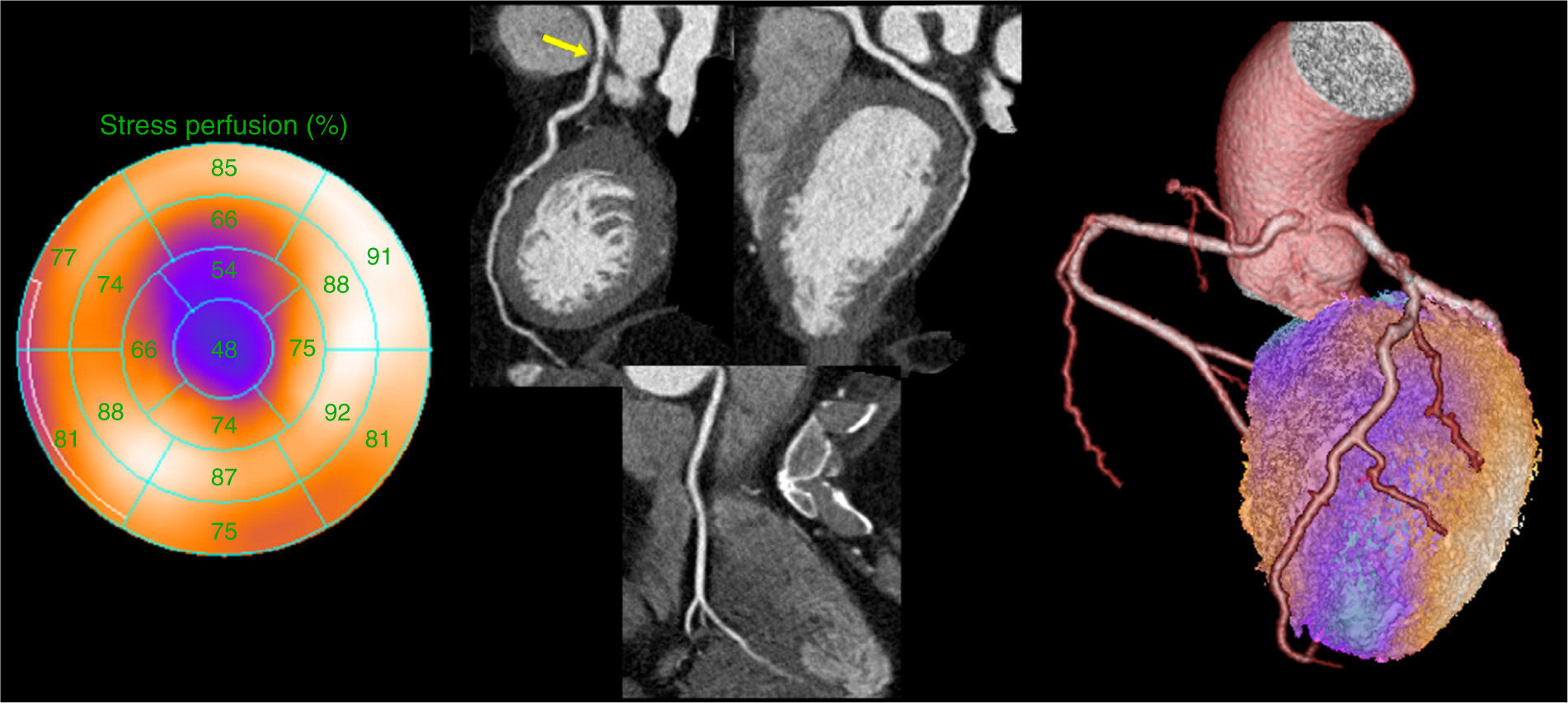
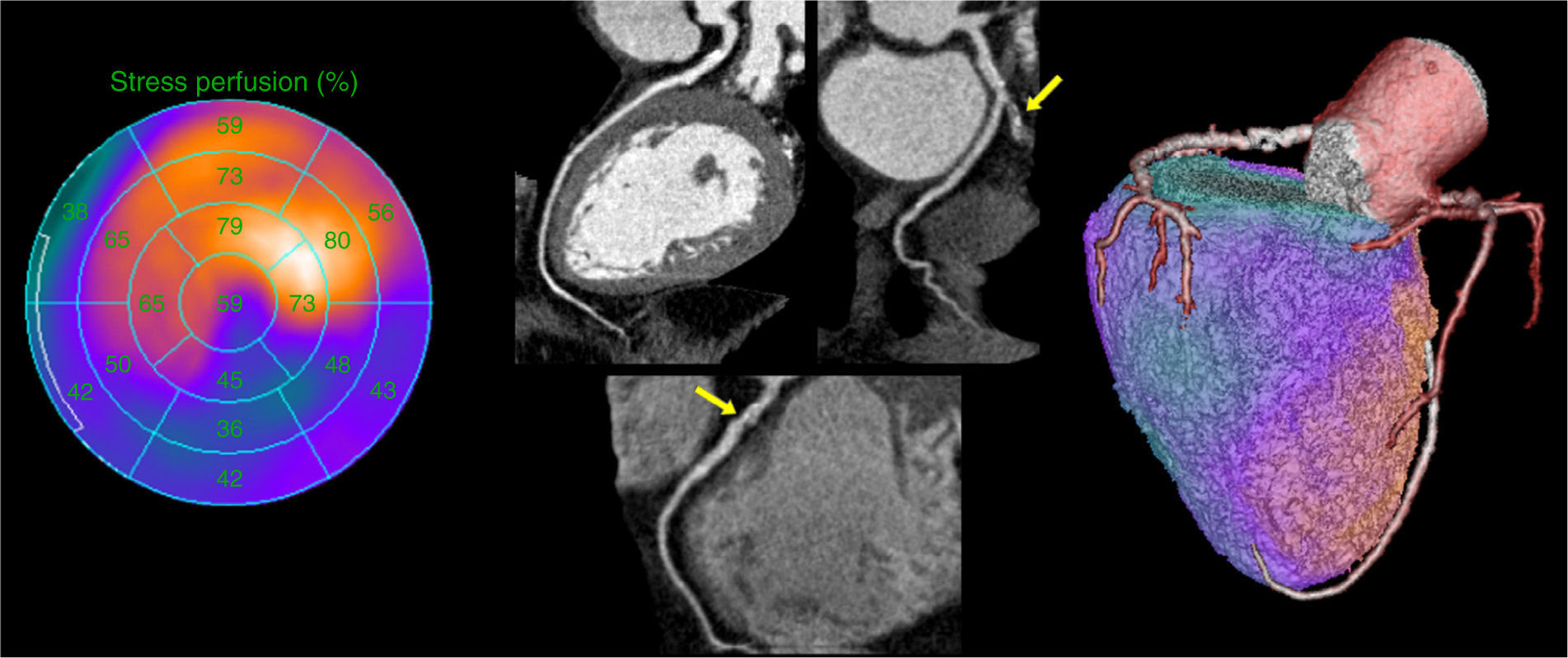
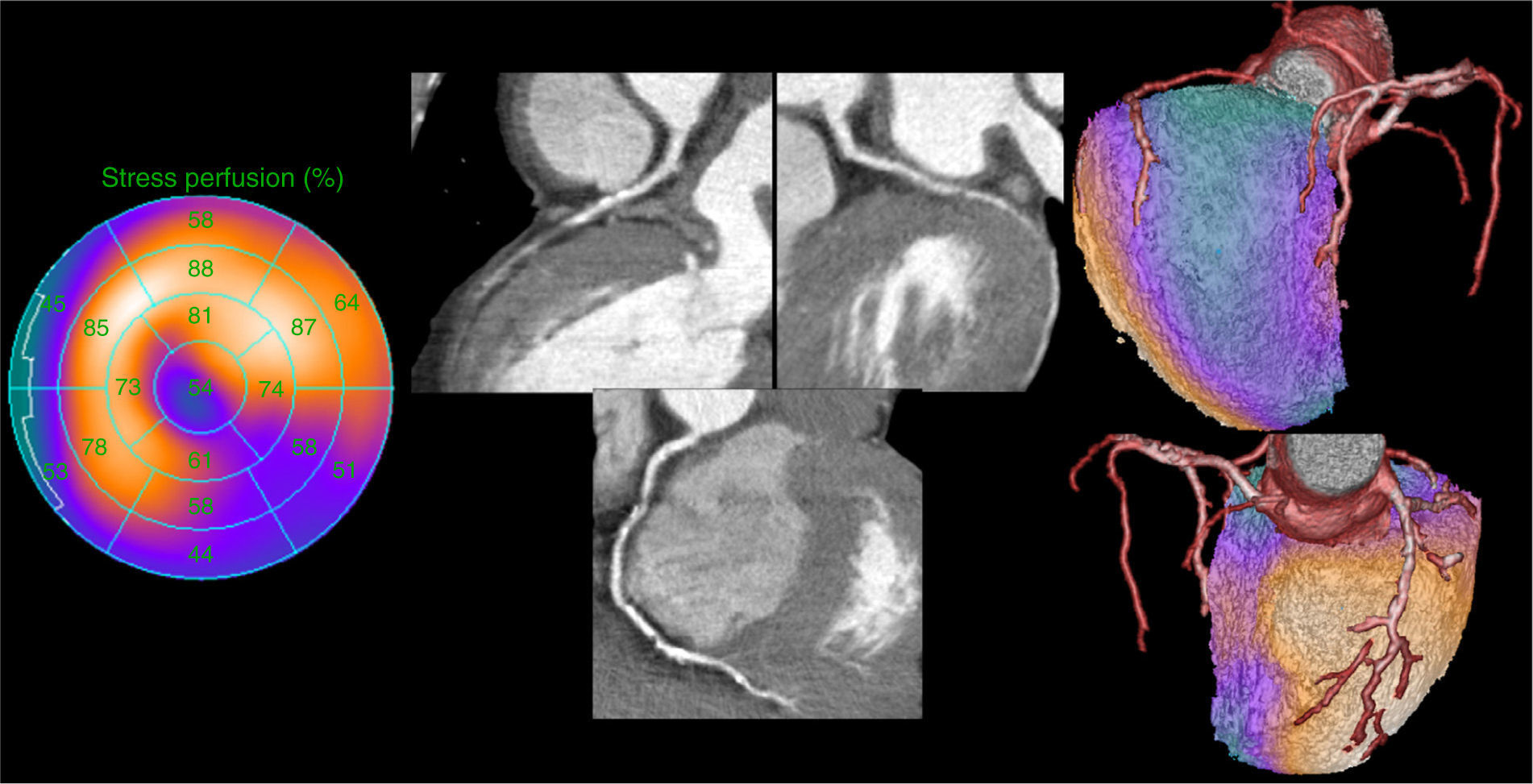
To evaluate the usefulness of the information obtained with SPECT, coronary angio-CT and fusion images, in patients with stable ischemic disease who need invasive coronary angiography (IA).
Material and methodsForty-six patients (65.98±8.3 years) with coronary disease were prospectively included. The fusion images generated after undergoing IA were used to evaluate the performance of these techniques in the diagnosis of multi-vessel coronary disease, the detection of the culprit vessel and the therapeutic management of these patients.
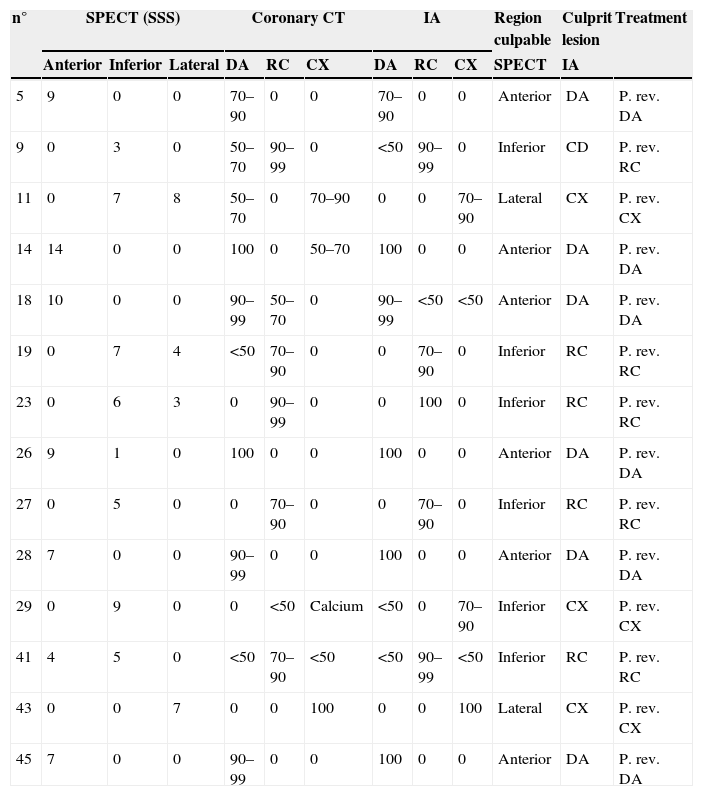
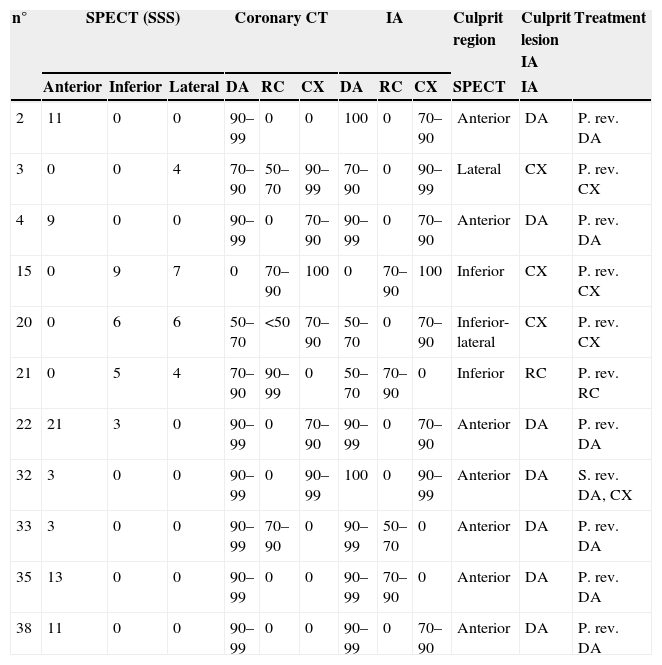
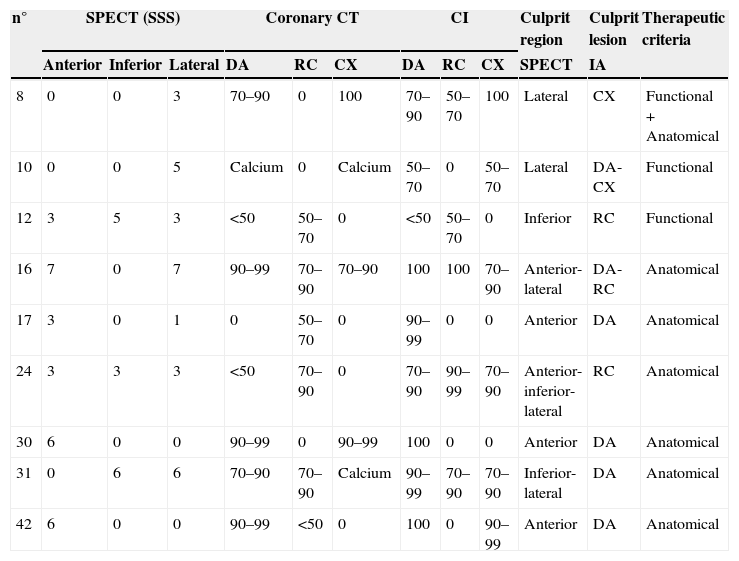
