To compare the usefulness of CT angiography against the gold standard, digital subtraction angiography (DSA), in the characterisation of cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVM) that present with bleeding.
Material and methodsWe retrospectively analysed patients with intracranial bleeding due to an AVM who were included in a prospective database in the period comprising January 2007 through December 2012. We reviewed radiologic variables such as the characteristics of the AVM (size, location, presence of deep venous drainage), involvement of eloquent areas, and the presence of associated aneurysms. Two neuroradiologists blinded to clinical and radiological information analysed the CT and DSA in consensus.
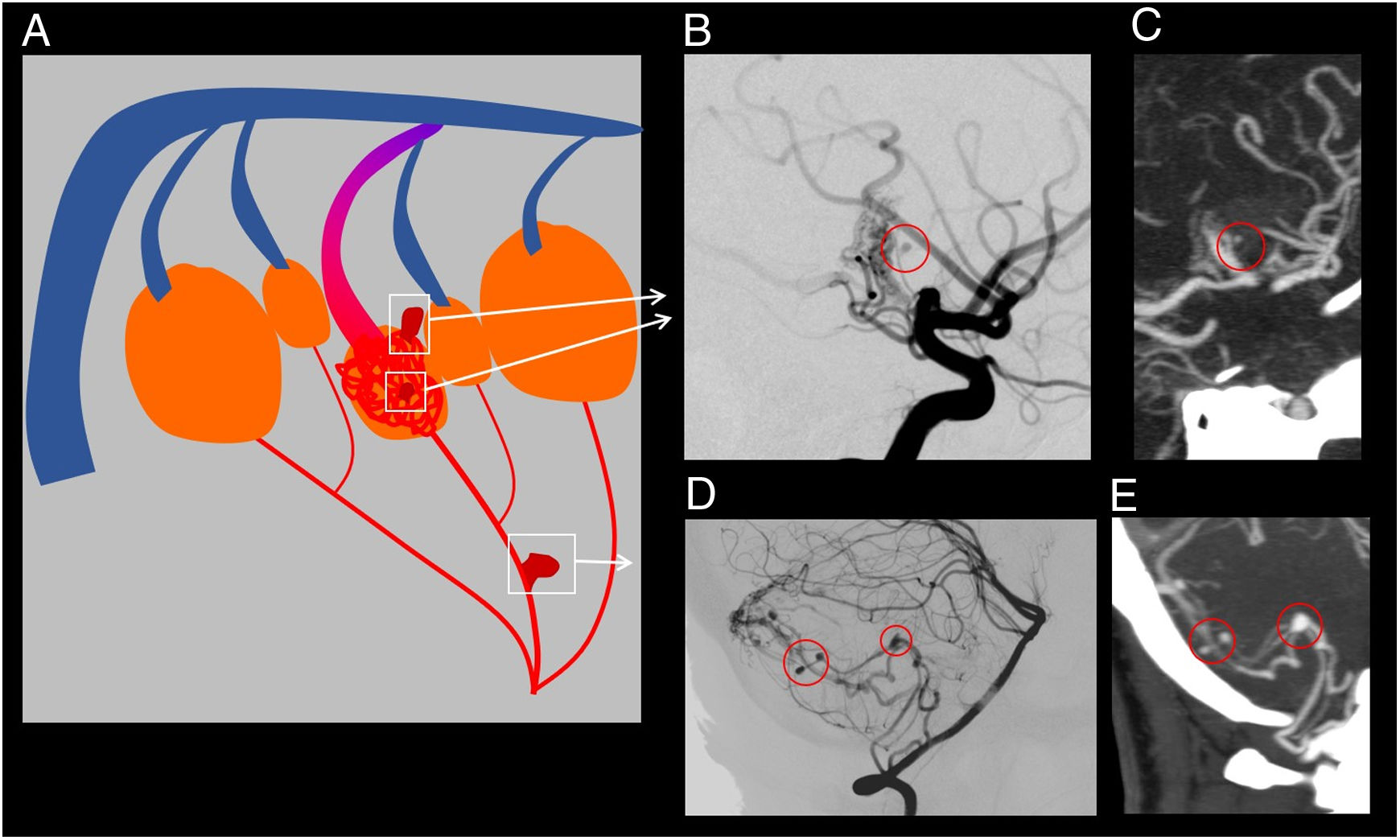
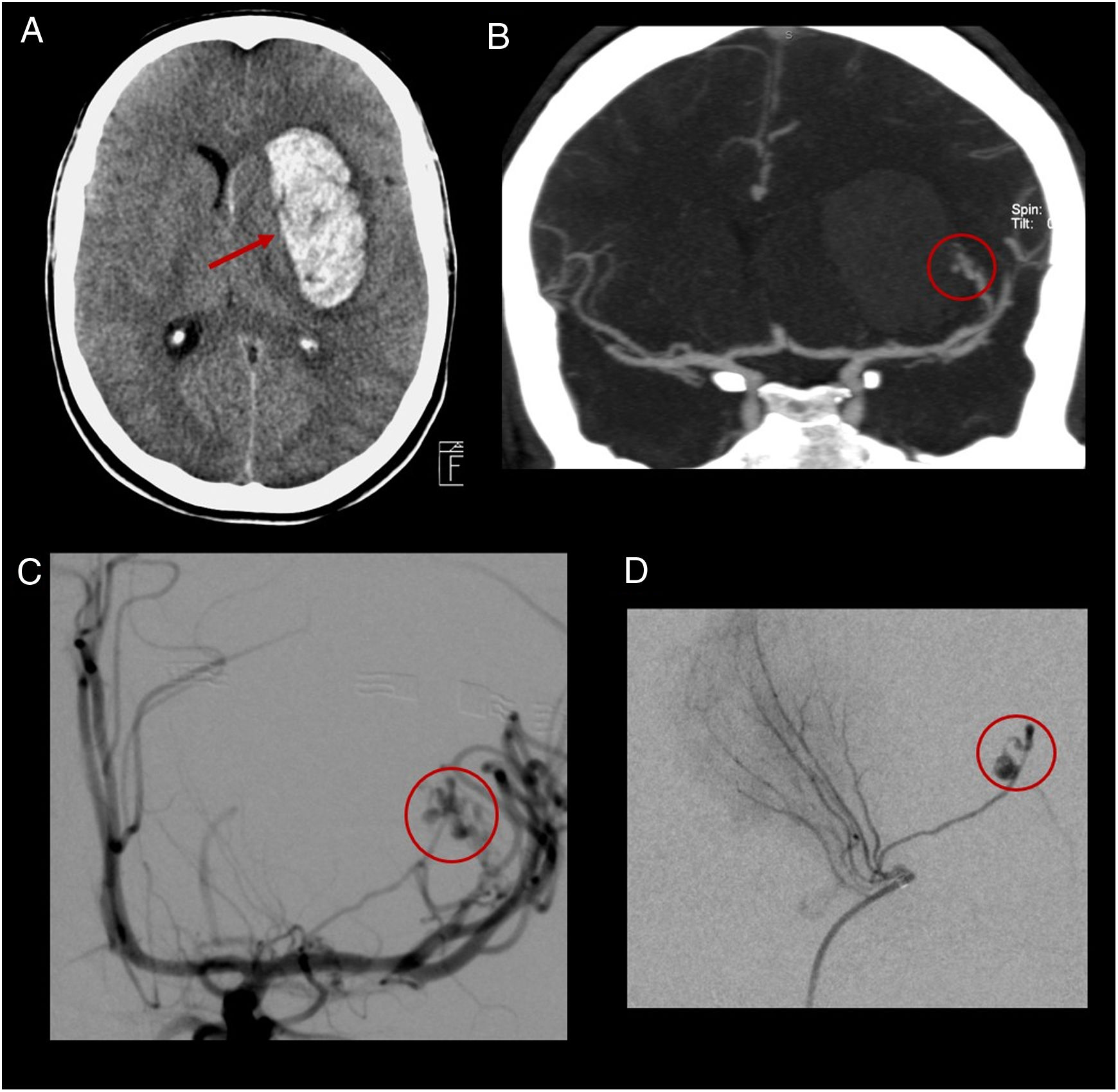
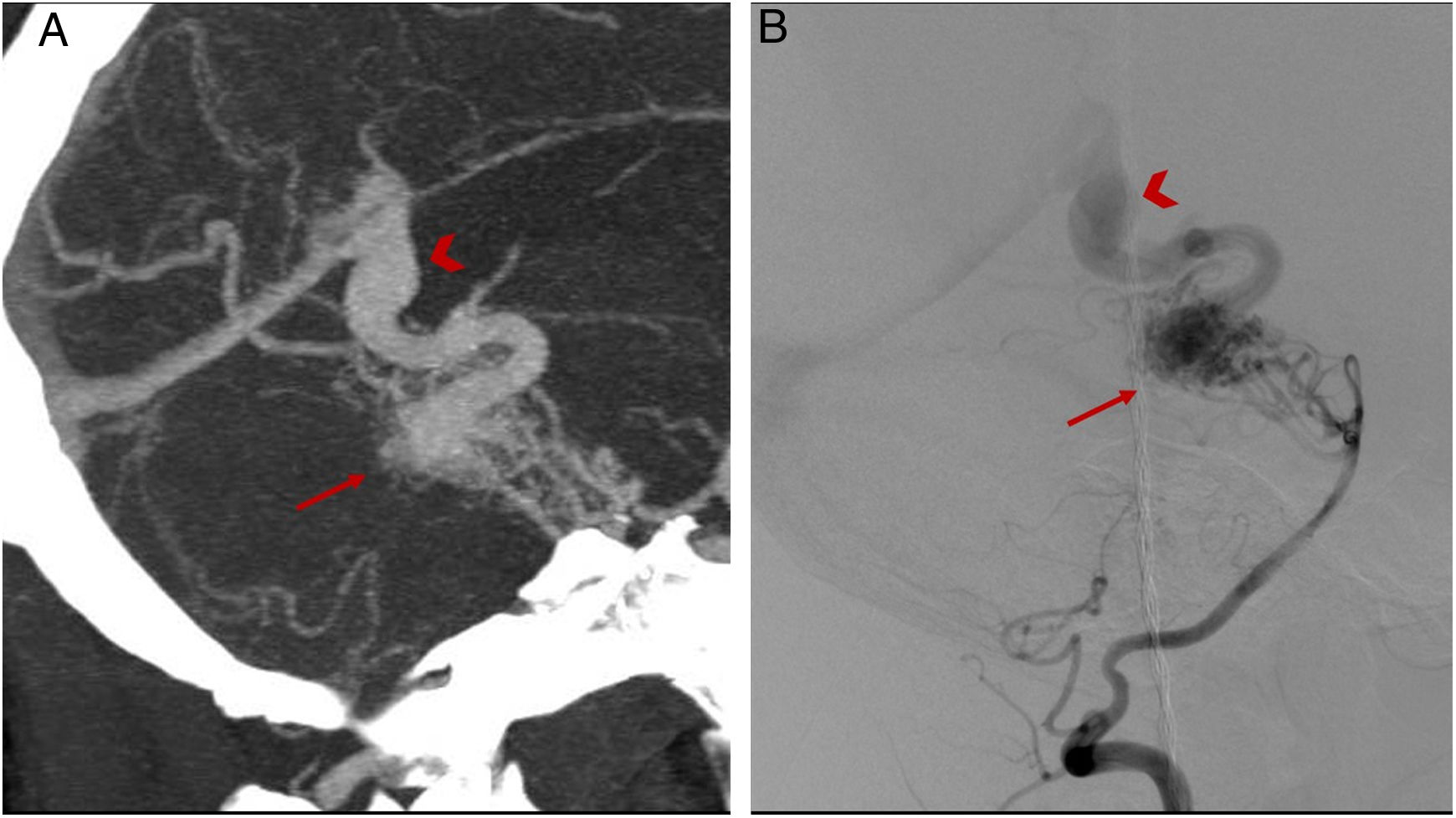
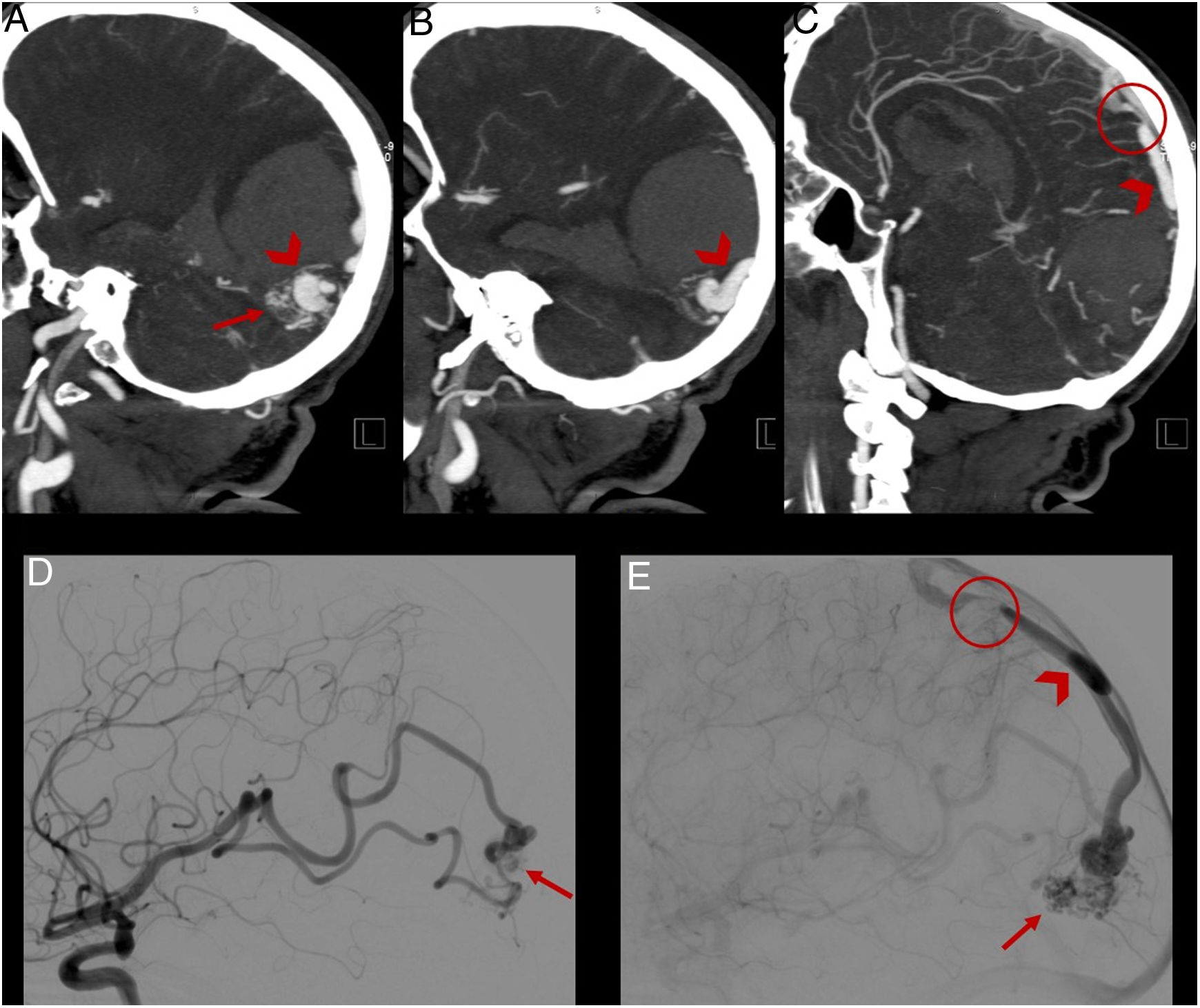
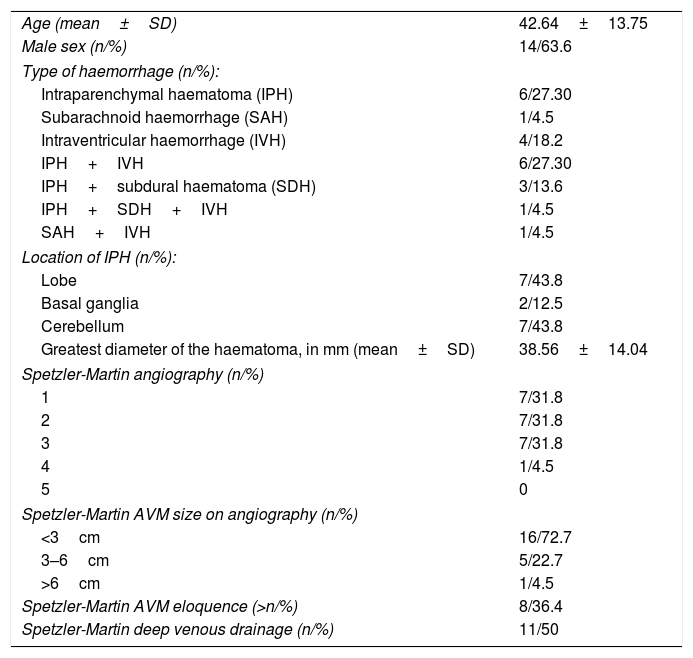
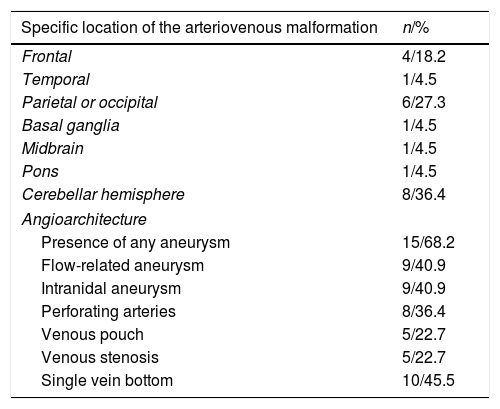
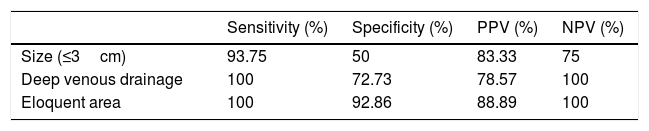
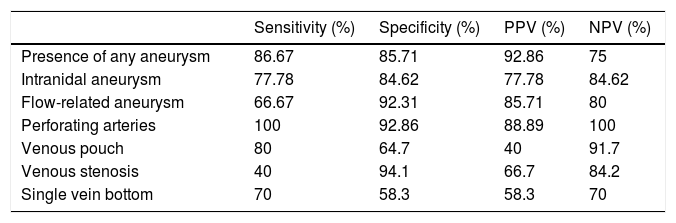
ResultsA total of 22 patients were included in the study. CT angiography correctly classified 15 of the 16 cases of AVM measuring less than 3cm (93.75% sensitivity). All cases of deep venous drainage and all those located in eloquent areas were correctly detected (100% sensitivity). The presence of any type of aneurysm related with the AVM was detected in 13 of 15 cases (86.6% sensitivity); 7 of 9 of the intranidal aneurysms were detected (77.78% sensitivity), as were 6 of the 9 flow aneurysms (66.67% sensitivity).
