Determining the efficacy, safety, and prognostic factors affecting overall survival (OS) among metastatic prostate cancer patients undergoing PSMA-targeted radioligand therapy (PRLT).
MethodIn this retrospective study, from November 2016 and December 2019, 43 heavily pretreated (90.7% on 1st line androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), 53.5% on 2nd line ADT, 58.1% on docetaxel) metastatic prostate cancer patients with median age of 71 years (range: 51−88 years) were enrolled. Treatment cycles were repeated every 8 weeks (range: 6–12 weeks). To evaluate the biochemical response after each cycle, prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels were measured and analyzed according to the Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 (PCWG3) criteria cutoffs. Possible adverse events after therapy were retrospectively classified according to the Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v.5.0. Kaplan-Meier and multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression analyses were used to identify factors associated with OS.
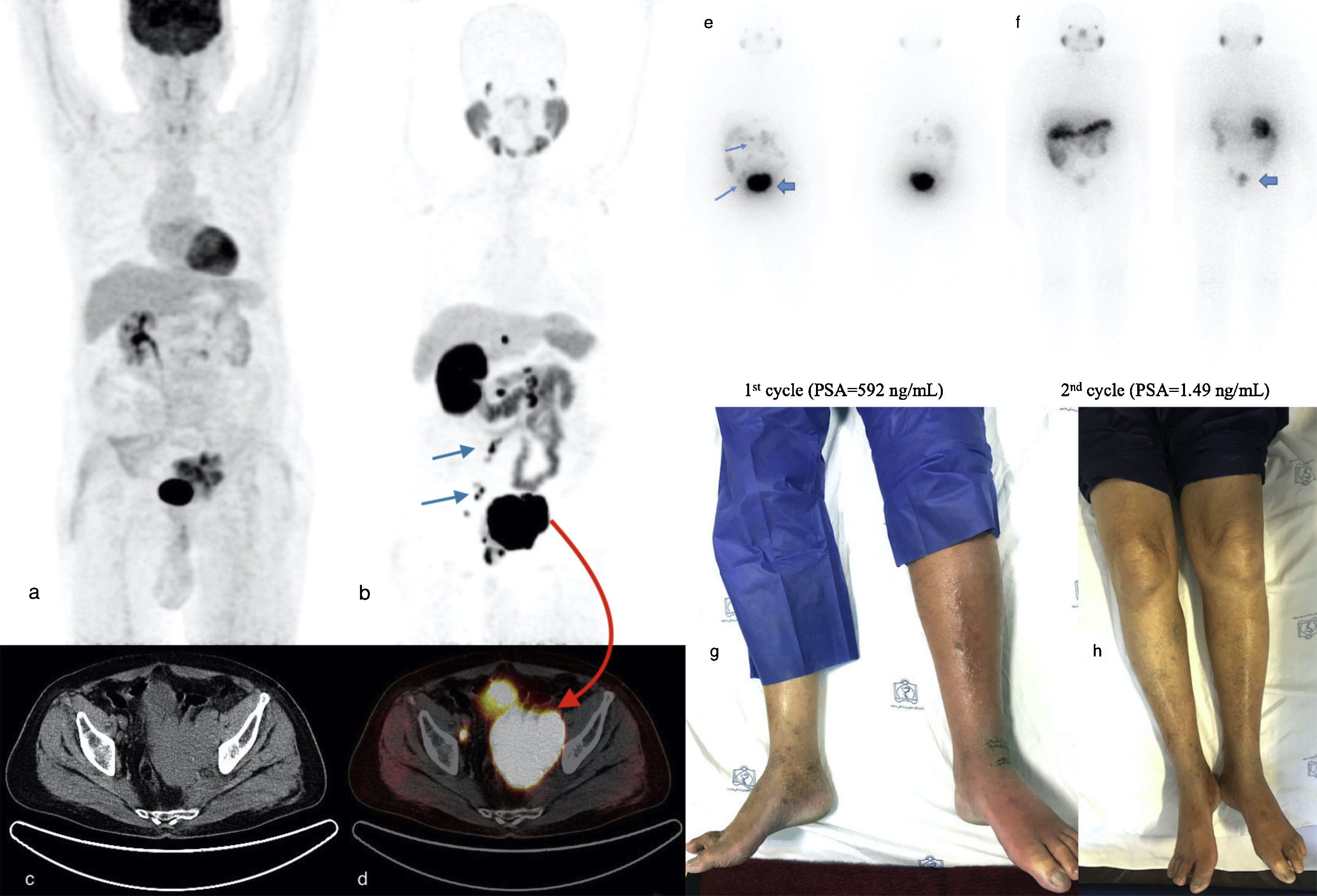
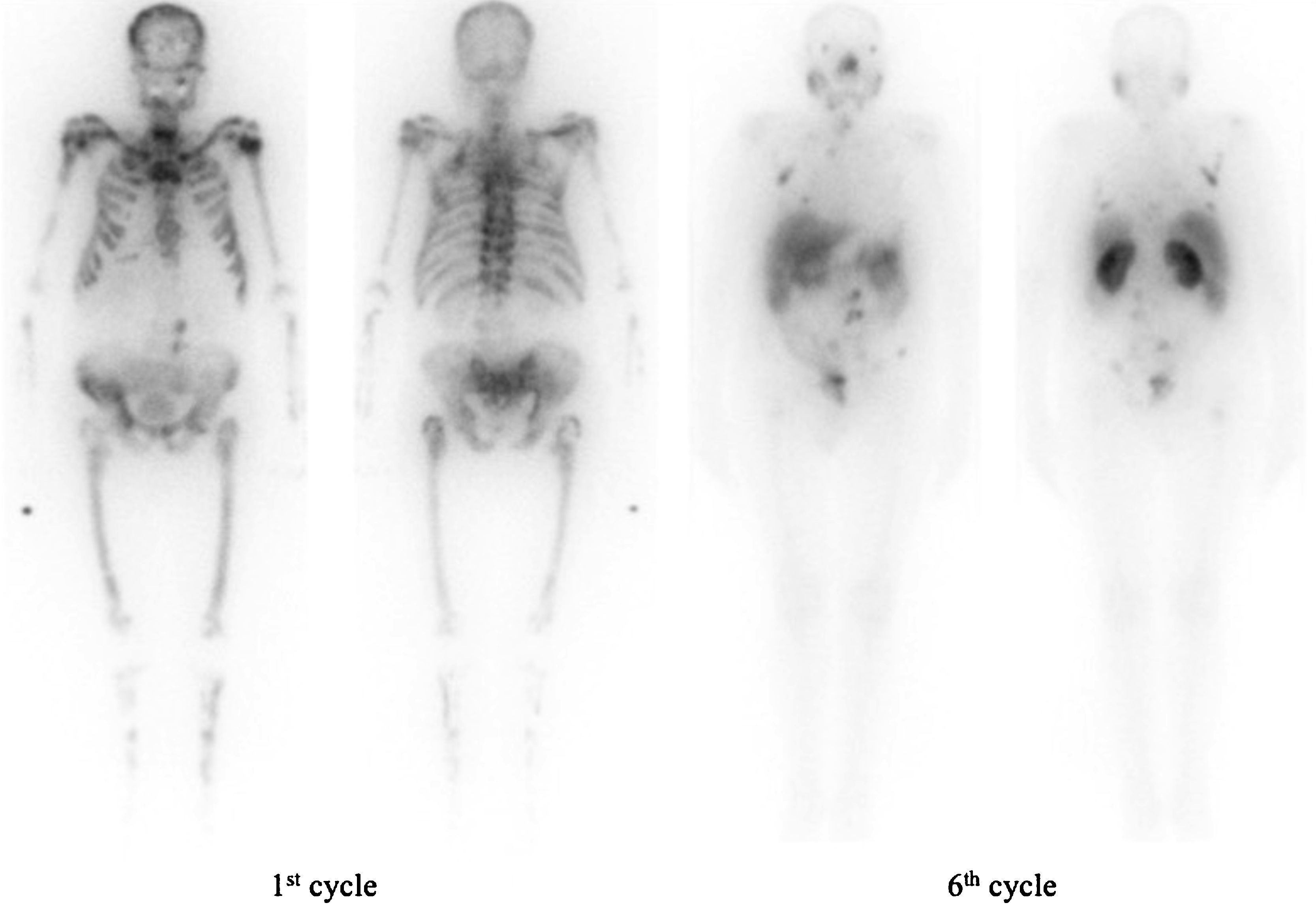
