To evaluate the efficacy and clinical impact of the FDG-PET in the diagnosis of suspicion of recurrence of medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) in patients with elevated serum calcitonin and negative imaging test.
Material and methodsWe performed a retrospective study of 31 consecutive cases from February 2001 to October 2007 of 17 women and 14 men, mean age 56.2 years (range: 26–88), with anatomical-pathology diagnosis of MTC and suspicion of recurrence due to abnormal elevation of calcitonin and negative imaging tests. All the patients underwent whole body FDG-PET scan with a dedicated PET or PET-CT 60min after intravenous injection of 333–434 MBq of 18F-FDG. Results were confirmed by pathology study in 45.2% of the patients and by clinical follow-up with a mean of 4 years (range: 16 months–8 years).
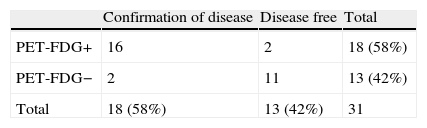
ResultsSensitivity was 88%, specificity 84.6%, positive predictive value (PPV) 88%, negative predictive value (NPV) 84.6% and diagnostic accuracy 87%. The results of the FDG PET modified the therapeutic strategy in 14 cases (45.2%). A comparison was made of the mean values of calcitonin using the Student's t-test between positive PET studies for the disease and negative ones. No significant differences were found (p=0.3).
ConclusionsIn patients with MTC and suspected recurrence with elevated calcitonin and negative imaging test, the FDG is the best test for the diagnosis of occult recurrence in MTC with elevated calcitonin and negative imaging techniques with elevated clinical impact. It facilitates the therapeutic management of the patients with MTC recurrence, and should be included in the diagnosis algorithm in these patients.
Evaluar la eficacia y el impacto clínico de la PET-FDG en el diagnóstico de sospecha de recurrencia de carcinoma medular de tiroides (CMT), en pacientes con calcitonina elevada y pruebas de imagen negativas.
Material y métodosEstudiamos retrospectivamente a 31 pacientes consecutivos de febrero de 2001 a octubre de 2007; 17 mujeres y 14 hombres con una edad media de 56,2 años (rango: 26-88), diagnóstico anatomopatológico de carcinoma medular de tiroides y sospecha de recurrencia por elevación patológica de calcitonina y pruebas de imagen negativas. A todos los pacientes se les realizó PET/PET-TAC corporal 60min post-inyección intravenosa de 333-434 MBq de 18F-FDG. Los resultados se confirmaron mediante anatomía patológica en el 45,2% de los pacientes y por seguimiento clínico/radiológico en el 54,8% durante un período de seguimiento medio de 4 años (rango: 16 m-8 años).
ResultadosSe obtuvo una sensibilidad del 88%, especificidad del 84,6%, valor predictivo positivo del 88%, valor predictivo negativo del 84,6% y exactitud diagnóstica del 87%. Los resultados de la PET-FDG modificaron la actitud terapéutica en 14 casos (45,2%). Se compararon las medias de los valores de calcitonina entre PET positivos para enfermedad y negativos, mediante la prueba de la «t» de Student no encontrando diferencia significativa (p=0,3).
ConclusionesLa PET-18F-FDG es la prueba idónea para el diagnóstico de recurrencia oculta en CMT con calcitonina elevada y técnicas de imagen negativas, con elevado impacto clínico facilitando el manejo terapéutico de los pacientes con recurrencia de CMT, debiendo ser incluida en el algoritmo diagnóstico de estos pacientes.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)