ConclusionCT angiography is highly sensitive in the characterisation of cerebral AVMs measuring less than 3cm, of those located in eloquent areas, and of those with deep venous drainage; it is also highly sensitive in detecting aneurysms related with AVMs. However, CT angiography is less sensitive in detecting intranidal and flow aneurysms related with AVMs.
El objetivo es determinar la utilidad de la angio-TC cerebral en la caracterización de las malformaciones arteriovenosas (MAV) cerebrales con presentación hemorrágica comparada con la angiografía por sustracción digital (DSA) como patrón de referencia.
Material y métodosSe realizó un análisis retrospectivo de una base de datos prospectiva de pacientes con sangrado intracraneal debido a una MAV cerebral desde enero de 2007 hasta diciembre de 2012. Se revisaron variables radiológicas, como las características de la malformación (tamaño, localización, presencia de drenaje venoso profundo), afectación de un área elocuente y presencia de aneurismas relacionados. Dos neurorradiólogos ciegos a cualquier información clínico-radiológica analizaron por consenso las imágenes de tomografía computarizada y DSA.
ResultadosVeintidós pacientes fueron incluidos en el estudio. La angio-TC clasificó correctamente 15 de los 16 casos de MAV menores de 3cm, con una sensibilidad del 93,75%. Todos los casos con drenaje venoso profundo y localizados en un área elocuente fueron correctamente detectados (sensibilidad 100%). La presencia de cualquier tipo de aneurisma relacionado con la MAV fue detectada en 13 de 15 pacientes (sensibilidad 86,6%); 7 de 9 en los intranidales (sensibilidad 77,78%) y 6 de 9 de los aneurismas de flujo (sensibilidad 66,67%).
ConclusiónLa angio-TC tiene una alta sensibilidad en la caracterización de MAV cerebrales en cuanto al tamaño menor de 3cm, localización en área elocuente, presencia de drenaje venoso profundo y la detección de cualquier aneurisma relacionado con la MAV. Sin embargo, la angio-TC tiene una menor sensibilidad en la detección de aneurismas intranidales y de flujo relacionados con la MAV.