This study delves into the impact of open innovation on the performance of e-commerce, with moderation by accounting information systems (AIS) and artificial intelligence (AI). Data were gathered through a survey with 29 scale items adapted from established measures to assess seven crucial variables of open innovation and e-commerce performance. The participants, 427 senior-level employees from various e-commerce enterprises, were chosen using purposive sampling to ensure their relevant expertise. PLS-SEM in SmartPLS 4.0 software was used to validate the scales and evaluate the hypotheses. The outcomes point toward the positive and significant influence of management orientation on digital competency, innovation capability, and e-commerce performance. Moreover, the results suggest that digital competency and innovation capability significantly enhance e-commerce performance. Furthermore, strong e-commerce performance positively impacts unique innovations, technological advancement, and customer satisfaction. The moderating effects of AIS and AI are positive and significant, strengthening the connection between management orientation and e-commerce performance. The moderating effect of digital competency and innovation capability is positive in the relationship between management orientation and e-commerce performance. These findings emphasize the critical role of strategic management, digital and innovative capabilities, and sophisticated technological systems in increasing the success of e-commerce within the realms of open innovation.
In the modern digital era, electronic commerce has triggered a profound transformation in the operational strategies of businesses, thereby transforming e-commerce paradigms and reconfiguring market behaviors. The rapid proliferation of online platforms, coupled with incessantly changing consumer preference, has compelled electronic commerce enterprises to perpetually innovate and adapt to maintain a competitive edge (Almaqtari et al., 2024; Darmiono & Pratiwi, 2024; Nurhayati et al., 2023). Adopting open innovation strategies has emerged as a critical determinant influencing organizational effectiveness. Open innovation transcends the limitations of organizational boundaries, fostering the interchange of knowledge, co-creation, and alliances with various stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and competitors (Mariani et al., 2023). By leveraging external knowledge and resources, electronic commerce firms can accelerate product development, enhance service offerings, and identify novel revenue opportunities. As a result, it has become imperative for organizations aiming to thrive in the contemporary, highly interconnected marketplace to understand the influence of open innovation on electronic commerce performance (Lutfi et al., 2022).
In the rapidly changing realm of electronic commerce, adopting open innovation strategies has emerged as a critical determinant influencing organizational effectiveness. Open innovation, marked by cooperation with external entities, fosters the exchange of ideas, hastens product development, and bolsters competitive advantage within the electronic commerce sector (Rana et al., 2022; Zhang & Ambonese, 2023). Even with its acknowledged significance, the precise impact of open innovation on electronic commerce performance remains to be determined, particularly when considering the moderating effects of accounting information systems (AIS) and artificial intelligence (AI). The evolving roles of AIS and AI in electronic commerce operations introduce additional complexities and prospects (Adigwe et al., 2024; Faccia & Petratos, 2021). AIS help in managing financial data and decision-making processes, furnishing essential insights for strategic decision-making and resource allocation. Similarly, AI technologies, with their data analysis capabilities and predictive modeling, provide unmatched opportunities to enhance various facets of electronic commerce, spanning from personalized recommendations to supply chain management (Faccia & Petratos, 2021; Hasan, 2021). Nevertheless, the interplay between open innovation, AIS, and AI in shaping electronic commerce performance is yet to be thoroughly explored.
Notwithstanding the increasing scholarly interest in open innovation and its prospective advantages for the performance of e-commerce, extant literature has concentrated on technological innovation, consumer experience, and prevailing market trends (Bogers et al., 2019; Chesbrough & Brunswicker, 2014). Previous investigations have examined the impact of open innovation in manufacturing industries and start-up enterprises (Randhawa et al., 2016), overlooking its potential to augment e-commerce performance through enhanced data management, immediate decision-making, and operational efficacy, as facilitated by AIS and AI. Furthermore, although the applications of AI within the e-commerce sector have been analyzed (Benbya et al., 2020), the interplay between AI and open innovation practices in conjunction with AIS remains inadequately explored. Consequently, this study aims to fill this void by examining the extent to which AIS and AI influence the relationship between open innovation and e-commerce performance, thereby contributing to a more nuanced understanding of the digital ecosystem’s significance in enhancing performance within e-commerce enterprises. Given the gaps in existing literature and the significance of the subject matter, this study aims to address the following research questions:
- •
What is the nature and extent of the influence of open innovation on e-commerce performance?
- •
How do AIS moderate the relationship between open innovation and e-commerce performance?
- •
How does AI moderate the relationship between open innovation and e-commerce performance?
The present study aims to examine the impact of the determinants of open innovation on the performance of electronic commerce, explicitly focusing on the moderating influences of AIS and AI. It also examines the mediating effects of digital competency and innovation capability on the relationships between management orientation and e-commerce performance. By clarifying the intricate connections among these variables, this investigation strives to offer valuable insights for professionals, policymakers, and scholars in the e-commerce field. The results of this research endeavor are intended to guide strategic decision-making processes and promote enduring competitive advantages for e-commerce firms in an increasingly dynamic and interconnected digital environment.
This research concentrates explicitly on electronic commerce, scrutinizing how open innovation, AIS, and AI affect the performance of organizations within this sector. While the implications of the findings may extend to other sectors, the study's scope is confined to e-commerce establishments. A key contribution of this study is combining the determinants of open innovation and examining their impact on e-commerce performance moderated by AIS and AI. It offers a novel perspective on how these technologies influence decision-making, data management, and operational efficiency in e-commerce, thus advancing the knowledge on the intersection of innovation, digitalization, and business performance. Understanding how open innovation impacts e-commerce performance while moderated by AIS and AI can give businesses valuable strategic perspectives. The outcomes of this study can aid in shaping decision-making processes within e-commerce entities, particularly concerning resource distribution, technological investments, and collaborative efforts. Insights into open innovation, AIS, and AI roles in e-commerce can also benefit policymakers and regulatory entities. Additionally, scholars, practitioners, and policymakers can recognize the potential consequences of the study's outcomes and comprehend the limitations under which the research has been conducted. Further, this study extends the resource-based view (RBV) theory and the theory of dynamic capabilities to the connection between management orientation and e-commerce performance moderated by AIS and AI.
Literature review and hypothesis developmentTheoretical backgroundInitially articulated by Radziwon and Chesbrough, open innovation (OI) underscores the significance of integrating external knowledge reservoirs to expedite internal innovation processes, augmenting competitive advantage in rapidly evolving sectors such as e-commerce (Radziwon and Chesbrough, 2024). Networked innovation theory substantiates this notion by elucidating how e-commerce enterprises depend on extensive collaborative networks for resource-sharing, swift adaptation, and resilience in the face of market fluctuations (Cohen & Levinthal, 1990). Moreover, absorptive capacity-a firm's capability to identify, assimilate, and utilize external knowledge—demonstrates its importance in adopting advanced technologies that enhance user experiences, thus maintaining a competitive advantage. Value co-creation theory accentuates the involvement of customers in the product development process, empowering firms to innovate adaptively based on real-time feedback, which reinforces the customer base (Prahalad & Ramaswamy, 2004). Furthermore, the ecosystem-based innovation framework highlights the significance of collaborative ecosystems, wherein e-commerce companies capitalize on relationships with suppliers, technology providers, and other stakeholders to address intricate challenges such as cybersecurity, thus accelerating the pace and efficacy of innovation (Adner, 2006).
