To evaluate if the estimation of the maximal oxygen consumption (MO2C) in METs (metabolic equivalents) by means of the table proposed in the guidelines of the Spanish Society of Cardiology is a sufficiently reliable method when applied to the bicycle exercise test.
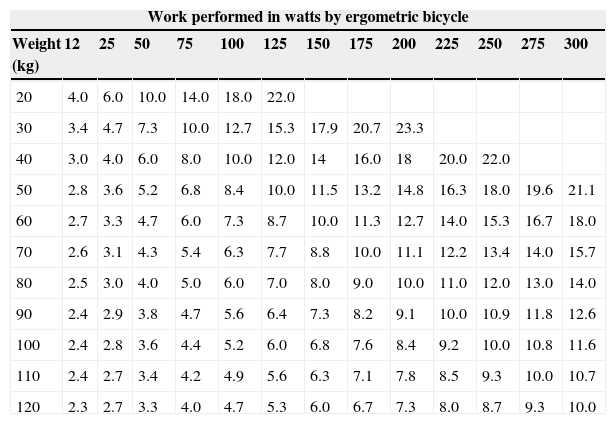
Material and methodsThe MO2C in METs was obtained by gas-exchange analysis on bicycle ergometer tests in 97 healthy subjects (group I). It was compared with the estimate of METs using the table in which only watts and patient's weight were included. A better-adjusted formula was validated in 289 subjects with normal exercise myocardial perfusion gated-SPECT (group II) using the introduction of clinical and ergometric variables.
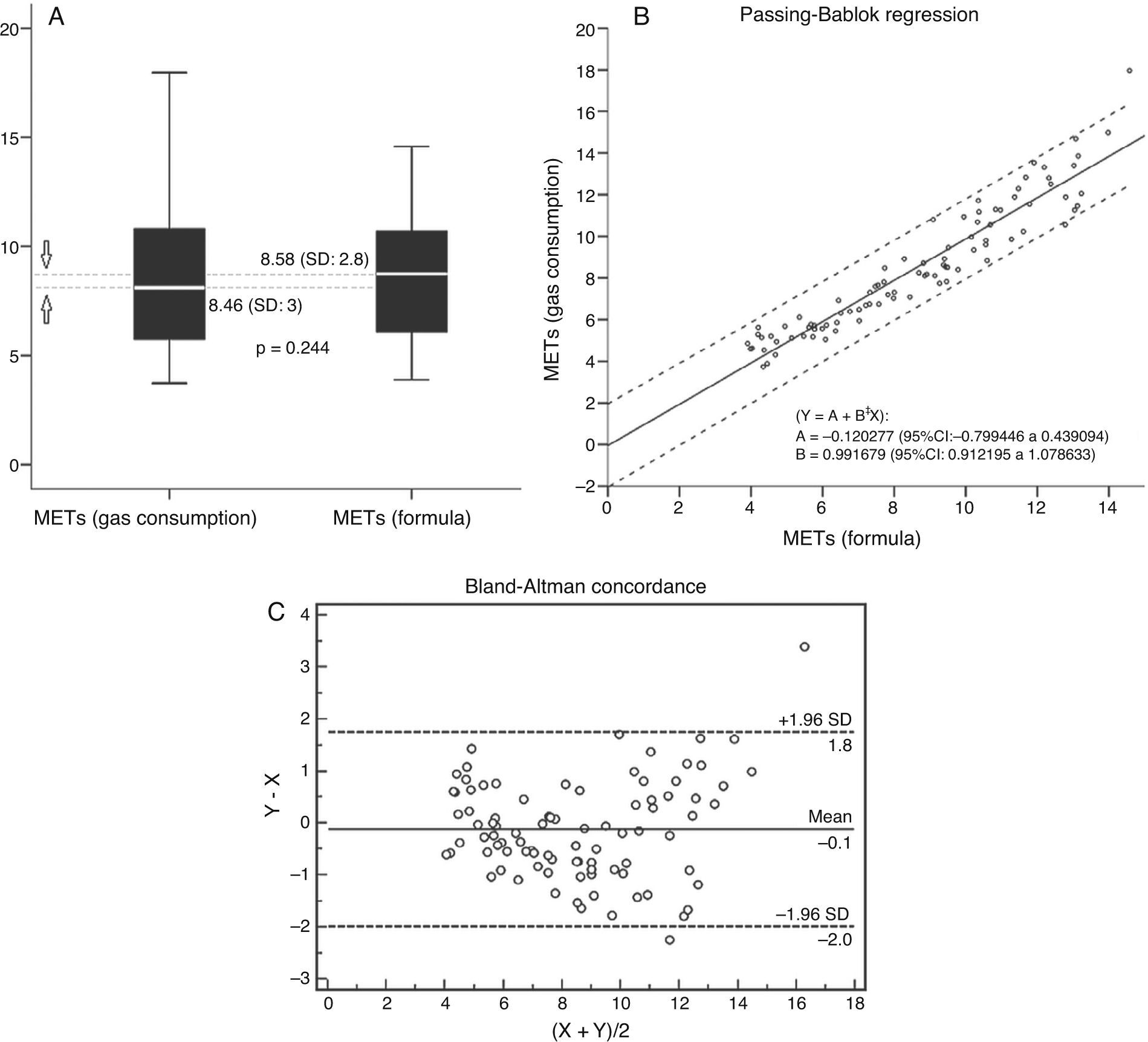
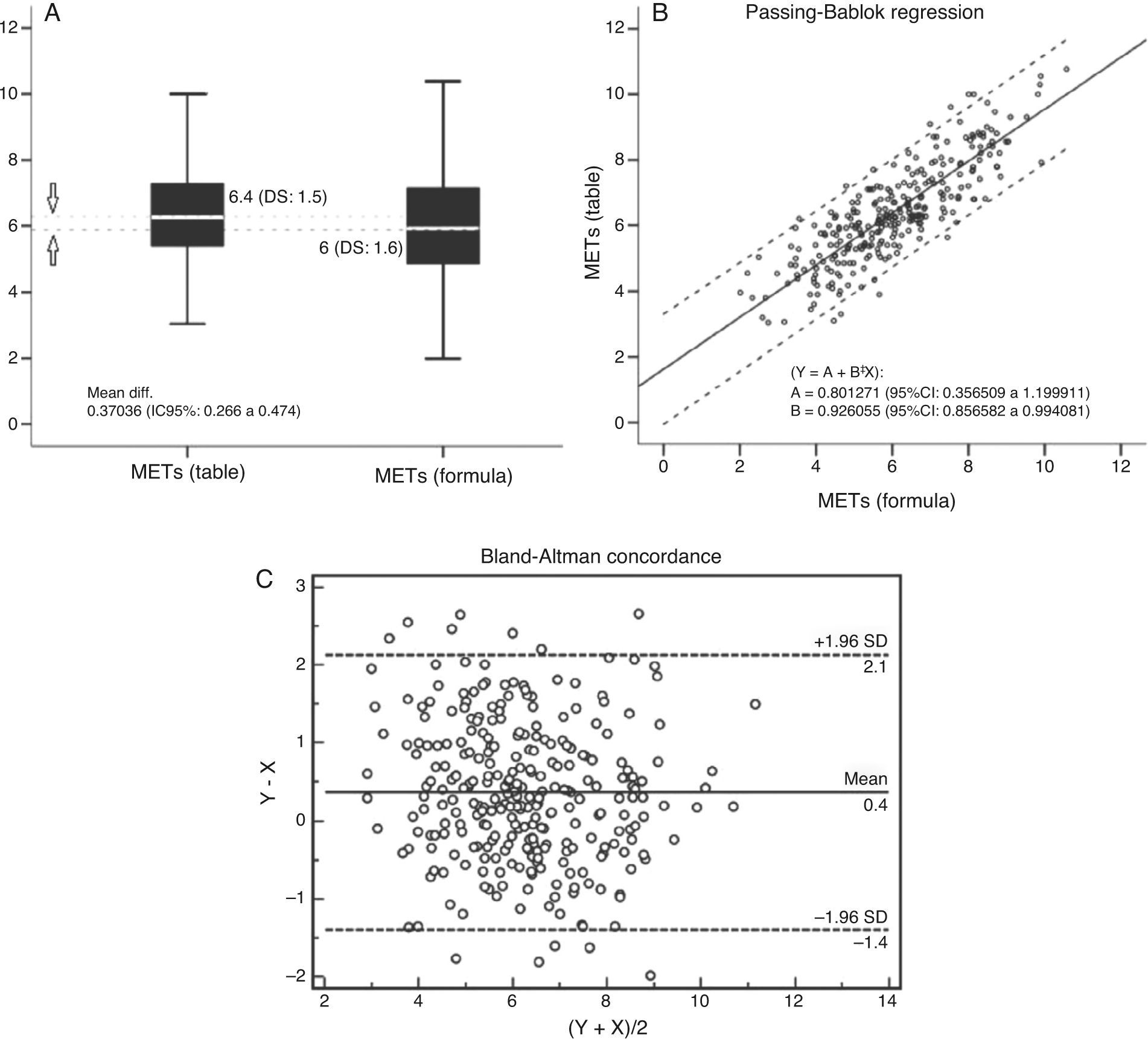
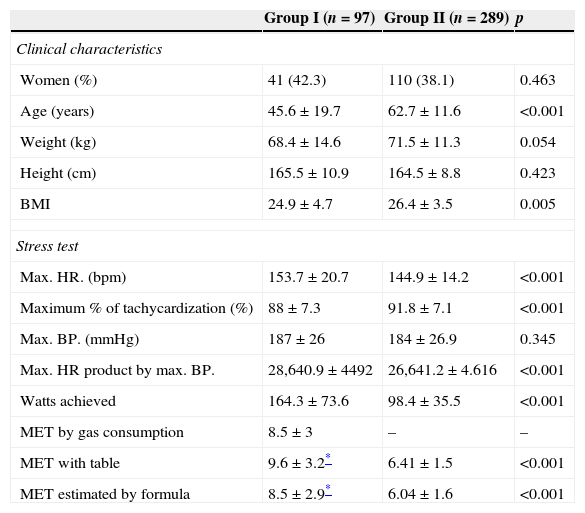
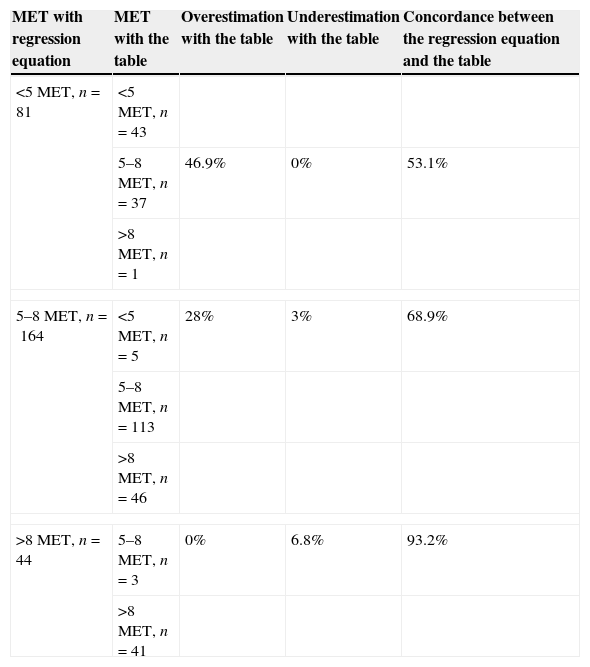
ResultsIn group I individuals a good correlation between METs estimated with the table and those obtained through gas-exchange analysis (CCI: 0.93) was observed. However, the best adjusted