eliminación de las medidas sociales (p = 0.033). En el 3º grupo, las infecciones por Streptococcus pyogenes aumentaron (p = 0.028), con la Amoxicilina convirtiéndose en el tratamiento predominante (p = 0.047), a diferencia de la Amoxicilina-ácido clavulánico que se utilizó para Fusobacterium en los periodos anteriores (p = 0.00).
Discusión y conclusionLa pandemia ha cambiado el perfil de las infecciones ORL, con un aumento en las infecciones otológicas y un incremento en el Streptococcus del grupo A post-pandemia. Esto subraya la necesidad de actualizar las estrategias de tratamiento para las infecciones ORL pediátricas.