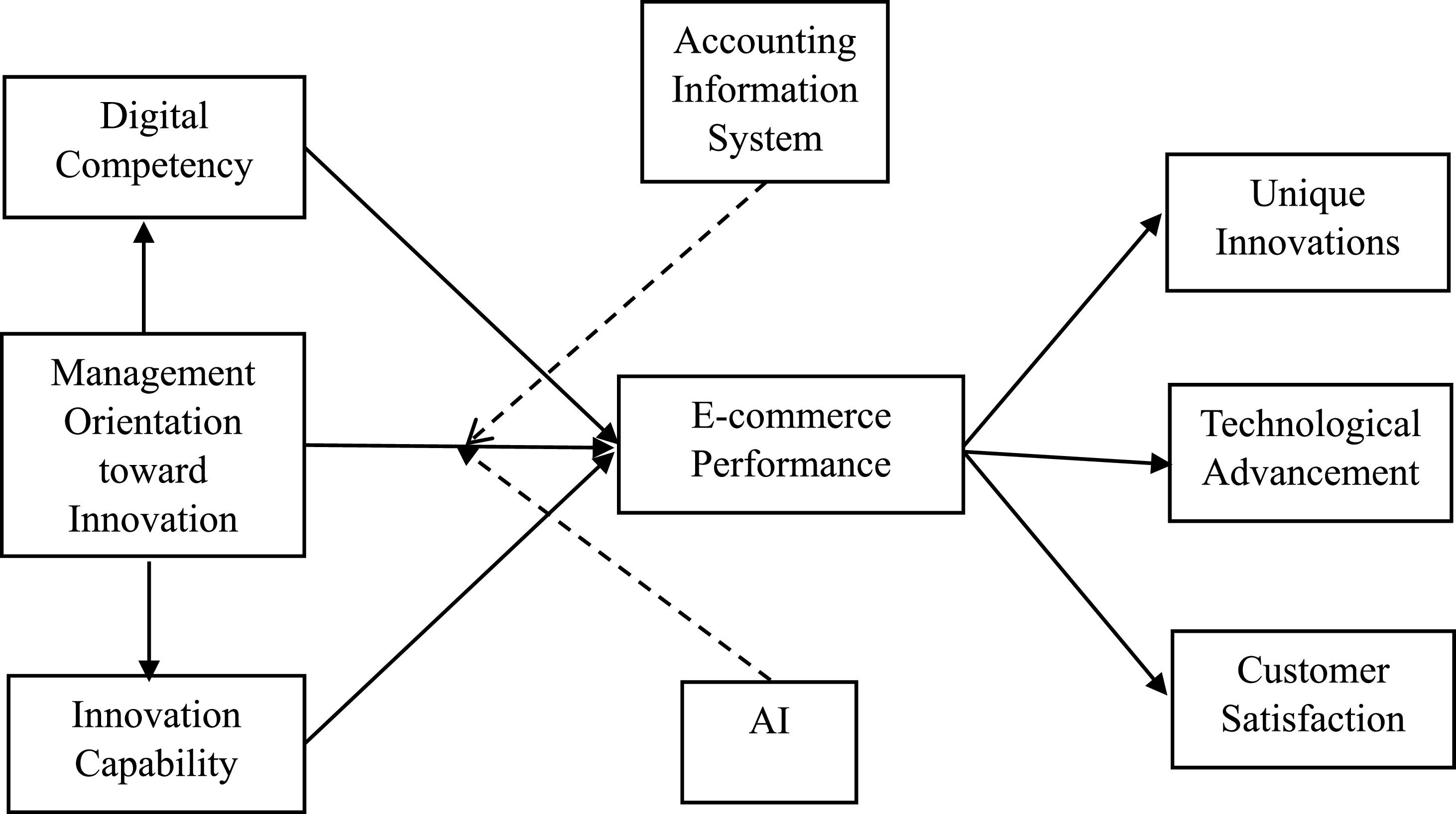
Conceptual frameworkThe comprehension of the impact of open innovation on e-commerce performance, moderated by AIS and AI, holds the potential to offer valuable strategic insights for enterprises. The conceptual framework depicted in Fig. 1 illustrates the relationship between open innovation and e-commerce performance, moderated by AIS and AI, showing the influence of open innovation determinants on e-commerce performance, along with the outcomes of e-commerce performance and the mediating role played by AIS and AI.
Determinants of open innovationThe determinants of open innovation encompass digital competency, management orientation, and innovation capability, with prior research revealing their positive effects on e-commerce performance. Drawing from earlier studies, hypotheses regarding these relationships are now formulated and discussed.
Management orientationE-commerce organizations characterized by leadership, strategic agility, and initiative-taking are likely to achieve superior performance outcomes such as sales growth, market share expansion, and customer satisfaction. By aligning organizational objectives with market opportunities and leveraging technology-driven capabilities, management can establish a conducive environment for e-commerce success (Al-Okaily et al., 2024a; Hasan, 2021). The RBV and the theory of dynamic capabilities offer theoretical underpinnings for understanding the connection between management orientation and e-commerce performance. According to the RBV, firms can attain sustainable competitive advantage by utilizing their distinctive resources and capabilities. Management orientation, as a crucial determinant of resource allocation and strategic emphasis, impacts the accumulation and utilization of these resources, thereby influencing organizational performance (Al-Kofahi et al., 2024; Yathiraju, 2022). In the context of this study, management orientation is a valuable intangible resource that influences a firm's ability to foster innovation capability and enhance digital competency. These unique managerial capabilities serve as critical resources that enable the firm to innovate and leverage digital technologies to improve e-commerce performance. By aligning leadership focus with innovation goals, the RBV supports the hypothesis that management orientation positively impacts innovation capability and digital competency as essential strategic resources for e-commerce success.
The theory of dynamic capabilities further elucidates the significance of managerial functions in orchestrating organizational responses to environmental fluctuations, thereby helping firms to adapt and thrive within challenging market landscapes. The theory of dynamic capabilities extends the RBV by accentuating a firm’s capacity to adapt, reconfigure, and rejuvenate its resources in alignment with evolving environmental conditions. Managerial focus on innovation can be conceptualized as a dynamic capability that empowers the organization to proficiently identify opportunities, capitalize on them through innovative methodologies, and restructure existing processes to enhance digital competency. Management's commitment to fostering innovation cultivates an organizational culture characterized by agility and adaptability, augmenting the firm’s capacity to deploy digital technologies and respond to market exigencies with greater efficacy. This capacity for dynamic adaptation and innovation, bolstered by robust leadership, resonates with the principles of the dynamic capabilities framework and fortifies the interrelationship among management orientation, innovation capability, and digital competency.
Various empirical studies have explored the correlation between management orientation and e-commerce performance, generating diverse results. While some studies suggest a positive link between initiative-taking management strategies and e-commerce achievements, others propose that this impact may vary based on contextual factors and industry dynamics. For instance, a study conducted by Al-Okaily et al. (2024) revealed that firms with a strategic e-commerce orientation, characterized by initiative-taking investments in technology infrastructure and market expansion endeavors, exhibited higher online sales and customer retention rates. Similarly, research by Chandra et al. (2022) emphasized the significance of transformational leadership in nurturing an innovative and agile culture within e-commerce enterprises, which can lead to enhanced product innovation and market responsive performance outcomes.
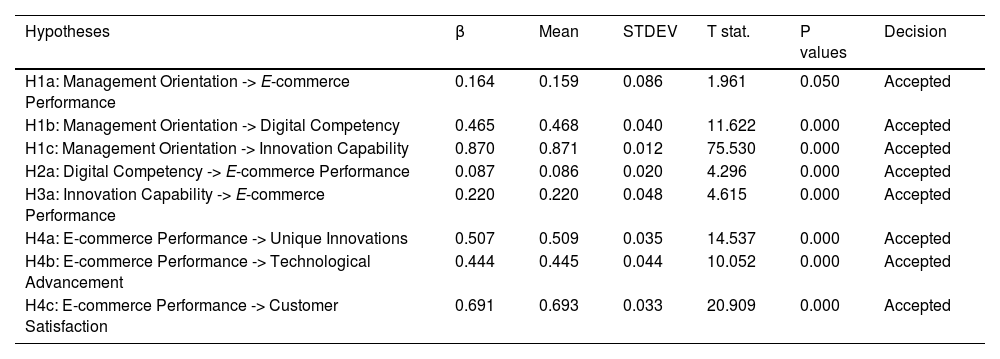
H1a: Management orientation toward innovation positively impacts e-commerce performance.
