Viral load is a very useful marker for monitoring patients infected with HBV and HCV. This work compares assays based on transcription-mediated amplification (TMA) and on real-time PCR (RT-PCR) to verify whether they can be interchangeable.
Material and methodsA bicentric study, in which 147 plasma samples from patients infected with HBV and 229 with HCV were analyzed, was carried out. TMA-based assays (Aptima® HBV Quant and Aptima® HCV Quant Dx, employing Panther system (Hologic®)) and RT-PCR (COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan® and COBAS® 6800) were used and the degree of concordance between them was calculated.
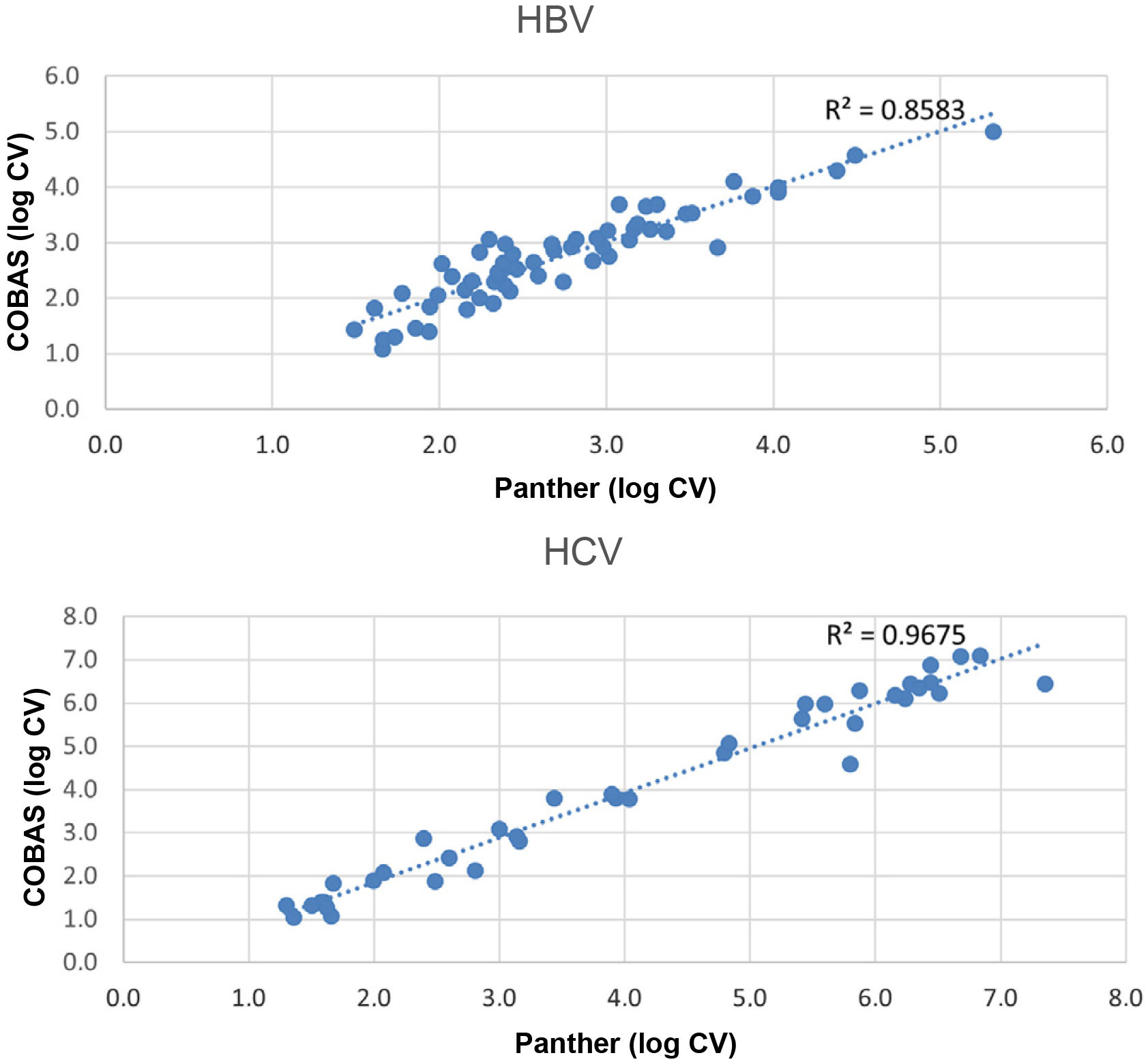
ResultsViral load was detected in both systems in 60 (40.82%) HBV samples (median log viral load: COBAS: 2.51IU/mL (IQR 2.20–3.17), Panther: 2.71IU/mL (IQR 2.21–3.22)) and in 39 (16.96%) HCV samples (median log viral load: COBAS: 3.93IU/mL (IQR 2.24–6.01), Panther: 3.80IU/mL (IQR 1.99–6.14)). The agreement between both systems was κ=0.943 for HBV and κ=0.925 for HCV. Comparison of viral load samples detected by both assays showed a hight correlation for HBV (R2=0.86) and for HCV (R2=0.97).