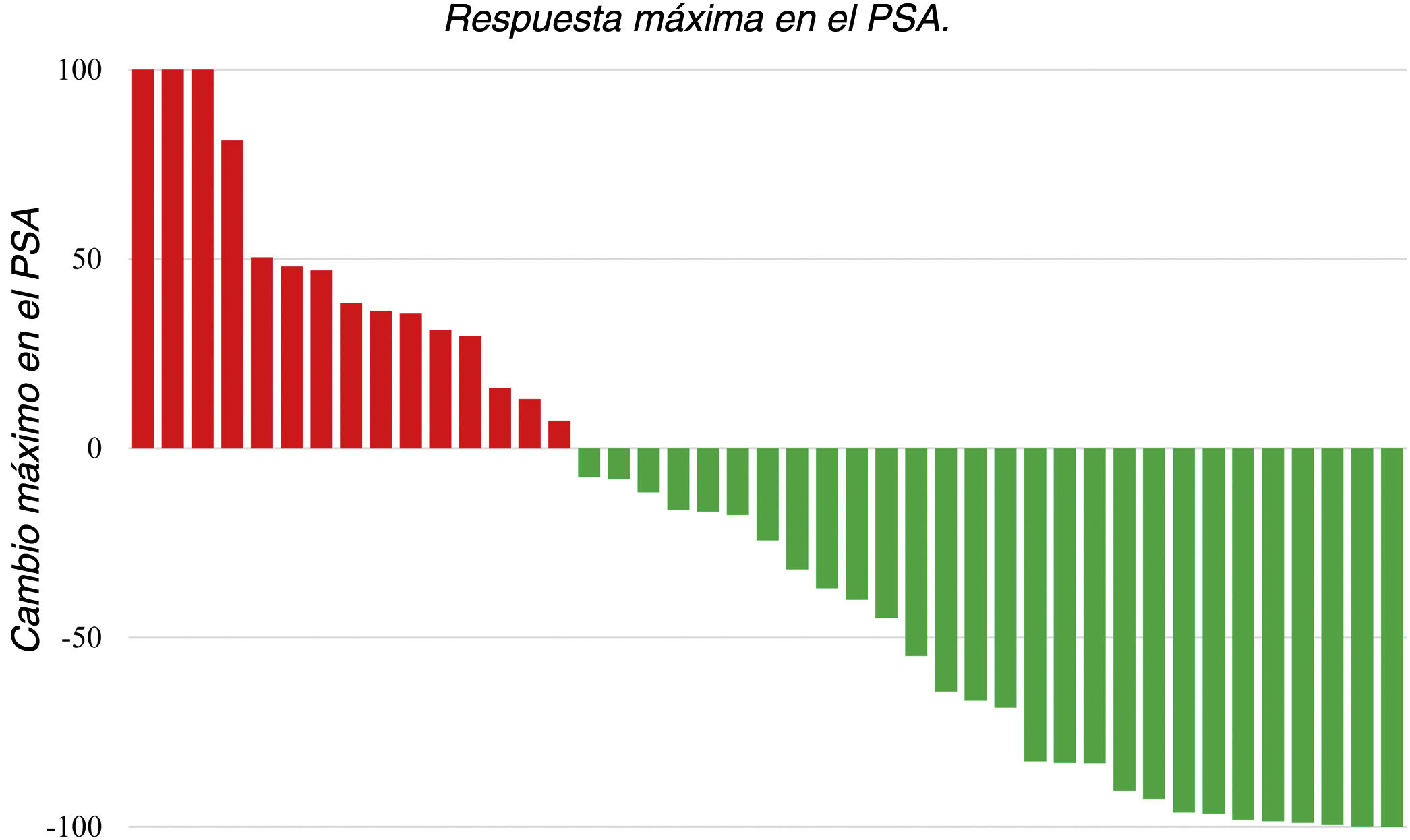
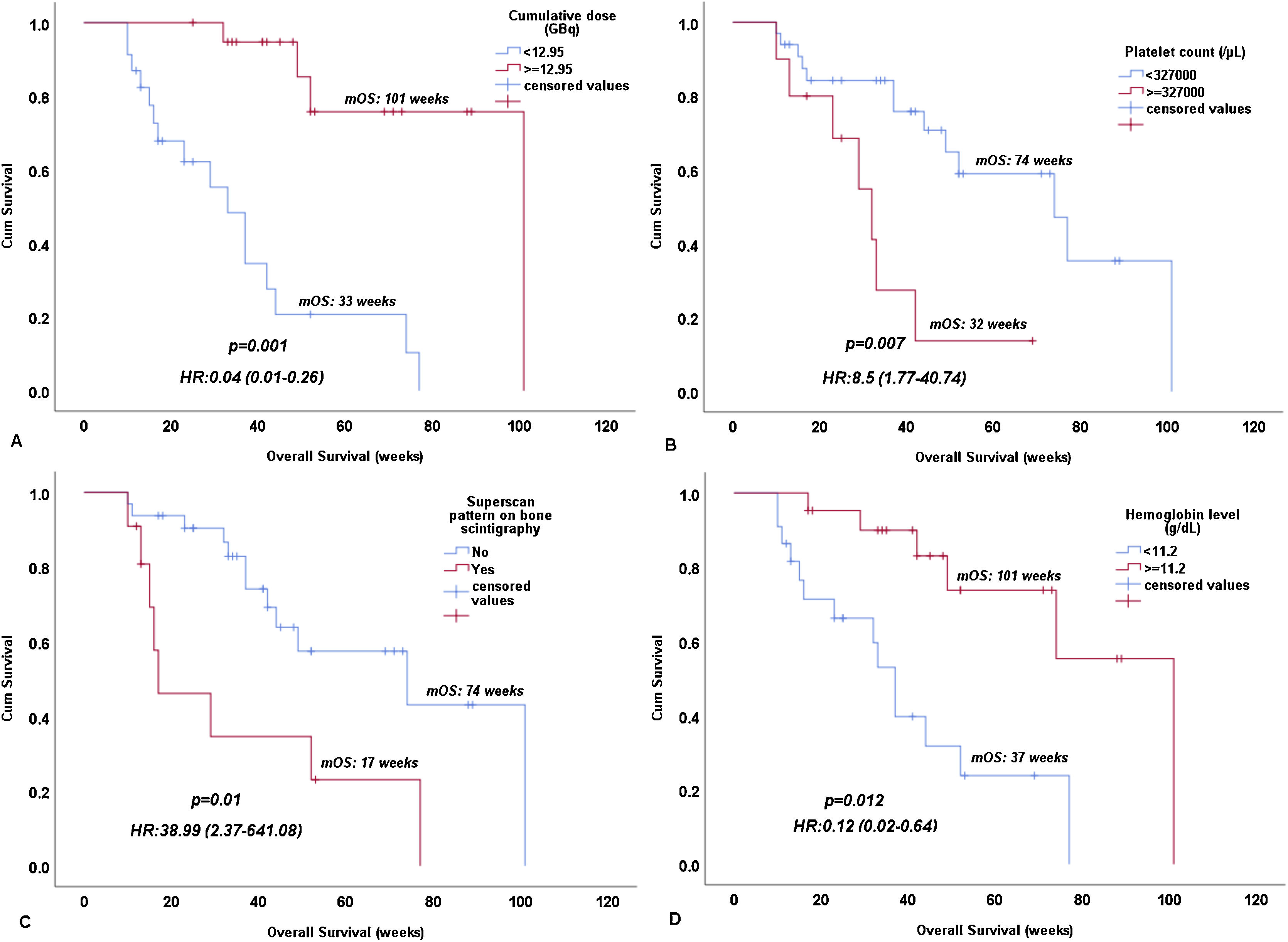
ResultsA total of 112 cycles of PRLT with a median of 3 cycles (range: 1–6) and median administered activity per cycle of 6.29 GBq (range: 4.45–7.7 GBq) were used. PSA decline was observed in 65.1% of patients, and best PSA decline of ≥50% and ≥90% were achieved in 39.5% and 23.3% of patients, respectively. Major (grade III) anemia and thrombocytopenia occurred in 11.6% and 7% of patients, respectively. Median OS and median PSA progression-free survival were 52 and 20 weeks, respectively. In univariate analysis, baseline hemoglobin <11.2 g/dL, baseline platelets count ≥327,000/μL, PSA decline <20.94% after first cycle of therapy, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) >2, baseline PSA ≥ 115 ng/mL, cumulative dose of 177Lu-PSMA <12.95 GBq, initial alkaline phosphatase ≥196.5 U/L, initial lactate dehydrogenase ≥380 U/L and superscan pattern in bone scintigraphy were associated with worse OS. In multivariable Cox regression analysis, higher baseline platelet count, lower baseline hemoglobin, superscan pattern, and lower cumulative dose of 177Lu-PSMA remained significant predictors of poor OS.