Organizations guided by initiative-taking and visionary leadership are more inclined to effectively cultivate and utilize digital competencies, thereby enabling them to leverage digital opportunities, mitigate threats, and attain sustainable competitive advantages in the digital realm. Empirical research exploring the nexus between management's mindset and digital proficiency consistently shows the beneficial influence of initiative-taking leadership and strategic foresight on digital preparedness and organizational effectiveness (Lutfi, 2023; Nguyen et al., 2022). A study conducted by Wijayanti et al. (2024) revealed that companies with visionary leadership and a strategic focus on digital transformation exhibited higher levels of digital competencies, evident in their adeptness at leveraging technology for innovation, engaging customers, and enhancing operational efficiency. Likewise, research by Perdana et al. (2022) and Pratt et al. (2023) established a robust connection between transformational leadership and digital agility, underscoring the significance of adaptive leadership methodologies in cultivating a climate of innovation and continual learning (Salah & Ayyash, 2024).
H1b: Management orientation toward innovation positively impacts digital competency.
Innovation capability is critical to organizational success, particularly in today’s dynamic and competitive business environment. It refers to an organization’s capacity to generate, implement, and sustain innovative ideas, products, or processes that create customer value and drive competitive advantage (Das, 2021). At the heart of innovation capability lies the strategic orientation and leadership provided by top management, which shapes the organizational culture, resource allocation, and decision-making processes necessary for fostering innovation (Thottoli & Ahmed, 2022; Wang et al., 2023). Empirical studies investigating the relationship between management orientation and innovation capability have consistently demonstrated a positive association between initiative-taking leadership and organizational innovation performance. For instance, research by Bhardwaj (2022) found that firms with visionary leadership and strategic orientation toward innovation exhibited higher levels of innovation capability, as evidenced by their ability to generate and implement novel ideas, products, or processes. Similarly, studies by Pizzi et al. (2021) and Fichman et al. (2014) identified transformational leadership as a key driver of innovation capability, emphasizing the importance of fostering a culture of creativity, experimentation, and risk-taking within the organization (Shawabkah et al., 2022).
H1c: Management orientation toward innovation positively impacts innovation capability.
Digital competencyThe digital proficiency of an organization is increasingly acknowledged as a pivotal determinant affecting e-commerce performance. Digital proficiency entails the competencies, instruments, and assets for utilizing digital technologies in business operations and customer interaction. According to Rahi et al. (2021), entities possessing elevated digital proficiencies are more effectively positioned to adjust to swiftly evolving digital landscapes, augmenting their operational efficacy and customer contentment (Salah & Ayyash, 2024). This capacity for adaptation is crucial for sustaining competitiveness within the ever-evolving e-commerce environment. Similarly, Awan and Asad (2021) discovered that organizations allocating resources toward enhancing digital skills and infrastructure observe significant advancements in their e-commerce performance indicators, encompassing sales expansion and customer loyalty. Moreover, a study by Li et al. (2023) corroborates this claim, suggesting that digital proficiency positively correlates with e-commerce performance by empowering enterprises to execute efficient digital marketing initiatives and refine user experiences (Salah & Ayyash, 2024). Consequently, these revelations emphasize the necessity of promoting digital proficiency as a strategic imperative for organizations aspiring to elevate their e-commerce performance.
H2a: Digital competency positively impacts e-commerce performance.
Research has shown that the initiative-taking stance of management toward digital technologies has a significant impact on e-commerce performance, wherein digital competency plays a pivotal role as a mediator. Soto-Acosta et al., 2018 conducted a study revealing that companies with a strategic focus on digital aspects witnessed enhanced e-commerce performance facilitated by establishing digital proficiencies. The scholars underscored the significance of management's dedication to digital transformation, which facilitates the acquisition and augmentation of digital expertise, consequently propelling e-commerce achievements. Another investigation by Mikalef et al. (2020) substantiated the mediating role of digital competency, illustrating that digital skills and knowledge in an enterprise bridge the gap between strategic digital focus and performance results. Entities that prioritize the enhancement of digital competency are better prepared to deploy efficient e-commerce strategies, thereby fostering enhanced business performance. The strategic inclination of management toward digitalization stimulates the development of digital competencies, enriching e-commerce performance. Subsequent research endeavors should delve deeper into this mediating impact across varied environments and sectors to enrich our comprehension of the interplay among management approaches, digital proficiencies, and e-commerce consequences.
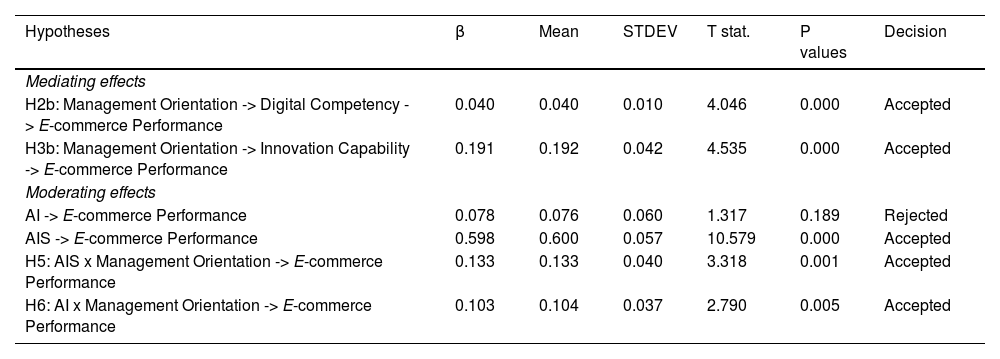
H2b: Digital competency positively mediates the relationship between management orientation toward innovation and e-commerce performance.
Innovation capabilityLawson and Samson (2001) opined that innovation capability constitutes a multifaceted construct encompassing the capacity to originate and execute novel concepts, the strategic harmonization of innovative endeavors, and the organizational ethos conducive to innovation. A study by Lee et al. (2011) unveiled that e-commerce enterprises with robust innovation capabilities exhibited superior performance metrics such as sales expansion, market share augmentation, and customer retention rates (Salah & Ayyash, 2024). The scholars posited that innovation capability empowers firms to present distinctive products and services, attracting a larger clientele and strengthening loyalty. Similarly, Ozuem et al. (2019) shed light on the significance of innovation in the digital marketing strategies of e-commerce entities. Their findings indicated that innovative digital marketing methodologies, underpinned by a robust innovation capability, significantly enhanced customer interaction and conversion metrics. Organizations fostering robust innovation capabilities are strategically positioned to thrive in the competitive e-commerce arena by delivering unique offerings, enriching customer experiences, and refining operational efficacy.
H3a: Innovation capability positively impacts e-commerce performance.
In the contemporary era, innovation capability's significance is increasingly acknowledged as a fundamental element contributing to the success of electronic commerce enterprises. Several empirical investigations substantiate the mediating function of innovation capability in the correlation between management orientation and e-3 commerce efficacy. Moreover, a scholarly inquiry by Prajogo and Sohal (2006) revealed that organizations with a robust innovation-centric managerial ethos highlighted elevated levels of innovation capabilities, subsequently resulting in superior electronic commerce performance. The scholars underscored that the strategic emphasis of management on innovation facilitates the evolution of novel products and procedures, thus amplifying competitive advantage. Correspondingly, research conducted by Calantone et al. (2002) illustrated that an innovation-focused managerial approach positively impacts a company's capacity to innovate, consequently augmenting its performance in electronic commerce. The scholars emphasized that innovation capability serves as a conduit between the strategic orientation of management and success in electronic commerce, empowering enterprises to address market requisites and technological progress adeptly (Almaqtari et al., 2024; Salah & Ayyash, 2024). The strategic inclination of management toward innovation propels the establishment of innovation capabilities, thereby enhancing electronic commerce performance. Subsequent scholarly endeavors should investigate this mediating impact across diverse sectors and contemplate the influence of emerging technologies on innovation capabilities (Nurhayati et al., 2023).
H3b: Innovation capability positively mediates the relationship between management orientation toward innovation and e-commerce performance.