ConclusionsBoth TMA and RT-PCR based assays may be interchangeable for the management of patients infected with HBV and HCV.
La carga viral es un marcador muy útil para realizar el seguimiento de los pacientes infectados por VHB y VHC. Este trabajo compara ensayos basados en amplificación mediada por transcripción (TMA) y en PCR a tiempo real (RT-PCR) con el objetivo de comprobar si pueden ser intercambiables.
Material y métodosEstudio bicéntrico en el que se analizó la carga viral de 147 muestras de plasma de pacientes infectados por VHB y 229 por VHC, mediante ensayos basados en TMA (Aptima® HBV Quant y Aptima® HCV Quant Dx, que utilizan el sistema Panther (Hologic®)) y RT-PCR (COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan® y COBAS® 6800), calculando el grado de concordancia entre ellos.
ResultadosSe detectó carga viral en ambos equipos en 60 (40.82%) muestras de VHB (mediana del log de la carga viral: COBAS: 2.51UI/mL (IQR 2.20–3.17), Panther: 2.71UI/mL (IQR 2.21–3.22)) y en 39 (16.96%) muestras de VHC (mediana del log de la carga viral: COBAS: 3.93UI/mL (IQR 2.24–6.01), Panther: 3.80 UI/mL (IQR 1.99–6.14)). La concordancia entre ambos equipos fue de κ=0.943 para VHB y κ=0.925 para VHC. La comparación de las muestras con carga viral detectada mediante los dos ensayos mostró una correlación alta tanto para VHB (R2=0.86) como para VHC (R2=0.97).
ConclusionesLos ensayos basados tanto en TMA como en RT-PCR pueden ser intercambiables para el manejo de pacientes infectados con VHB y VHC.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections are major health concerns worldwide. Identifying people infected by these viruses and monitoring how their disease evolves is therefore extremely important.
According to the World Health Organization, the global prevalence of HBV infection is 3.5%, which varies depending on the region1. The World Health Organization also states that 820,000 deaths in 2019 were due to HBV-related disease2.
Nearly 300,000 people died from disease caused by HCV in 20193. Although the global prevalence of HCV infection is approximately 3%, in Spain it is estimated to be in the region of 2%–2.5%4. Chronic HCV hepatitis is the leading cause of liver cirrhosis and liver transplantation4.
Viral load is a direct indicator of virus replication and its quantification is essential for the management of patients infected with these viruses. It is a useful marker in the diagnosis of the infection, disease progression, monitoring of treatment and decision-making when it needs to be modified, and evaluation of the infectivity of infected patients5–8. Also, for HCV-infected patients, clinical practice guidelines recommend measuring viral load at the start of treatment and 12 weeks after completion to confirm the sustained viral response9. Sensitive, specific, safe, precise and reproducible tests that can be automated and have a wide dynamic range of quantification are therefore needed to enable reliable interpretation of viral load results5–8.
There are at present various different molecular assays performed through available automated commercial systems to quantify the genetic material of these viruses in plasma or serum. All these systems can detect and quantify HBV DNA and HCV RNA, making it possible to monitor and diagnose the infection.
The Aptima® HBV Quant and Aptima® HCV Quant Dx assays use the Panther system (Hologic®) based on transcription-mediated amplification (TMA). Meanwhile, the Roche COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan® and COBAS® 6800 systems (Roche Molecular Systems, Inc.) use real-time PCR-based amplification.