ConclusionPRLT with 177Lu-PSMA is well-tolerated and effective in metastatic prostate cancer patients who have no other treatment options available. The novel prognostic markers found in this study (high platelet count, superscan pattern) were associated with poor overall survival.
Determinación de los factores pronósticos de eficacia y seguridad que afectan la supervivencia global (SG) entre los pacientes con cáncer de próstata metastásico que han sido sometidos a terapia con radioligandos (RLT) con PSMA.
MétodoEstudio retrospectivo, desde el noviembre del año 2016 a diciembre del año 2019, se incluyeron 43 pacientes con cáncer de próstata metastásico, con una media de edad 71 años (entre 51 y 88 años), los cuales habían recibido varias líneas de tratamiento previas (90.7%, primera línea de la terapia de privación de andrógenos (ADT), 53.5% en la segunda línea ADT, y 58.1% en docetaxel). Los ciclos del tratamiento con RLT se repetían cada ocho semanas (entre 6 y 12 semanas). Con el fin de evaluar la respuesta bioquímica tras cada ciclo, los niveles del antígeno específico prostático (PSA) se medían y se analizaban de acuerdo con los criterios del Equipo de Trabajo del Cáncer de Próstata 3 (PCWG3). Los eventos adversos posibles tras la terapia fueron retrospectivamente clasificados de acuerdo con los Criterios de Toxicidad Común para Eventos Adversos (CTCAE), v.5, Para identificar los factores asociados con SG se utilizaron las curvas de Kaplan-Meier, y los análisis de regresión de riesgos proporcionales de Cox.
ResultadosFueron administrados un total de 112 ciclos de RLT con una mediana de 3 ciclos (entre 1 y 6) y una actividad administrada mediana por ciclo de 6.29 GBq (entre 4.45 y 7.7). Se observó una disminución en la PSA en el 65.1% de los pacientes, la mayor disminución en la PSA, de ≥50% y ≥90%, se obtuvo en los 39.5% y 23.3% de los pacientes respectivamente. El mayor grado de anemia (grado III) y trombocitopenia ocurrió en los 11.6% y 7% de los pacientes respectivamente. La mediana de SG y mediana de supervivencia libre de progresión fueron 52 y 20 semanas respectivamente. En los análisis univariantes, la hemoglobina basal <11.2 g/dl; el recuento de plaquetas basales ≥327,000/μL; la disminución de la PSA < 20.94% después del primer ciclo de terapia, ECOG > 2, PSA ≥ 115 ng/mL, una dosis acumulada de 177Lu-PSMA <12.95 GBq, una fosfatasa de alcalina inicial, ≥196.5 U/L, una lactato deshidrogenasa inicial ≥380 U/L, y un patrón de súperscan en la gammagrafía ósea se asociaron con una peor SG. En los análisis de regresión de Cox, un recuento basal de plaquetas mayor, niveles mas bajos de hemoglobina basal, un patrón de súperscan y una dosis acumulada menor de 177LuPSMA fueron predictores significativos de peor SG.
ConclusiónRLT con 177Lu-PSMA es bien tolerada y efectiva en los pacientes con cáncer de próstata metastásico que no tienen ningún otro tratamiento disponible. Los novedosos marcadores pronósticos encontrados en este estudio (recuento elevado de plaquetas, patrón de súperscan) se asociaron con una pobre supervivencia global.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)