E-commerce performanceIn the digital milieu, the performance of electronic commerce enterprises not only mirrors their current accomplishments but also acts as a catalyst for prospective innovation. Empirical investigations substantiate that commendable electronic commerce performance nurtures distinctive innovations (Lutfi et al., 2022; Mariani et al., 2023). A scholarly exploration by Zhu and Kraemer (2002) disclosed that entities exhibiting robust electronic commerce performance were more inclined to invest in pioneering technologies and processes, yielding unique product offerings. The scholars posited that success in electronic commerce furnishes both the financial means and the market feedback essential for propelling innovation. Another scholarly inquiry by Kim and Mauborgne (2005) highlighted that thriving electronic commerce enterprises frequently spearhead unique innovations by tailoring their offerings to meet customer demands (Zhang & Aumeboonsuke, 2023). Their investigation hinted that high-achieving electronic commerce enterprises leverage data analytics and customer insights to pinpoint innovation prospects, culminating in creating distinctive products and services. Satisfactory electronic commerce performance equips entities with resources, customer insights, and market feedback imperative for steering the evolution of unique innovations (Rana et al., 2022; Zhang & Aumeboonsuke, 2023).
H4a: E-commerce performance positively impacts unique innovations.
The exponential growth of electronic commerce has revolutionized the commercial terrain, instigating incessant technological progress. A research endeavor by Zhu and Kraemer (2002) ascertained that entities boasting robust electronic commerce performance were more predisposed to investing in novel technologies, thereby triggering noteworthy technological advancements (Adigwe et al., 2024). The scholars contended that success in electronic commerce furnishes financial resources and market feedback that are indispensable for propelling technological advancement. Another scholarly exploration by Bharadwaj et al. (2013) highlighted that high-performing electronic commerce enterprises stand at the vanguard of technological innovation, ceaselessly embracing innovative technologies to enrich their operations and customer interactions (Faccia & Petratos, 2021). Their research intimated that robust electronic commerce performance empowers entities to harness innovative technologies such as big data analytics, AI, and cloud computing. Commendable electronic commerce performance equips entities with resources, customer insights, and market feedback requisite for propelling technological innovation (Al-Okaily et al., 2024a; Hasan, 2021).
H4b: E-commerce performance positively impacts technological advancement.
A study by Collier and Bienstock (2006) revealed that high-performing e-commerce websites, distinguished by their ease of use, dependable service, and prompt delivery, notably amplified customer satisfaction. The authors posited that proficient e-commerce operations augment the overall customer experience, resulting in heightened satisfaction levels (Al-Okaily et al., 2024b). Similarly, a study by Liu et al. (2008) illustrated that different facet of e-commerce performance, such as website functionality, service reliability, and customer support, positively correlate with customer satisfaction. Their investigation suggested that customers express greater contentment when e-commerce platforms excel in delivering a smooth and dependable shopping experience (Chandra et al., 2022). Superior e-commerce platforms feature user-friendly interfaces and effortless navigation, enriching the customer experience and satisfaction. Achieving high e-commerce performance frequently involves the utilization of data analytics to customize shopping experiences, address individual customer preferences, and augment satisfaction. Enhancing various dimensions of customer experience, high e-commerce performance contributes to increased satisfaction (Al-Kofahi et al., 2024; Yathiraju, 2022).
H4c: E-commerce performance positively impacts customer satisfaction.
Accounting information system (AIS)AIS play a crucial role in contemporary business operations, particularly within e-commerce. AIS encompass systems that amass, retain, and process financial and accounting data to furnish meaningful information for decision-making purposes (Perdana et al., 2022; Wijayanti et al., 2024). Effective AIS bolster strategic management decisions by furnishing precise and timely financial information. Contingency theory posits that the efficacy of organizational practices hinges on the congruence between the organization's structure and its external milieu (Pratt et al., 2023). AIS can fortify this alignment by furnishing pertinent information that bolsters strategic decisions, thereby moderating the association between management orientation and e-commerce performance (Otley, 1980). In a study by Grande et al. (2011), it was discerned that the assimilation of AIS amplifies the favorable impact of strategic management practices on organizational performance. The researchers contended that AIS supply the financial insights that empower management to make well-informed strategic decisions. Another investigation by Nicolaou (2000) highlighted that enterprises equipped with robust AIS capabilities are better situated to harness their strategic orientation toward attaining superior e-commerce performance (Lutfi, 2023). The study revealed that effective AIS facilitate enhanced decision-making processes, culminating in an improved alignment between strategic objectives and operational consequences (Das, 2021; Nguyen et al., 2022). AIS deliver precise and timely financial information, empowering management to make informed strategic decisions that align with e-commerce goals. Efficient AIS rationalize financial procedures, diminish errors, and enhance overall operational efficiency, thereby buttressing improved e-commerce performance (Bhardwaj, 2022; Pizzi et al., 2021). AIS ensure financial data harmonize with strategic objectives, facilitating superior monitoring and evaluation of e-commerce strategies. AIS heighten the capacity to identify and alleviate financial risks, underpinning sustainable e-commerce operations. Effective AIS amplifies the influence of management's strategic direction on e-commerce success by furnishing indispensable financial insights and operational efficiencies (Fichman et al., 2014; Shawabkah et al., 2022).
H5: AIS moderate the relationship between management orientation toward innovation and e-commerce performance.
Artificial intelligence (AI)AI has emerged as a disruptive technology across various sectors, including electronic commerce. AI denotes the replication of human cognitive abilities in machinery that is programmed to cogitate, acquire knowledge, and execute tasks independently (Thottoli & Ahmed, 2022; Wang et al., 2023). Within the e-commerce domain, AI applications encompass recommendation systems, chatbots for customer service, management of inventory, dynamic pricing strategies, and tailored marketing initiatives (Russell & Norvig, 2020). The theory of contingency posits that the efficacy of organizational methodologies hinges on the harmonization between the structural framework of the entity and its external milieu. AI can fortify this harmony by furnishing insights and mechanization that bolster strategic determinations, thereby regulating the correlation between the managerial outlook and the performance of e-commerce (Otley, 1980). A research endeavor by Brynjolfsson et al. (2013) unearthed those enterprises integrating AI technologies observed significant enhancements in their e-commerce performance (Mensah et al., 2023). They contended that AI applications furnish refined data analysis, customer understandings, and operational efficiencies that magnify the repercussions of strategic administrative choices. Another scholarly work by Huang and Rust (2018) illustrated that AI-propelled personalization and tools for customer service notably elevate customer contentment and the performance of e-commerce. Their investigations suggested that AI empowers enterprises to synchronize their strategic stance with consumer requisites, culminating in enhanced performance outcomes. By automating mundane tasks, refining the management of supply chains, and augmenting inventory oversight, AI leads to heightened operational effectiveness. The real-time scrutiny of data provided by AI enables enterprises to adapt to alterations in the marketplace and consumer behavior promptly. Advanced data analytics and predictive modeling empower management to render more discerning and strategic judgments. The adept utilization of AI heightens the repercussions of strategic managerial decisions on the success of e-commerce by dispensing advanced data analytics, mechanization, and personalization for customers (Alles, 2018; Saad et al., 2022).
H6: AI moderates the relationship between management orientation toward innovation and e-commerce performance.
Research methodologyThis examination adopts a descriptive and cross-sectional framework to scrutinize the impact of open innovation on e-commerce performance and the mediating effects of AIS and AI. Data for this investigation were amassed through a survey mechanism. The questionnaire comprised 29 scale items refined and adjusted from established scales in prior inquiries. These scales were devised to gauge seven pivotal variables relevant to open innovation and e-commerce performance. The scale items are derived from the scholarly works of Chesbrough and Brunswicker (2014), Zhang and Aumeboonsuke (2023), Rana et al. (2023), Darmiono and Pratiwi (2024), and Kofahi et al. (2024).