formula to estimate METs in group II subjects included watts, body mass index (BMI), age and gender (METS=11.820−0.054×age−0.189×BMI+1.031×gender+0.020×watts) (women: 0, men: 1). This formula allowed the reclassification of 46.9% of group ii subjects into the category <5METs versus the estimation by table.
ConclusionsEstimating the METs with the conventional table is reliable. However, the best adjustment in subjects with normal bicycle exercise SPECT was obtained when, in addition to watts and BMI, age and gender were also considered.
Valorar si la estimación del consumo máximo de oxígeno (CMO2) en MET (unidad metabólica) mediante las tablas propuestas en las guías de la Sociedad Española de Cardiología (SEC) es un método suficientemente fiable cuando se aplica a las pruebas de esfuerzo con bicicleta ergométrica.
Material y métodosSe obtuvo el CMO2 en MET por consumo de gases en bicicleta ergométrica en 97 sujetos sanos (grupo i) y se comparó con la estimación de los MET obtenida mediante tabla en la que solo intervienen los vatios y el peso del paciente. Mediante la introducción de variables clínicas y ergométricas se obtuvo una fórmula con mejor ajuste para el cálculo de los MET validándose en 289 pacientes (grupo ii) con gated-SPECT de perfusión miocárdica normal.
ResultadosEn los individuos del grupo i se observó una buena correlación entre los MET estimados con la tabla y los MET obtenidos mediante consumo de gases (CCI: 0,93). Sin embargo, la fórmula con mejor ajuste para la estimación de los MET en los pacientes del grupo ii incluyó los vatios, el índice de masa corporal (IMC), la edad y el sexo (MET=11,820−0,054×edad−0,189×IMC+1,031×sexo+0,020×vatios) (mujer: 0, hombre: 1). Esta fórmula permitió la reclasificación de un 46,9% de los individuos del grupo ii en la categoría <5MET con respecto a la estimación por tabla.
ConclusionesLa estimación de los MET mediante la tabla convencional es fiable, aunque el ajuste óptimo, cuando se aplica a sujetos con gated-SPECT de perfusión miocárdica de esfuerzo normal, se obtiene al considerar, además de los vatios, el IMC, la edad y el sexo.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)