ResultsIn the IA, 29 of the 46 patients (63%) had multi-vessel disease. SPECT could detect it in 48.2% and coronary angio-CT could detect it in 89.6%. Concordance between coronary angio-CT and IA in the diagnosis of the culprit vessel was 77% (kappa 0.6), and between SPECT and IA it was 73% (kappa 0.56). Although fusion images could have been obtained prior to IA, they would not have changed the therapeutic approach derived from SPECT and IA.
ConclusionsCoronary angio-CT has a high ability for the diagnosis of multi-vessel disease and the culprit lesion, and SPECT is a good functional complement of the IA in the detection of the most ischemic territory. However, the performance of fusion images in patients with stable ischemic disease, who have undergone a SPECT as the first non-invasive study and need IA, does not seem indicated because they would not have changed the therapeutic management derived from SPECT and IA information.
Valorar la información de la SPECT, de la angio-TC coronaria y de las imágenes híbridas de fusión en los pacientes con cardiopatía isquémica estable en los que se practica una coronariografía invasiva (CI).
Material y métodosSe ha incluido en forma prospectiva a 46 pacientes (65,98±8,3 años) con enfermedad coronaria, valorándose la información de dichas técnicas en el diagnóstico de la enfermedad multivaso, en la detección del vaso culpable y en el manejo de los pacientes.
ResultadosEn la CI, 29 de los 46 pacientes (63%) presentaban enfermedad multivaso: la SPECT la diagnosticó en un 48,2% y la angio-TC en un 89,6%. La concordancia entre la angio-TC y la CI en el diagnóstico del vaso culpable fue del 77% (kappa 0,6) y entre la SPECT y la CI del 73% (kappa 0,56). Las imágenes híbridas obtenidas después del cateterismo no habrían aportado nueva información a la ya obtenida mediante la SPECT y la CI de cara al manejo terapéutico.
ConclusionesLa angio-TC destaca en el diagnóstico de la enfermedad multivaso y en la detección del vaso culpable respecto a la CI. La SPECT resulta un buen complemento funcional de la CI en la detección del territorio más isquémico. No obstante, en los pacientes con cardiopatía isquémica estable en los que se ha realizado una SPECT como primer estudio no invasivo, si la decisión de practicar posteriormente una CI es clara, la realización de una angio-TC y la obtención de imágenes de fusión SPECT-TC no parecen indicadas, ya que no cambiaría el manejo terapéutico que se adopta sobre la base de la información de la SPECT y la CI.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)