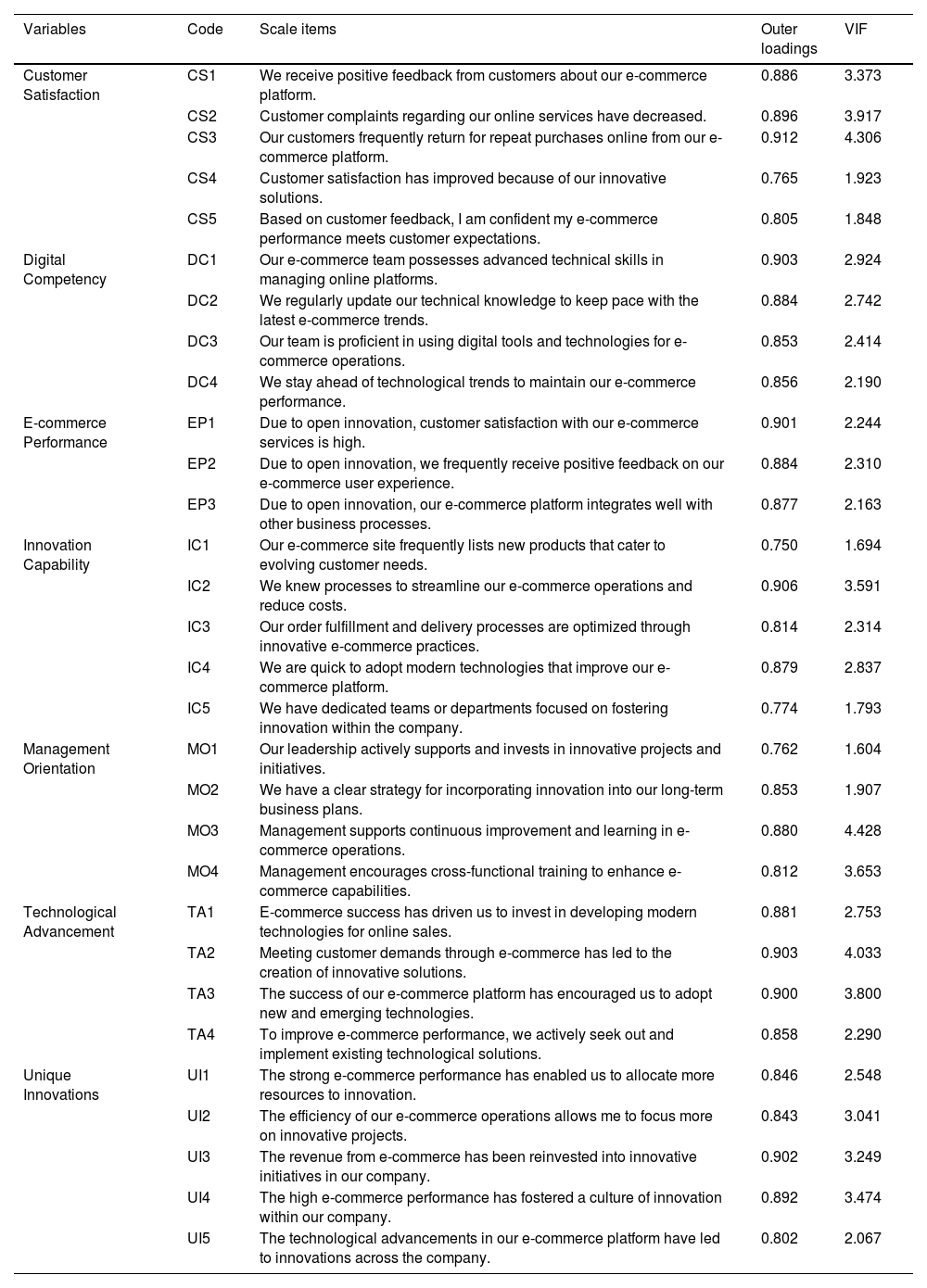
Chesbrough and Brunswicker (2014) investigated the implementation of open innovation within substantial enterprises. Additionally, Zhang and Aumeboonsuke (2023) explored the significance of digital capabilities in organizational innovation and AIS. Rana et al. (2023) analyzed the influence of artificial intelligence on operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Darmiono and Pratiwi (2024) examined the correlation between AIS and the performance of e-commerce businesses. Concurrently, Kofahi et al. (2024) investigated the relationship between AIS and consumer satisfaction in e-commerce. The adopted scale aligns closely with the contextual framework of this research; consequently, the appropriateness of this scale is significantly high. Further, the scale items are kept clear, concise, and unbiased, minimizing the potential for response bias. To further ascertain the reliability of this scale and minimize the impact of common method bias (CMB), we executed a pilot study involving a sample size of 56 participants and performed a reliability assessment. In the reliability evaluation, we determined that Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for all items linked to the variables exceeded the threshold value of 0.70 (Bland & Altman, 1997). Therefore, we retained all the adopted items. Nevertheless, we refined the wording of specific scale items, namely CS3, DS4, and IC1, which posed comprehension challenges for the participants. Furthermore, multicollinearity among scale items was checked using VIF (please see Table 1) to ascertain common method bias issues.
Measurement items assessment/ assessment of survey items.
The survey spanned from January 2023 to March 2024. A purposive sampling method was utilized to select respondents, encompassing 427 senior-level personnel from assorted e-commerce entities. Using purposive sampling allowed us to obtain in-depth insights from participants with relevant expertise, which ensures the data's relevance and practical applicability (Etikan et al., 2016). Senior-level executives were included in this study because they were the ultimate decision-makers and policymakers about open innovation. This ensured that the participants possessed substantial knowledge and expertise concerning the subjects under scrutiny. This strategy facilitated the acquisition of pertinent and enlightening data from individuals actively engaged in the decision-making processes within e-commerce activities (Hollenbeck, 2015). The survey was conducted via self-administration, and participants were engaged through the arrangement of prior appointments; consequently, the response rate achieved was 93%. A subset of participants was requested to submit a copy of the questionnaire and retrieve it later; in these instances, the response rate was limited to 57%. Follow-up communications were conducted exclusively with the highly engaged participants. To mitigate non-response bias, only completely filled questionnaires were accepted.
This study used a reflective scale to measure the variables. The main reason for the reflective scale is the nature of the variables and literature. Past empirical studies and theories also support this approach. Further, partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) is more suitable for reflective models, which provides more reliable results in complex relationships among variables. This statistical approach is advantageous for investigations forecasting variance in pivotal target variables. Because this research explores intricate relationships among latent variables and evaluates direct and indirect effects, PLS-SEM is deemed suitable as it maximizes explained variance.
Furthermore, PLS-SEM is more adept at accommodating complex models comprising multiple indicators and variables, even when distributional assumptions may not be satisfied. SmartPLS 4.0 was appropriate for the data analysis due to its intuitive interface and capability to manage complex models, including mediation pathways, while simultaneously addressing potential multicollinearity concerns. The software’s emphasis on predictive accuracy and explained variance rendered it the optimal instrument for fulfilling the research objectives.
Results and analysisDescriptive statisticsThe examination involved 427 senior-level staff members from various e-commerce enterprises, ensuring that the individuals possessed sufficient expertise and familiarity with the investigated subjects. The gender distribution indicates that 63% of the respondents are male, while 37% are female. Likewise, the participants' educational background suggests that 34% have obtained bachelor's degrees, 52% have acquired postgraduate qualifications, and 14% have finished secondary education. Concerning professional experience, 21% have less than three years of experience, 43% have between three and five years of experience, and 36% have more than five years of experience in their respective fields. Examining the participants' roles reveals that 27% are general managers, 36% are entrepreneurs, 15% are CEOs/MDs, and 22% are chief financial officers. These demographic data demonstrate that a substantial proportion of participants from various demographic backgrounds are incorporated in this research to mitigate demographic bias. Further, representations from different demographic backgrounds increase the accuracy of the research outcomes.
Outer model assessmentTable 1 illustrates the metrics and reliability associated with the outer model. It presents the scale items' standardized external loading and variance inflation factor (VIF). A total of 30 scale items are utilized for the evaluation of 7 latent variables. The external loading figures for all items surpass the critical value of 0.70, denoting the individual contributions of each item toward gauging the relevant variable (Sarstedt et al., 2017). Correspondingly, the VIF figures for all items are under 5, signifying the absence of multicollinearity among the measurement items (Hair et al., 2019). Consequently, the measurement instruments meet the standards for reliability and validity for further evaluation.