The analytical sensitivity (LoD≥95%) of the Aptima® assays is superior to that of the COBAS® assays for determining HBV and HCV: for HBV, these values are 5.58 IU/mL for the Aptima® assays and 20.0 IU/mL and 7.6 IU/mL for the Roche assays. For HCV, the analytical sensitivities are 3.9 IU/mL and 15.0 IU/mL and 12.0 IU/mL, respectively.
In this study, we compared the performance of two molecular assays with different designs (TMA vs real-time PCR) using the Aptima® Quant and Roche COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan® or Roche COBAS® 6800 systems for the determination of both HBV DNA and HCV RNA. Previous publications show results of comparative studies between quantitative tests of HBV and HCV individually10–14. The aim of this study was to question the belief that these determinations must always be carried out with the same technique and the same equipment, and to demonstrate that the assays studied are indeed interchangeable.
Material and methodsClinical samplesThis study included plasma samples obtained from patients infected with HBV and HCV received by the Microbiology and Parasitology Departments of two Spanish hospitals: the Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Santiago de Compostela [University Hospital Complex of Santiago de Compostela] in A Coruña, and the Hospital Universitario San Cecilio [San Cecilio University Hospital] in Granada.
A total of 147 samples for HBV DNA determination and 229 samples for HCV RNA determination were analysed. The molecular techniques compared were TMA and real-time PCR using the Aptima® Quant and Roche COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan® or Roche COBAS® 6800 systems. Each sample was tested in parallel in the Aptima and Roche assays (at Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Santiago de Compostela, the system assessed was Roche COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan®, while Hospital Universitario San Cecilio used the Roche COBAS® 6800) following the manufacturer's instructions, with no other selection criteria than the available sample volume. Complejo Hospitalario de Santiago de Compostela analysed 105 samples (71.43%) for HBV and 161 (70.31%) for HCV, and Hospital Universitario de San Cecilio analysed 42 (28.57%) for HBV and 68 (29.69%) for HCV.
Statistical method usedAgreement between qualitative results (negative, detected but below limit of quantitation, quantified and above upper limit of quantitation) was assessed by calculating kappa (κ) to measure the degree of agreement. For clinical samples quantified by both assays, the median viral load, interquartile range (IQR) and Pearson's correlation coefficient squared (R2) were determined.
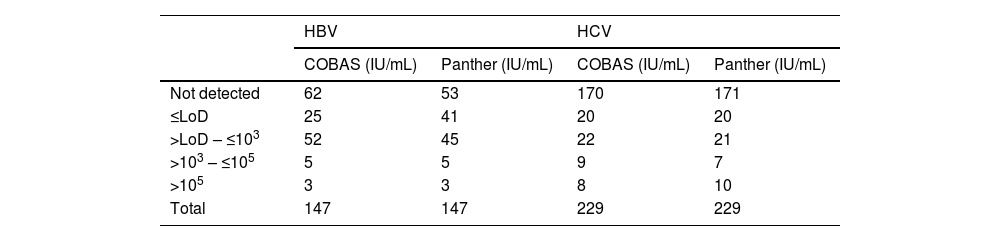
ResultsThe number of samples stratified by range of IU/mL according to their result are shown in Table 1.
Results using the COBAS and Panther systems for HBV and HCV.
| HBV | HCV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COBAS (IU/mL) | Panther (IU/mL) | COBAS (IU/mL) | Panther (IU/mL) | |
| Not detected | 62 | 53 | 170 | 171 |
| ≤LoD | 25 | 41 | 20 | 20 |
| >LoD – ≤103 | 52 | 45 | 22 | 21 |
| >103 – ≤105 | 5 | 5 | 9 | 7 |
| >105 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 10 |
| Total | 147 | 147 | 229 | 229 |
LoD: limit of detection for each technique.
Of the 147 HBV samples tested, 87 were negative or below the COBAS® limit of detection and in 60 (40.82%), HBV viral load was detected on both systems, with the median log viral load using COBAS® being 2.51 IU/mL (IQR 2.20–3.17), and using Panther, 2.71 IU/mL (IQR 2.21–3.22), with no significant differences between the two values (P=.9343). The agreement between the two systems for HBV measured by the kappa index was 0.943.
