The aim of our study was to evaluate the contribution of 18Fluorine-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography (18F-FDG PET) radiomic data obtained from both the tumoral and peritumoral area in predicting pathological complete response (pCR) in patients with locally advanced breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC).
MethodsFemale patients with a diagnosis of invasive ductal carcinoma who received NAC were evaluated retrospectively. The volume of interest (VOI) of the primary tumor (VOI-T) was manually segmented, then a voxel-thick VOI was added around VOI-T to define the peritumoral area (VOI-PT). Morphological, intensity-based, histogram and texture parameters were obtained from VOIs. The patients were divided into two groups as pCR and non-complete pathological response (npCR). A “radiomic model” was created with only radiomic features, and a “patho-radiomic model” was created using radiomic features and immunohistochemical data.
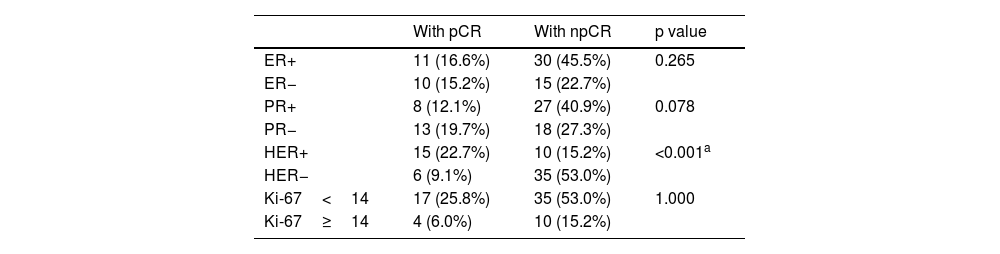
ResultsOf the 66 patients included in the study, 21 were in the pCR group. The only statistically significant feature from the primary tumor among patients with pCR and npCR was Morphological_Compacity-T (AUC: 0.666). Between response groups, a significant difference was detected in 2 morphological, 1 intensity, 4 texture features from VOI-PT; no correlation was found between Morphological_Compacity-PT and NGTDM_contrast-PT. The obtained radiomic model’s sensitivity and accuracy values were calculated as 61.9% and 75.8%, respectively (AUC: 0.786). When HER2 status was added, sensitivity and accuracy values of the patho-radiomic model increased to 85.7% and 81.8%, respectively (AUC: 0.903).
ConclusionsEvaluation of PET peritumoral radiomic features together with the primary tumor, rather than just the primary tumor, provides a better prediction of the pCR to NAC in patients with breast cancer.
El objetivo de nuestro estudio fue evaluar la contribución de los datos radiómicos de la tomografía por emisión de positrones con 18flúor-fluorodesoxiglucosa (PET con 18F-FDG) obtenidos tanto del área tumoral como peritumoral en la predicción de la respuesta patológica completa (pCR) en pacientes con cáncer de mama localmente avanzado que reciben quimioterapia neoadyuvante (NAC).
MétodosSe evaluaron retrospectivamente pacientes femeninas con diagnóstico de carcinoma ductal invasivo que recibieron NAC. El volumen de interés (VOI) del tumor primario (VOI-T) se segmentó manualmente, luego se agregó un VOI de espesor de vóxel alrededor de VOI-T para definir el área peritumoral (VOI-PT). Los parámetros morfológicos, basados en intensidad, histogramas y textura se obtuvieron de los VOI. Los pacientes se dividieron en dos grupos: pCR y respuesta patológica no completa (npCR). Se creó un “modelo radiómico” únicamente con características radiómicas y un “modelo pato-radiómico” utilizando características radiómicas y datos inmunohistoquímicos.
ResultadosDe los 66 pacientes incluidos en el estudio, 21 estaban en el grupo pCR. La única característica estadísticamente significativa del tumor primario entre los pacientes con pCR y npCR fue Morphological_Compacity-T (AUC: 0.666). Entre los grupos de respuesta, se detectó una diferencia significativa en 2 características morfológicas, 1 de intensidad y 4 de textura de VOI-PT; no se encontró correlación entre Morphological_Compacity-PT y NGTDM_contrast-PT. Los valores de sensibilidad y precisión del modelo radiómico obtenidos se calcularon como 61.9% y 75.8%, respectivamente (AUC: 0.786). Cuando se agregó el estado de HER2, los valores de sensibilidad y precisión del modelo pato-radiómico aumentaron al 85.7 % y 81.8 %, respectivamente (AUC: 0.903).
ConclusionesLa evaluación de las características radiómicas peritumorales de la PET junto con el tumor primario, en lugar de solo el tumor primario, proporciona una mejor predicción de la pCR a NAC en pacientes con cáncer de mama.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)