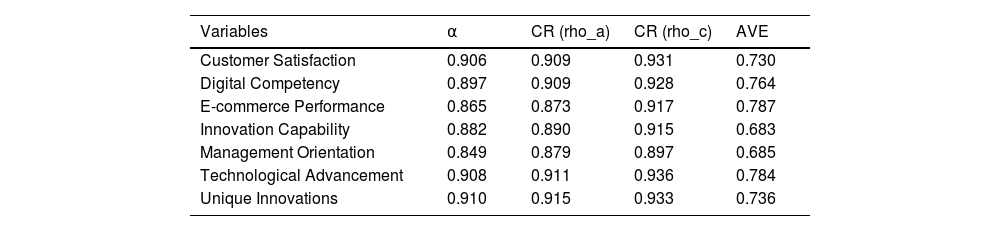
Inner model assessmentTable 2 delineates the internal consistency and validity of the constructs employed in this investigation. The Cronbach’s alpha values for all constructs exceed the conventional threshold of 0.70 (Bland & Altman, 1997), indicating the internal coherence of all constructs and affirming the reliability of the scale adopted for each construct measurement. Moreover, the composite reliability (CR) rho_a and CR rho_c values surpass 0.70, demonstrating construct consistency and validity (Saari et al., 2021; Hair et al., 2022). The average variance extracted (AVE) values surpass the 0.50 benchmark, confirming convergent validity for all constructs (Hair et al., 2022). Hence, the outcomes of Table 2 above fulfill all criteria for quality assessment.
Construct reliability and validity assessment.
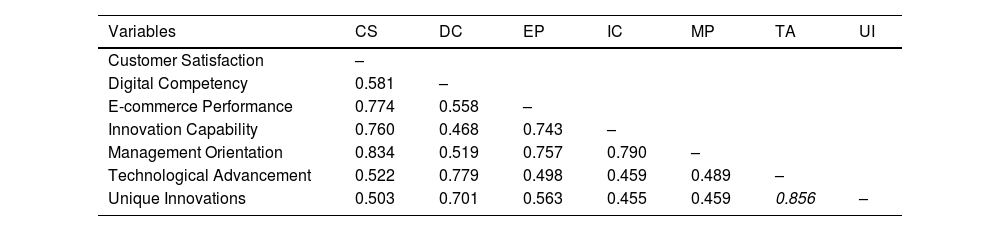
Table 3 displays the heterotrait-monotrait (HTMT) correlation ratio of all variables utilized in this research. The HTMT ratio values vary from 0.455 to 0.856. The accepted standard range for HTMT ratio values is below 0.85; nevertheless, one value surpasses 0.85 but remains below 0.90. It is admissible to consider a variable with an HTMT ratio of up to 0.90 (Henseler et al., 2015). Consequently, discriminant validity is established among the reflective constructs in this study (Hair et al., 2022).
Heterotrait-Monotrait ratio of correlations.
Note: CS = customer satisfaction, DC = digital competency, EP = e-commerce performance, IC = innovation capability, MO = management orientation, TA = technological advancement, UI = unique innovations.
The examination was conducted on the goodness-of-fit indices of the model, with a specific focus on utilizing the standardized root mean square residual (SRMR) for this particular purpose. The SRMR value, amounting to 0.079, falls below the designated threshold of 0.08. Similarly, the NFI value is 0.846, lower than the critical value of 0.90. These results indicate that the model has strong explanatory power, as previously proposed by Hu and Bentler (1998). The f-square values related to digital competency, innovation capability, and management orientation concerning e-commerce performance are 0.039, 0.068, and 0.022, respectively. Such f-square values suggest a minimal size effect on e-commerce performance. Moreover, the f-square values associated with e-commerce performance concerning customer satisfaction, technological advancement, and unique innovations are 0.914, 0.246, and 0.346, respectively. This indicates a significant effect of e-commerce performance on customer satisfaction, while technological advancement and unique innovations exhibit a moderate impact (Cohen, 1988).
Additionally, the r-square value for customer experience is 0.30, indicating a weak predictive capacity. The r-square values for customer satisfaction, e-commerce performance, technological advancement, and unique innovations are 0.476, 0.856, 0.195, and 0.255, highlighting that e-commerce performance has high predictive power. Customer satisfaction holds moderate predictive power. In contrast, technological advancement and unique innovations offer low predictive power (Hair et al., 2013).
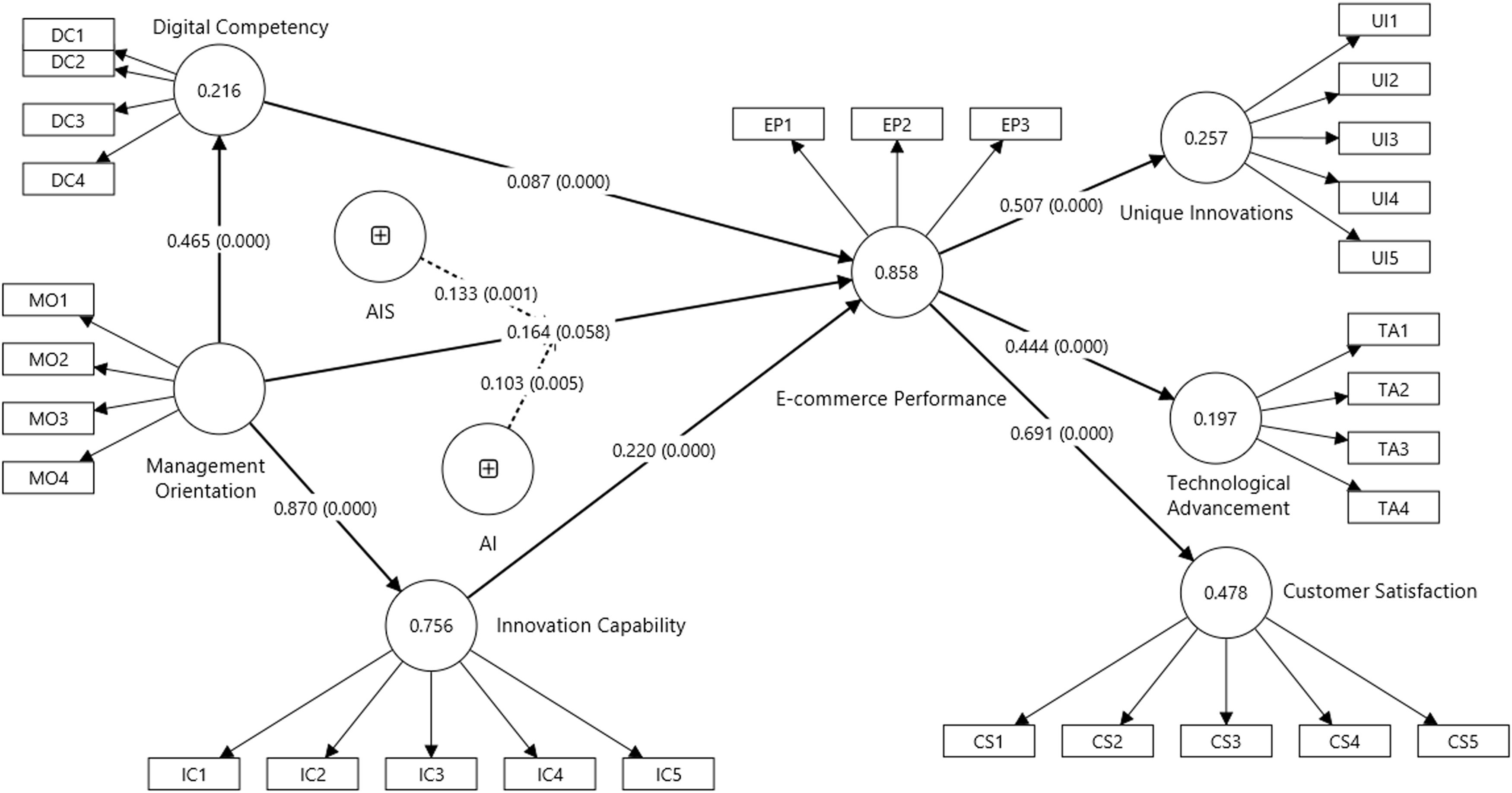
Structural model assessmentFigure 2 and Table 4 provide insights into the bootstrapping outcomes across 5,000 subsamples and the decisions concerning hypotheses. All hypotheses, including H1a, H1b, H1c, H2a, H3a, H4a, H4b, and H4c, are validated at a significance level of 0.05. Consequently, a positive and significant influence of management orientation on digital competency (β = 0.465; p < 0.05), innovation capability (β = 0.870; p < 0.05), and e-commerce performance (β = 0.164; p < 0.05) is observed. Likewise, a positive and significant impact of digital competency (β = 0.087; p < 0.05) and innovation capability (β = 0.220; p < 0.05) on e-commerce performance is identified. Correspondingly, a positive and significant correlation between e-commerce performance and unique innovations (β = 0.507; p < 0.05), technological advancement (β = 0.444; p < 0.05), and customer satisfaction (β = 0.691; p < 0.05) is noted.