For the HCV determinations, of the 229 samples analysed, 190 were negative or below the COBAS limit of detection and 39 (16.96%) had a positive viral load in both systems, the median log viral load using COBAS® being 3.93 IU/mL (IQR 2.24–6.01), and using Panther, 3.80 IU/mL (IQR 1.99–6.14), with no significant differences between the two values (P=.9764). The agreement between the two systems for HCV measured by the kappa index was 0.925.
The comparison of the samples with viral load through the two assays (Fig. 1) showed a high correlation for both HBV (R2=0.86) and HCV (R2=0.97).
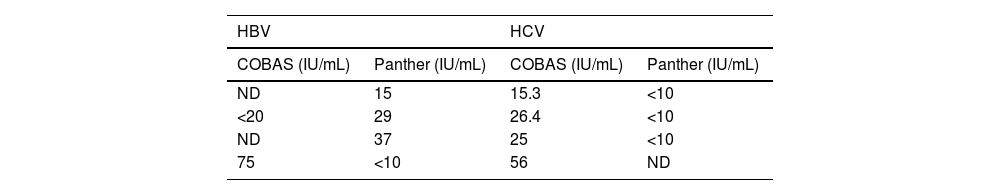
With regard to samples for which the results from the two systems were discordant, in those for the determination of HBV DNA, four (2.7%) were detected: three with a positive viral load using Panther, but below the limit of quantitation or not detectable (ND) using COBAS®; and one with a positive viral load using COBAS® and below the limit of quantitation using Panther (Table 2).
With regard to the samples for determination of HCV RNA, four discordant samples (1.7%) were detected with positive viral load in the COBAS® system and below the limit of quantitation or undetectable viral load in the Panther system (Table 2). No samples were detected with positive viral load for HCV in Panther and negative in COBAS®.
DiscussionIn view of how important it is to detect HBV and HCV infections, as well as to know the viral load of infected patients, techniques are needed that offer reliable results. In this study, we compared two molecular assays by performing automated methods for the determination of HBV and HCV viral load. The assays compared were TMA using the Aptima® Quant (Hologic®) system, and real-time PCR using the Roche COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan® and Roche COBAS® 6800 systems. Both techniques are suitable for the qualitative detection and quantification of HBV DNA and HCV RNA in clinical samples from infected patients. The equipment used is highly sensitive, accurately detects all HBV and HCV genotypes and is completely automated, with the advantages that this entails for the workflow in a laboratory. In addition, with the Aptima® system, samples can be continuously loaded and time-sensitive samples prioritised. Another advantage of this system is the possibility of performing more than one determination at the same time from the same sample, so speeding up the results.
The results obtained in this study show a high level of correlation between the systems when determining both HCV and HBV, showing no significant differences in clinically important situations. We are therefore able to state that these assays are interchangeable and are suitable for use in situations such as the characterisation of hepatitis or chronic infection, and in the monitoring of treatment in patients infected with HBV or in the diagnosis of HCV and the detection of sustained viral response in HCV-infected patients.
Previous studies have shown results similar to ours. For samples from patients infected with HBV, Schønning et al. and Schalasta et al. demonstrated that the Aptima® HBV Quant Assay and the COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan® HBV test v2.0 were highly correlated and comparable for quantification of the majority of these samples, using plasma samples in the first case and both plasma and serum in the second10,11. For samples from HCV-infected patients, the aforementioned authors obtained comparable results when comparing the above techniques, once again with Schønning et al. using plasma samples and Schalasta et al., serum and plasma12,13. Worlock et al. also achieved good correlations between the above assays and the Abbott RealTime HCV Assay14.
The main limitation of this study is the low number of positive samples analysed by both methods to study each viral load. Although the correlation we found was good, a study with a larger number of samples is recommended to give it greater statistical power.
In our experience, the Aptima® Quant TMA-based molecular assays (Hologic®) and the Roche COBAS® AmpliPrep/COBAS® TaqMan® and Roche COBAS® 6800 real-time PCR-based molecular assays are suitable methods for the molecular study of HBV DNA and HCV RNA in clinical samples from infected patients, and these systems are interchangeable for the management of patients infected with HBV and HCV.
FundingThis study received no specific funding from public, private or non-profit organisations.
Conflicts of interestNone.