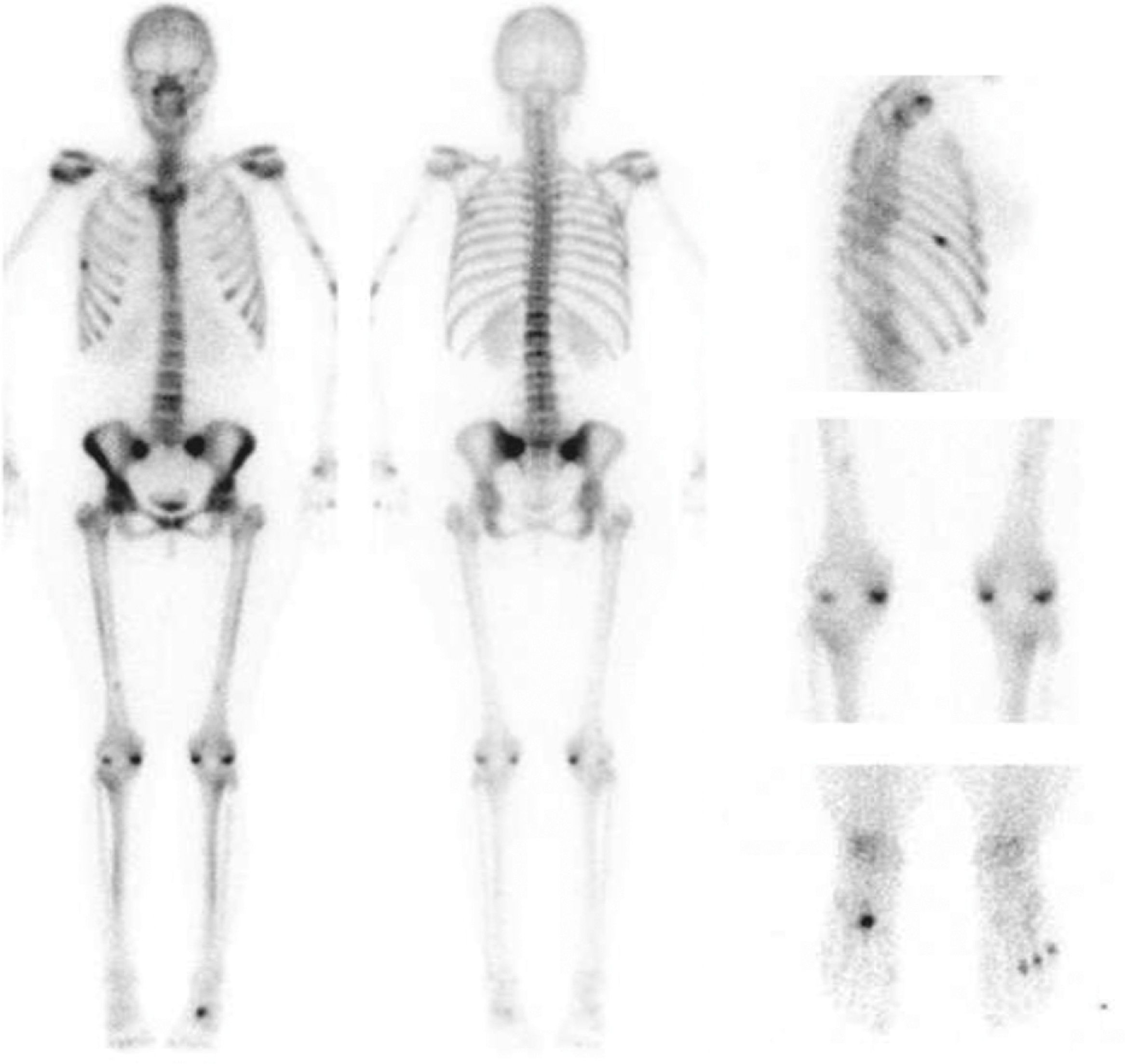
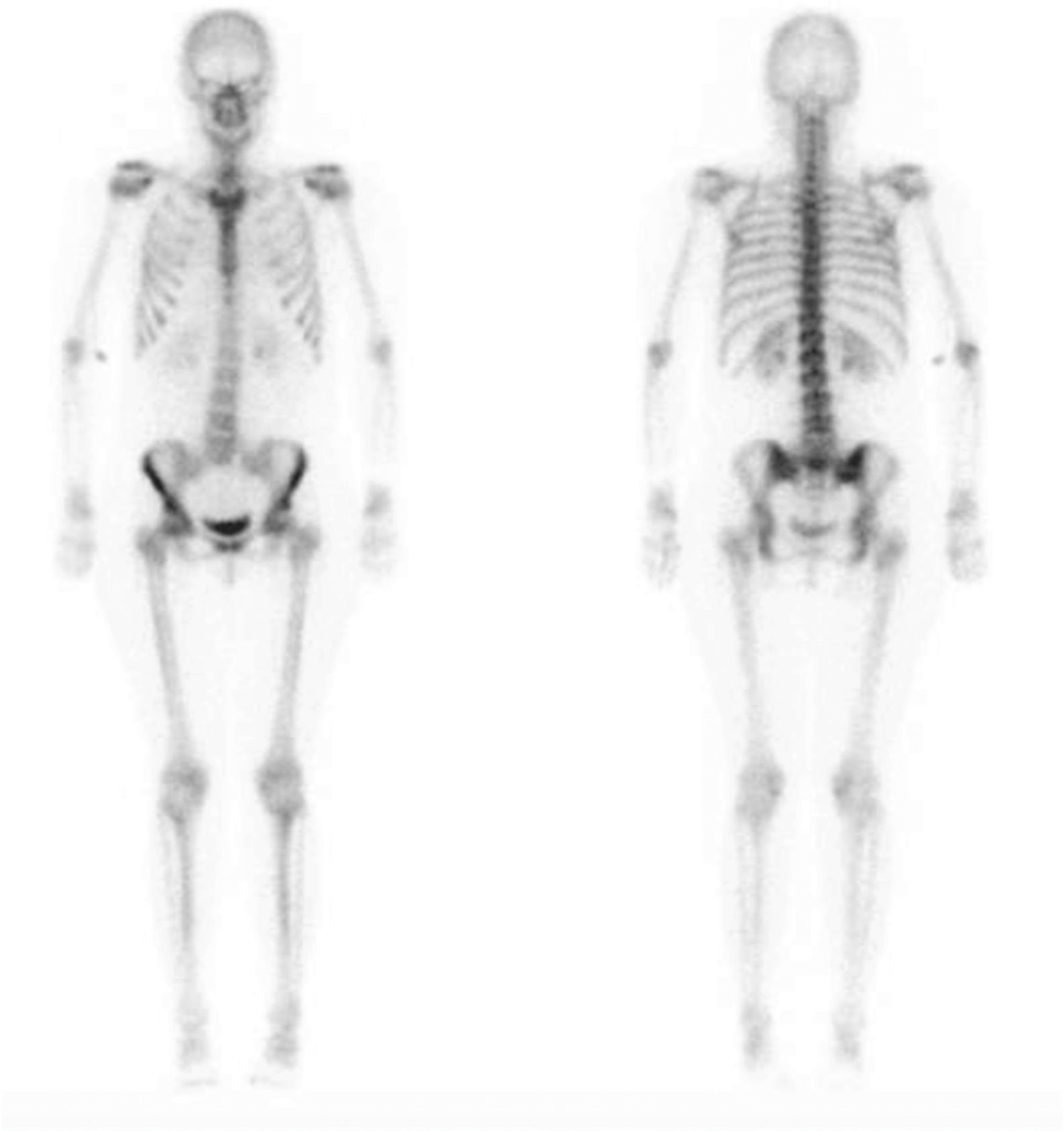
The development of hypophosphataemic osteomalacia has been linked with several treatments, mainly antiretroviral and intravenous iron administration. The frequency of the hypophosphataemia requires monitoring the phosphate after the administration of iron carboxymaltose. We describe a case of a woman with no calcium-phosphorous metabolism disorder, to whom this treatment was prescribed for anemia due to menorrhagia and intolerance to oral iron. She started with oligoarticular pain, which was spreading with a significant functional loss. The relationship with the administration of intravenous iron was discovered when scintigraphic findings together with laboratory results led to a diagnosis of hypophosphataemic osteomalacia. The patient responded satisfactorily to treatment with phosphate both clinically and in the follow-up bone scintigraphy.
El desarrollo de osteomalacia hipofosfatémica se ha relacionado con diversos tratamientos, fundamentalmente antirretrovirales y administración de hierro por vía intravenosa. La frecuencia de la hipofosfatemia hace necesario vigilar el fosfato tras la administración de hierro carboximaltosa. Presentamos el caso de una mujer sin antecedentes de alteración del metabolismo fosfo-cálcico a la que se pautó este tratamiento por anemia debida a hipermenorrea e intolerancia al hierro por vía oral. Comenzó con dolor oligoarticular que se generalizó más tarde, con importante impotencia funcional y cuya relación con la administración por vía intravenosa de hierro fue descubierta cuando los hallazgos gammagráficos junto con la analítica orientaron hacia una osteomalacia hipofosfatémica. Respondió de forma satisfactoria al tratamiento con fosfato como se objetivó clínicamente y en la gammagrafía ósea de control.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)