Hypothesis testing (direct effect).
Table 5 presents the results and conclusions of the hypotheses testing for indirect effects. At a significance level of 0.05, H2b and H3b are deemed valid. This result suggests a significant and positive mediating impact of digital competency and innovation capability in the correlation between management orientation and e-commerce performance. Moreover, the significance of H1a, H1b, and H2a implies partial mediating effects of digital competency in the association between management orientation and e-commerce performance. Likewise, the significance of H1a, H1c, and H3a indicates partial mediating effects of innovation capability in the relationship between management orientation and e-commerce performance. The findings further reveal the positive and significant moderating effects proposed in hypotheses H5 and H6. This suggests that the moderating effects of AIS (β = 0.133; p < 0.05) and AI (β = 0.103; p < 0.05) are positive and significant in the nexus between management orientation and e-commerce performance. Additionally, the direct influence of AIS on e-commerce performance (β = 0.598; p < 0.05) is positive and significant. However, the direct effect of AI on e-commerce performance (β = 0.078; p < 0.05) is positive but nonsignificant on e-commerce performance.
Hypothesis testing (indirect effect).
The outcomes of this investigation unveil a significant and positive influence of management orientation on digital proficiency within the realm of open innovation and the performance of e-commerce. The orientation of management toward digital proficiency encompasses creating a culture that places importance on continual learning, adjustment, and the assimilation of novel technologies. Within the dynamic e-commerce environment characterized by rapid technological progress and ever-changing consumer expectations, the presence of a management team that prioritizes digital proficiency is of utmost importance (Darmiono & Pratiwi, 2024). This finding agrees with the findings of Chandra et al. (2022). This orientation ensures the organization's competitiveness by adopting and utilizing innovative digital tools and procedures.
Additionally, the research suggests that management dedicated to fostering an innovative culture significantly boosts the organization's innovation capacity (Almaqtari et al., 2024), supporting the findings of Pratt et al. (2023). It entails investing in research and development (R&D) and establishing an environment where employees are encouraged to experiment and offer innovative solutions. By nurturing a supportive environment for innovation, management can unleash the potential of its workforce, resulting in more efficient and inventive problem-solving. The positive influence of management orientation on innovation capacity implies that leadership is crucial in facilitating open innovation (Nurhayati et al., 2023). Open innovation hinges on the capability to combine internal and external concepts and assets. Management oriented toward innovation is more inclined to pursue collaborative ventures, form alliances, and utilize external knowledge. This strategy enhances the organization's innovativeness, developing new products, services, and procedures that enhance e-commerce performance. Similarly, the investigation suggests that management's commitment to enhancing e-commerce capabilities significantly enhances overall performance. This dedication involves investment in advanced e-commerce platforms, streamlining supply chain activities, improving customer service, and employing data analytics for well-informed decision-making. These endeavors enhance operational efficiencies and enrich the customer’s experience, increasing satisfaction and loyalty. Management orientation toward e-commerce performance encompasses establishing a distinct strategic vision, nurturing a culture conducive to innovation, and efficiently leveraging digital technologies. An initiative-taking and adaptable management approach is essential in the swiftly evolving e-commerce sector, where consumer behavior and market conditions can change rapidly. A strategic emphasis from management ensures that the organization remains flexible and receptive to new opportunities and challenges (Lutfi et al., 2022).
Further, digital competency and innovation capability significantly influence e-commerce performance through open innovation. In the dynamic and exceedingly competitive e-commerce environment, digital competency is vital in streamlining operations, enhancing user experience, and making data-informed decisions. Companies with solid digital competency can swiftly adopt and integrate modern technologies, enhancing efficiency, customer satisfaction, and improved e-commerce performance. The finding is like the findings of Lutfi et al. (2022) and Mariani et al. (2023), which imply that firms with robust innovation capabilities are better equipped to adapt to market dynamics and customer requirements, thereby upholding their competitive advantage (Mariani et al., 2023; Rana et al., 2022). This entails internal innovation endeavors and the efficient assimilation of external knowledge and technologies through open innovation methodologies. The positive influence of digital competency and innovation capability on e-commerce performance underscores the synergistic impact of these elements. Organizations excelling in digital competency can more efficiently deploy and expand innovative solutions, while a strong innovation capability guarantees that digital tools and technologies are utilized creatively and strategically. This collaboration leads to heightened agility, responsiveness, and market adaptability, which is essential for attaining superior e-commerce performance (Adigwe et al., 2024; Zhang & Aumeboonsuke, 2023).
Furthermore, the incorporation of open innovation further magnifies these effects. By leveraging external concepts and technologies, companies can supplement their internal competencies and capabilities, resulting in more resilient and adaptable e-commerce strategies. This comprehensive approach empowers e-commerce enterprises to keep abreast of technological progress and market tendencies and establish new benchmarks in customer service and operational excellence.
Moreover, the results demonstrate a considerable influence of e-commerce performance on unique innovations, technological advancement, and customer satisfaction within the context of open innovation. This finding is like the findings of Adigwe et al. (2024), Faccia and Petratos (2021), and Chandra et al. (2022), which imply that robust e-commerce performance frequently furnishes essential resources and drives organizations to pursue distinctive innovations (Al-Okaily et al., 2024a; Faccia & Petratos, 2021). Effective e-commerce activities increase profits, which can then be allocated toward R&D endeavors. This financial security enables organizations to investigate and execute fresh concepts that set them apart. Additionally, a flourishing e-commerce platform is a fertile environment for experimenting with and perfecting new products and services, thus cultivating a culture of continual innovation (Al-Okaily et al., 2024b; Chandra et al., 2022). The favorable effect of technological progress is also considerable. High-performing e-commerce enterprises invest in state-of-the-art technologies to elevate their operational effectiveness and customer journey. This encompasses adopting advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other digital mechanisms that streamline operations, customize customer engagements, and offer deeper insights into consumer behavior. Therefore, success in e-commerce serves as a driving force for broader technological advancements within the enterprise, thereby ensuring its leadership in the industry (Al-Kofahi et al., 2024; Yathiraju, 2022). Customer contentment represents another crucial domain positively impacted by robust e-commerce performance. Efficient and effective e-commerce operations result in improved service quality, quicker delivery times, and a personalized customer shopping journey. A strong e-commerce performance enables organizations to address customer demands and expectations better, leading to heightened customer satisfaction and allegiance. Pleased customers subsequently offer valuable feedback and perspectives that can further stimulate innovation and enhancements. Companies excelling in their e-commerce endeavors can uphold and expand their market presence and propel considerable progress in innovation and technology. This progress boosts customer satisfaction, establishing a cycle of enhancement and competitive edge. This interconnected relationship underscores the significance of open innovation as a strategic method for leveraging e-commerce performance toward broader organizational success (Perdana et al., 2022; Wijayanti et al., 2024).
Furthermore, the result shows a significant mediating role of digital competency and innovation capability in the correlation between management orientation and e-commerce performance. The finding is like the findings of Salah and Ayyash (2024) and Nurhayati et al. (2023), which imply that the orientation of management toward digital transformation plays a crucial role in shaping an organization's digital competency. A strategic emphasis by management on adopting digital tools and technologies ensures the establishment of resilient digital capabilities (Nguyen et al., 2022; Pratt et al., 2023). These proficiencies encompass the efficient utilization of digital platforms, data analytics, and digital marketing strategies, which are fundamental for optimizing e-commerce operations. Prioritizing digital competency by management establishes groundwork for enhanced e-commerce performance by ensuring the company's technological proficiency and adaptability to digital trends. Likewise, management orientation profoundly impacts the organization's innovation capability. By fostering an innovative environment, stimulating creativity, and investing in R&D, management enhances the firm's capacity to innovate new products, services, and processes (Bhardwaj, 2022; Das, 2021). This capacity is essential for sustaining competitiveness in the e-commerce industry, where continuous innovation is imperative to address evolving customer needs and market dynamics. A culture of innovation encouraged by strategic management results in a stream of distinctive offerings and enhancements, elevating e-commerce performance. The mediating roles of digital competency and innovation capability are vital in the association between management orientation and e-commerce performance. These mediators translate management's strategic vision and priorities into tangible operational and market achievements (Fichman et al., 2014; Shawabkah et al., 2022). Digital competency ensures the organization can effectively utilize technology to enrich e-commerce endeavors, while innovation capability guarantees a continuous evolution and enhancement of offerings. When management aligns with these mediators, the organization is better prepared to navigate the intricacies of the digital market. The incorporation of advanced digital tools and the establishment of an innovative culture contribute to improved customer experiences, operational efficiencies, and overall market competitiveness (Thottoli & Ahmed, 2022; Wang et al., 2023). As a result, the positive influence of management orientation on e-commerce performance is significantly reinforced by establishing digital competency and innovation capability.
The findings suggest that AIS and AI significantly moderate the correlation between management orientation and e-commerce performance. The inclination of management toward strategic innovation and technological assimilation plays a pivotal role in shaping the performance of e-commerce platforms (Alles, 2018; Saad et al., 2022). The finding is like the findings of Shawabkah et al. (2022), Wang et al. (2023), and Wijayanti et al. (2024), which highlight the importance of establishing clear objectives for digital transformation, cultivating an environment conducive to innovation, and promoting state-of-the-art technologies. Nevertheless, the direct impact of management orientation on e-commerce performance can be significantly bolstered through the moderating effects of AIS and AI. AIS play a critical function by furnishing precise, timely, and pertinent financial data that underpin decision-making processes. Prioritizing the integration of robust AIS by management ensures that the organization possesses the requisite tools to monitor financial performance, streamline resource allocation, and ensure adherence to regulatory frameworks (Aloulou et al., 2024). Efficient AIS heighten management's capacity to make well-informed strategic choices, optimize resource allocation, and pinpoint areas necessitating enhancement. Consequently, this positively influences e-commerce performance by enhancing operational efficiency, curbing costs, and augmenting profitability. AI further enhances the positive influence of management orientation on e-commerce performance. AI tools enable sophisticated data analytics, predictive modeling, and automation of routine tasks, thereby substantially augmenting operational capabilities. Embracing AI-oriented approaches empowers management to derive enhanced customer insights, devise personalized marketing tactics, and refine supply chain oversight. AI-driven innovations culminate in more precise demand projections, streamlined inventory supervision, and elevated customer satisfaction. These enhancements translate into heightened customer contentment, augmented sales figures, and reinforced market positioning (Mensah et al., 2023).
ImplicationsThe theoretical implications of this investigation yield significant insights into the confluence of open innovation, e-commerce performance, and the moderating effects of AIS and AI. Initially, this study augments the prevailing comprehension of open innovation by accentuating its pivotal function in augmenting e-commerce performance, particularly within the context of rapidly transforming digital markets. It enhances the theoretical underpinnings of innovation management by elucidating how open innovation methodologies promote knowledge dissemination, collaborative efforts, and co-creation. Subsequently, incorporating AIS and AI as moderating variables presents a novel lens through which to examine how digital instruments and frameworks amplify or impede the association between open innovation and e-commerce performance. Moreover, the research addresses gaps in the literature by integrating RBV theory and dynamic capabilities theory with information systems and AI domains.
The investigation emphasizes the crucial role of management orientation in augmenting digital competence, innovation capacity, and overall e-commerce performance. E-commerce managers must prioritize strategic leadership that cultivates a culture of continual learning and innovation. This entails establishing precise goals for digital transformation and promoting initiative-taking involvement with emerging technologies. Organizations must allocate resources to cultivate strong digital skills within their workforce through initiatives such as training programs, workshops, and the integration of sophisticated digital tools. Improving digital competencies can enhance operational efficiencies and superior customer experiences, improving e-commerce performance.
Enhanced e-commerce performance resulting from optimizations leads to heightened customer satisfaction. To meet and surpass customer expectations, e-commerce enterprises should refine their digital interfaces, streamline operations, and deliver personalized experiences. Contented customers tend to become loyal clients, contributing to sustained business expansion. E-commerce businesses can amplify their innovative potential and operational efficiencies through investments in technological progress. This encompasses adopting AI-driven technologies for customer insights, inventory control, and supply chain optimization. Firms should contemplate allocating resources to technological enhancements, digital training schemes, and innovation endeavors. This research furnishes valuable perspectives for e-commerce enterprises, managers, and policymakers regarding the significance of strategic management, digital and innovative proficiencies, and technological assimilation. By addressing these domains, e-commerce establishments can advance performance, stimulate innovation, and attain enduring competitive superiority in the swiftly evolving digital domain.
ConclusionThis empirical investigation of the dynamic e-commerce landscape delves into the impact of open innovation on e-commerce performance, moderated by AIS and AI. The study offers significant insights into the crucial roles of management orientation, digital competency, and innovation capability in propelling e-commerce success. The outcomes demonstrate that management orientation significantly and positively affects digital competency, innovation capability, and e-commerce performance, emphasizing the critical significance of strategic leadership and an initiative-taking management approach in fostering an environment conducive to technological and innovative progress. Effective management orientation sets the stage for enhancing an organization's capacity to utilize digital tools and nurture innovative practices, which is essential for excelling in the competitive e-commerce domain. Moreover, the research underscores the significant positive influence of digital competency and innovation capability on e-commerce performance. Companies with strong digital skills and a solid innovation capacity are better prepared to navigate the intricacies of the digital market, resulting in enhanced operational efficiencies, improved customer experiences, and sustained competitive advantage. The findings also suggest that superior e-commerce performance contributes to unique innovations, technological advancement, and customer satisfaction, enabling high-performing e-commerce entities to invest in R&D and promoting ongoing innovation and enhancement. This positive cycle distinguishes these companies from their rivals and guarantees elevated customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Additionally, the study identifies the positive and significant moderating effects of AIS and AI on the correlation between management orientation and e-commerce performance. Incorporating robust AIS and advanced AI technologies amplifies the efficacy of strategic management endeavors, facilitating more informed decision-making, streamlined resource allocation, and heightened predictive capabilities. This study highlights the diverse advantages of open innovation in the e-commerce sector, especially when complemented by strategic management orientation and sophisticated technological infrastructure. E-commerce enterprises in emerging markets should prioritize the development of digital competencies and innovation capabilities while harnessing AIS and AI to optimize their performance. These initiatives will stimulate unique innovations and technological progress and improve customer satisfaction, ensuring sustained growth and a competitive edge in the digital realm.
The study is confined to India; thus, the conclusions are specifically relevant to business operations in India or similar contexts. Businesses in a similar operational environment could apply the findings of this study to inform them about their business-related choices. Further, given that the investigation is predicated on the viewpoints of senior management, the resulting data may manifest a managerial or top-down perspective, potentially neglecting insights from operational levels or grassroots endeavors that could equally impact performance. Another limitation of this study is its sampling technique; thus, forthcoming research endeavors could consider employing a random sampling methodology. Future studies might adopt a longitudinal perspective to scrutinize the evolution of the impact of open innovation on e-commerce performance.
Furthermore, exploring the role of organizational culture in either facilitating or impeding the influence of management orientation on digital competency and innovation capability could provide deeper insights. Subsequent research could delve into the effects of emerging technologies like blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced data analytics on e-commerce performance. This study is conducted in a single country; therefore, including participants from multinationals could provide findings that are applicable to the global business environment.
CRediT authorship contribution statementAmar Johri: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. Raj Kumar Singh: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. Bijay Prasad Kushwaha: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. Hamad Alhumoudi: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. Abdullah Alakkas: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. Maysoon Khoja: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization.