Rilpivirine (RPV) is an antiretroviral drug characterized by good tolerability and a favorable liver safety profile. Recent research has shown that RPV ameliorates liver fibrosis in animal models of various chronic liver diseases. Our study aimed to analyze the effect of RPV on liver fibrosis by assessing changes in liver stiffness using transient elastography.
MethodsRetrospective cohort study of HIV-infected patients who were exposed and not exposed to RPV. The change in liver stiffness during the period between two transient elastography measurements was analyzed and compared for patients exposed and not exposed to RPV.
ResultsWe selected 118 RPV-exposed and 118 non-RPV-exposed HIV-infected patients. Median time between transient elastography (TE) measurements was 50 (29–68) months. A repeated-measures general linear model based on the main clinical characteristics revealed a significant decrease in the TE value of −0.8kPa in non-RPV-exposed patients (p=0.254) and −1.6kPa in the RPV-exposed group (p<0.001). The subgroup analysis showed a significant reduction in the TE value only patients cured of hepatitis C (RPV-exposed, −2.8kPa [p<0.001]; non-RPV-exposed, −1.1kPa [p=0.22]).
ConclusionRPV-based antiretroviral regimens significantly reduced liver stiffness, as measured by TE, in patients cured of chronic hepatitis C.
La rilpivirina (RPV) es un fármaco antirretroviral caracterizado por una buena tolerabilidad y un perfil de seguridad hepática favorable. Las últimas investigaciones han mostrado que la RPV mejora la fibrosis hepática en modelos animales de varias enfermedades hepáticas crónicas. Nuestro estudio tenía como objetivo analizar el efecto de la RPV en la fibrosis hepática mediante la evaluación de cambios en la rigidez hepática utilizando una elastografía transitoria.
MétodosEstudio de cohortes retrospectivo de pacientes infectados por VIH expuestos y no expuestos a RPV. Se analizó el cambio en la rigidez hepática durante el período entre dos mediciones mediante elastografía transitoria y se comparó entre pacientes expuestos y no expuestos a RPV.
ResultadosSeleccionamos a 118 pacientes infectados por VIH expuestos a RPV y 118 pacientes infectados por VIH no expuestos a RPV. La mediana del tiempo entre las mediciones mediante elastografía transitoria (ET) fue de 50 (29-68) meses. Un modelo lineal general de medidas repetidas basado en las principales características clínicas reveló una reducción significativa en el valor de ET, −0,8kPa en el grupo de pacientes no expuestos a RPV (p=0,254) y de −1,6kPa en el grupo de pacientes expuestos a RPV (p<0,001). El análisis de subgrupos mostró una reducción significativa en el valor de ET solo en pacientes curados de hepatitis C (expuestos a RPV, −2,8kPa [p<0,001]; no expuestos a RPV, −1,1kPa [p=0,22]).
ConclusiónLas pautas antirretrovirales basadas en RPV redujeron significativamente la rigidez hepática, evaluada por las mediciones de ET, en los pacientes que se habían curado de hepatitis C crónica.
Antiretroviral treatment (ART) and its association with hepatotoxicity resulting from coinfection by hepatotropic viruses and HIV have been widely studied.1 The first-generation nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) nevirapine and efavirenz (EFV) have traditionally been associated with liver toxicity. In contrast, the second-generation NNRTIs etravirine and rilpivirine (RPV) have a good hepatic safety profile and are recommended for HIV-infected patients with chronic liver diseases.2–4
Fibrosis is the most defining trait of chronic liver disease. It is characterized by activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) in response to sustained liver damage, which in turn leads to excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, disorganization of liver architecture, and loss of function.5 Given that the stage of fibrosis is a major factor in the prognosis of patients with liver disease, amelioration or reversion of fibrosis is a key objective of treatment. However, no specific drugs have been approved for this indication, despite recent advances in knowledge of the cell mechanisms and molecules involved in pathophysiology and the large number of drugs currently under study for various targets.
Basic research based on murine models of chronic liver disease showed RPV to have an antifibrotic and regenerative effect. One study showed the antisteatotic, anti-inflammatory, and antifibrotic roles of RPV in a nutritional model of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease based on a fat-rich diet, as well as in fibrosis models induced by various harmful agents. In all cases, the antifibrotic effect of RPV was due to selective induction of apoptosis in activated HSCs via activation of the transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1, as shown in vivo and in vitro in human cells.6 Thus, the present study aimed to analyze the effect of RPV on liver fibrosis by assessing changes in liver stiffness using transient elastography (TE) and to determine whether RPV-based regimens led to improvement.
MethodsStudy design and settingWe performed a retrospective study of a group of patients nested in a large cohort of 4009 HIV-infected patients undergoing regular follow-up at a tertiary hospital. The current analysis of our cohort was performed during the first 6 months of 2019. Since tenofovir alafenamide-containing regimens were not approved at our center until late 2018, patients taking this agent were not included in the study.
PatientsWe selected patients with at least 2 TE measurements, the first of which had to be >5.2kPa, in order to confirm that they had liver fibrosis. This cut-off value was validated in a systematic review with meta-analyses as the best for identifying subjects with fibrosis (any grade).7 RPV-exposed patients (REP) had to have initiated treatment with RPV between the 2 TE measurements. Non-RPV-exposed patients (NREP) had not been exposed to RPV before or during the period between the 2 measurements. The time between the 2 TE measurements had to be at least 24 months. The exclusion criteria were history of alcohol abuse, regular consumption of drugs of abuse, drug-induced acute hepatitis, and HBV or HCV infection after the first TE measurement. Cases and controls were matched using the statistical program SPSS. NREP were matched 1:1 with REP by age (±3 years), time between TE measurements (±6 months), time since diagnosis of HIV infection (±3 years), and coinfection by HCV. The analysis included 118 REP and 118 NREP, thus enabling us to detect, with a confidence level of 95% and a power of 85%, a difference in the final TE over baseline >1.3kPa, assuming a standard deviation of the difference of 4.7kPa.
This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee for Clinical Research of La Paz University Hospital (C.E.I.C.) as a research project entitled: “Retrospective longitudinal descriptive registry of naive patients included in the cohort of patients with HIV infection at Hospital La Paz (Madrid)”. HIV-La Paz cohort. HULP code: PI-890.
Variable and measurementsFor each patient, we recorded demographic data, anthropometric data (body mass index [BMI]), data on HBV and HCV coinfection, antiretroviral treatments by family at baseline and at the end of the study, and the changes observed during the period between TE measurements. We analyzed patients who had been exposed to EFV and raltegravir (RAL), taking into account, respectively, the poor and favorable hepatic safety profile of these agents. We also recorded HCV status, sustained virological response (SVR), time since SVR, and time from SVR to TE measurement. Liver steatosis was diagnosed using an easily accessible, non-invasive serum biomarker, namely, the triglyceride and glucose index (TyG), calculated as Ln [triglycerides*glucose/2].8 The HIV-related variables were as follows: time since diagnosis of HIV, exposure to RPV, duration of exposure to RPV, and time from baseline TE to initiation of RPV. The TE measurement was expressed in kilopascals (kPa) as the median of 10 successful acquisitions.
TE was performed under fasting conditions using a FibroScan device (Probe M, FS402; Echosens, France). An experienced operator performed TE according to the manufacturer's protocol. An unreliable measurement was defined as an IQR/TE of 30%. Although the FibroScan device used was able to determine the CAP value, some patients underwent their first liver stiffness assessment with an older device that was not able to assess CAP. In order to avoid the bias arising from use of different diagnostic methods, we decided not to base diagnosis of steatosis on CAP values.
Statistical analysisCategorical variables were expressed as percentages; continuous variables were expressed as median and interquartile range (IQR). Continuous variables were analyzed using the t test or Mann–Whitney test, depending on the normality of the distribution (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test with a Lilliefors correction).
Changes in TE were assessed using a general linear model, which provides a repeated-measures analysis of variance, contrasts the effects of intrapatient and interpatient factors, and includes the covariate effect. Baseline and final TE were assessed based on intrapatient factors, exposure to RPV and HCV coinfection as interpatient factors and the nadir CD4 value, length of HIV infection, time between TE measurements, and final BMI as covariates.
Erroneous and non-recoverable data were not imputed and are considered lost. The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 25.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Statistical significance was set at p<0.05 (2-sided).
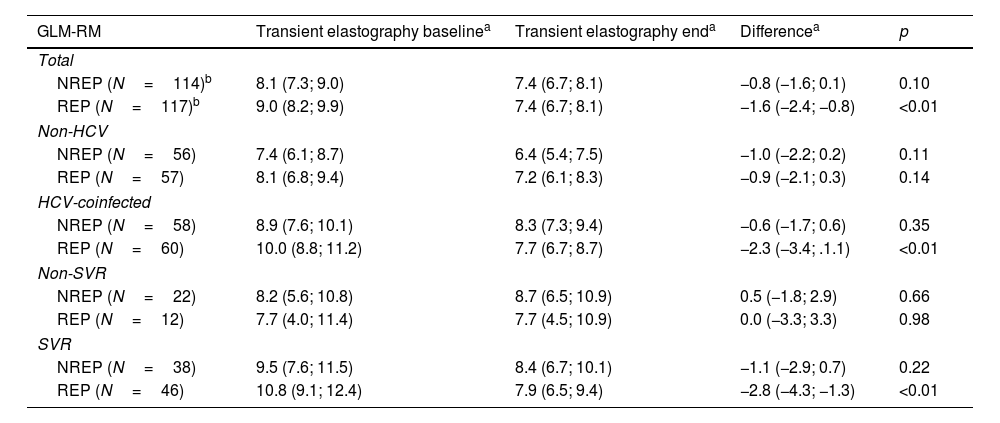
ResultsA total of 822 patients fulfilled the inclusion/exclusion criteria (195 REP, 627 NREP); of these, 451 were HCV-positive (diagnosed before the first TE measurement), and 371 were not. After the matching procedure, a total of 236 patients were included in the study: 118 REP and 118 NREP. In the REP group, most patients (more than 70%) had taken RPV for more than 1 year, and the median time between TE measurements was 51 (29–68) months (at least 24 months between TE measurements), with no differences between the groups. There were no significant differences between the groups for male sex (REP 86%, NREP 84% [p=0.6]), intravenous drug use as the route of transmission (REP 40%, NREP 47% [p=0.3]), CDC stage C (REP 23%, NREP 33% [p=0.08]), undetectable HIV viral load (REP 88%, NREP 81% [p=0.1]), HBV coinfection (REP 9%, NREP 12% [p=0.5]), anti-HBV medication (REP 100%, NREP 100% [p=0.9]), HCV coinfection (REP 52%, NREP 52% [p=1]), percentage of patients treated (REP 80%, NREP 71% [p=0.3]), or percentage cured of HCV infection (REP 91%, NREP 98% [p=0.2]). Table 1 shows quantitative variables for both groups at baseline (i.e., first TE measurement) and at the end of the study (i.e., second TE measurement). Only the median nadir CD4 count was significantly lower in REP, probably due to the recommendations not to use RPV-based regimens as initial treatment for patients with a CD4 cell count below 200/mm3. Therefore, median nadir CD4 was included as a covariate in the adjusted regression model.
Baseline and end-of-study characteristics of patients exposed and not exposed to rilpivirine.
| NREPn=118 | REPn=118 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | |||
| Agea | 45.6 (40.5; 49.5) | 47.2 (41.8; 51.8) | 0.07 |
| Time with HIV infectiona | 197.4 (65.0; 253.9) | 193.0 (47.7; 261.7) | 0.86 |
| Nadir CD4a | 173.5 (45.0; 243.0) | 208.0 (130.0; 302.4) | <0.01 |
| ART-based regimenb | <0.001 | ||
| NNRTI | 28 (23.7) | 55 (46.6) | |
| PIs | 58 (49.2) | 32 (27.1) | |
| II | 13 (11) | 25 (21.2) | |
| Other | 19 (16.1) | 6 (5.1) | |
| TE (kPa)a | 6.8 (6.0; 8.5) | 6.9 (5.9; 9.0) | 0.91 |
| TE IQR (kPa)a | 1.3 (0.9; 1.9) | 1.3 (0.9; 2.3) | 0.88 |
| TE IQR/median (%)a | 18.2 (12.5; 25.7) | 18.3 (13.1; 25.8) | 0.80 |
| TE (kPa) <7.9c | 76 (64.4) | 78 (66.1) | |
| TE (kPa) 7.9–9.5c | 19 (16.1) | 16 (13.6) | 0.86 |
| TE (kPa) ≥9.6c | 23 (19.5) | 24 (20.3) | |
| AST (IU/L)a | 32.0 (26.0; 49.0) | 33.0 (26.0; 48.0) | 0.99 |
| ALT (IU/L)a | 36.0 (27.0; 59.0) | 46.0 (28.0; 64.0) | 0.11 |
| GGT (IU/L)a | 49.5 (30.0; 92.0) | 49.0 (30.0; 99.0) | 0.98 |
| BMIa | 24.6 (22.0; 28.0) | 25.4 (22.3; 27.5) | 0.63 |
| Liver steatosis by TyG (>8.38)c | 82 (71.3) | 89 (76.1) | 0.46 |
| Liver steatosis by TyGa | 8.7 (8.3–9.2) | 8.8 (8.4–9.2) | 0.35 |
| Months from baseline TE to starting RPVa | – | 12.3 (7.1; 25.5) | – |
| End of study | |||
| TE (kPa)a | 6.2 (5.1; 8.1) | 6.6 (4.9; 7.8) | 0.86 |
| TE IQR (kPa)a | 1 (0.7; 1.5) | 1.1 (0.7; 1.5) | 0.86 |
| TE IQR/median (%)a | 17.2 (11.5; 22.7) | 17.9 (10.3; 22.8) | 0.63 |
| TE (kPa) <7.9c | 83 (70.3) | 89 (75.4) | |
| TE (kPa) 7.9–9.5c | 17 (14.4) | 13 (11.0) | 0.65 |
| TE (kPa) ≥9.6c | 18 (15.3) | 16 (13.6) | |
| AST (IU/L)a | 26.0 (23.0; 34.0) | 28.0 (22.0; 37.0) | 0.56 |
| ALT (IU/L)a | 27.0 (20.0; 36.0) | 32.0 (22.0; 52.0) | 0.02 |
| GGT (IU/L)a | 36.0 (24.0; 66.0) | 35.0 (23.0; 55.0) | 0.62 |
| BMIa | 25.4 (22.4; 28.0) | 25.5 (22.7; 28.7) | 0.49 |
| Liver steatosis by TyG (>8.38)c | 89 (76.1) | 82 (70.1) | 0.38 |
| Liver steatosis by TyGa | 8.8 (8.4–9.1) | 8.6 (8.3–9.1) | 0.15 |
| Months of RPVa | – | 28.0 (8.6; 44.4) | – |
| SVRc | 39 (64.0) | 48 (78.7) | 0.11 |
| Months from SVR to TEa | 19.6 (6.4; 50.3) | 22.1 (8.6; 36.5) | 0.95 |
| Months between TEa | 50.1 (28.7; 68.6) | 50.8 (29.1; 67.1) | 0.96 |
NREP: non-rilpivirine-exposed patients; REP: rilpivirine-exposed patients.
We observed a significant reduction in the TE value of −0.8kPa in NREP (p=0.254) and −1.6kPa in REP (p<0.001); this was adjusted for years since diagnosis of HIV infection, time between TE measurements, nadir CD4, and baseline and end-of-study alanine aminotransferase and BMI. Analysis of changes in TE between patients who were and were not coinfected by HCV revealed a significant difference for HCV-coinfected patients only in REP (−2.3kPa; p<0.001). Analysis of the changes in TE between patients depending on cure of HCV infection revealed a significant difference in cured patients (REP, −2.8kPa [p<0.001]; NREP −1.1kPa [p=0.22]). We did not observe significant changes in the remaining subgroups, the subgroups not coinfected with HCV, or in the subgroups of patients not cured of HCV coinfection (Table 2). There was no linear relationship between the time of exposure to RPV and the change in TE values. We analyzed the percentage change in TE as a function of different durations of exposure to RPV (
Changes in transient elastography measurement between baseline and end of study.
| GLM-RM | Transient elastography baselinea | Transient elastography enda | Differencea | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | ||||
| NREP (N=114)b | 8.1 (7.3; 9.0) | 7.4 (6.7; 8.1) | −0.8 (−1.6; 0.1) | 0.10 |
| REP (N=117)b | 9.0 (8.2; 9.9) | 7.4 (6.7; 8.1) | −1.6 (−2.4; −0.8) | <0.01 |
| Non-HCV | ||||
| NREP (N=56) | 7.4 (6.1; 8.7) | 6.4 (5.4; 7.5) | −1.0 (−2.2; 0.2) | 0.11 |
| REP (N=57) | 8.1 (6.8; 9.4) | 7.2 (6.1; 8.3) | −0.9 (−2.1; 0.3) | 0.14 |
| HCV-coinfected | ||||
| NREP (N=58) | 8.9 (7.6; 10.1) | 8.3 (7.3; 9.4) | −0.6 (−1.7; 0.6) | 0.35 |
| REP (N=60) | 10.0 (8.8; 11.2) | 7.7 (6.7; 8.7) | −2.3 (−3.4; .1.1) | <0.01 |
| Non-SVR | ||||
| NREP (N=22) | 8.2 (5.6; 10.8) | 8.7 (6.5; 10.9) | 0.5 (−1.8; 2.9) | 0.66 |
| REP (N=12) | 7.7 (4.0; 11.4) | 7.7 (4.5; 10.9) | 0.0 (−3.3; 3.3) | 0.98 |
| SVR | ||||
| NREP (N=38) | 9.5 (7.6; 11.5) | 8.4 (6.7; 10.1) | −1.1 (−2.9; 0.7) | 0.22 |
| REP (N=46) | 10.8 (9.1; 12.4) | 7.9 (6.5; 9.4) | −2.8 (−4.3; −1.3) | <0.01 |
NREP: non-rilpivirine-exposed patients; REP: rilpivirine-exposed patients.
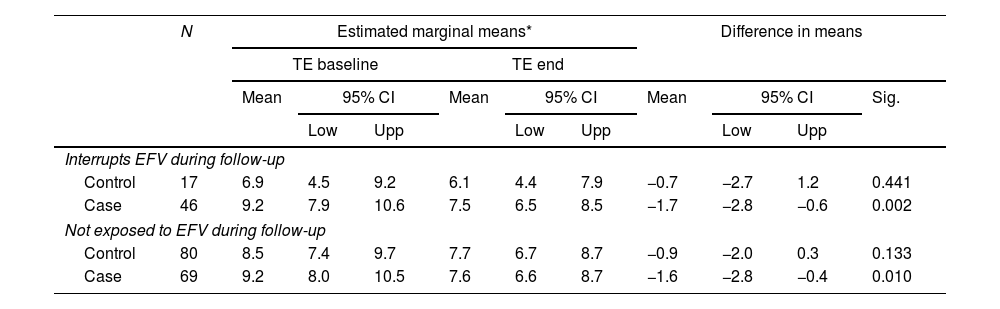
Analysis of the treatment patients were receiving at the time of the first TE scan by family showed that they were not similar (Table 1). Exposure to EFV (owing to its poor liver safety profile) and RAL (owing to its favorable liver safety profile) were analyzed specifically. We found no differences for exposure to RAL. The percentage of patients exposed/not exposed to EFV during follow-up did not differ significantly between cases and controls (p=0.135). The percentage of patients who interrupted EFV during follow-up was greater in the REP group (39% vs 14% p<0.001). (Table 3) In order to analyze whether discontinuation of EFV was more responsible for the reduced TE value than RPV, we ran the same GLM model on the subgroups of patients who interrupted EFV during follow-up and patients not exposed to EFV during follow-up (this was not possible in the subgroup of patients who did not interrupt EFV, because all patients in the REP group interrupted EFV). The results show that in both subgroups, the reduction in the TE value was significantly greater in REP (−1.6 [95% CI −2.4 to −0.8]; p<0.001) than in NREP (−0.8 [95% CI −1.6 to 0.2]; p=0.1). The magnitude of this change was similar to that observed in the overall sample (Table 2).
Analysis of EFV exposure on transient elastography changes.
| N | Estimated marginal means* | Difference in means | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TE baseline | TE end | ||||||||||
| Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | Mean | 95% CI | Sig. | |||||
| Low | Upp | Low | Upp | Low | Upp | ||||||
| Interrupts EFV during follow-up | |||||||||||
| Control | 17 | 6.9 | 4.5 | 9.2 | 6.1 | 4.4 | 7.9 | −0.7 | −2.7 | 1.2 | 0.441 |
| Case | 46 | 9.2 | 7.9 | 10.6 | 7.5 | 6.5 | 8.5 | −1.7 | −2.8 | −0.6 | 0.002 |
| Not exposed to EFV during follow-up | |||||||||||
| Control | 80 | 8.5 | 7.4 | 9.7 | 7.7 | 6.7 | 8.7 | −0.9 | −2.0 | 0.3 | 0.133 |
| Case | 69 | 9.2 | 8.0 | 10.5 | 7.6 | 6.6 | 8.7 | −1.6 | −2.8 | −0.4 | 0.010 |
In order to better understand the reduction in TE measurement among NREP and non-HCV-infected patients, we analyzed the proportion of EFV interruptions among NREP and their HCV status; no significant difference were found (HCV with no EFV interruptions, 47.6% vs HCV with EFV interruptions, 46.7%; p=1). No differences were found for changes in ART by family between baseline and the end of the study in the non-HCV-infected subgroup compared with the other groups. (Supplementary Material).
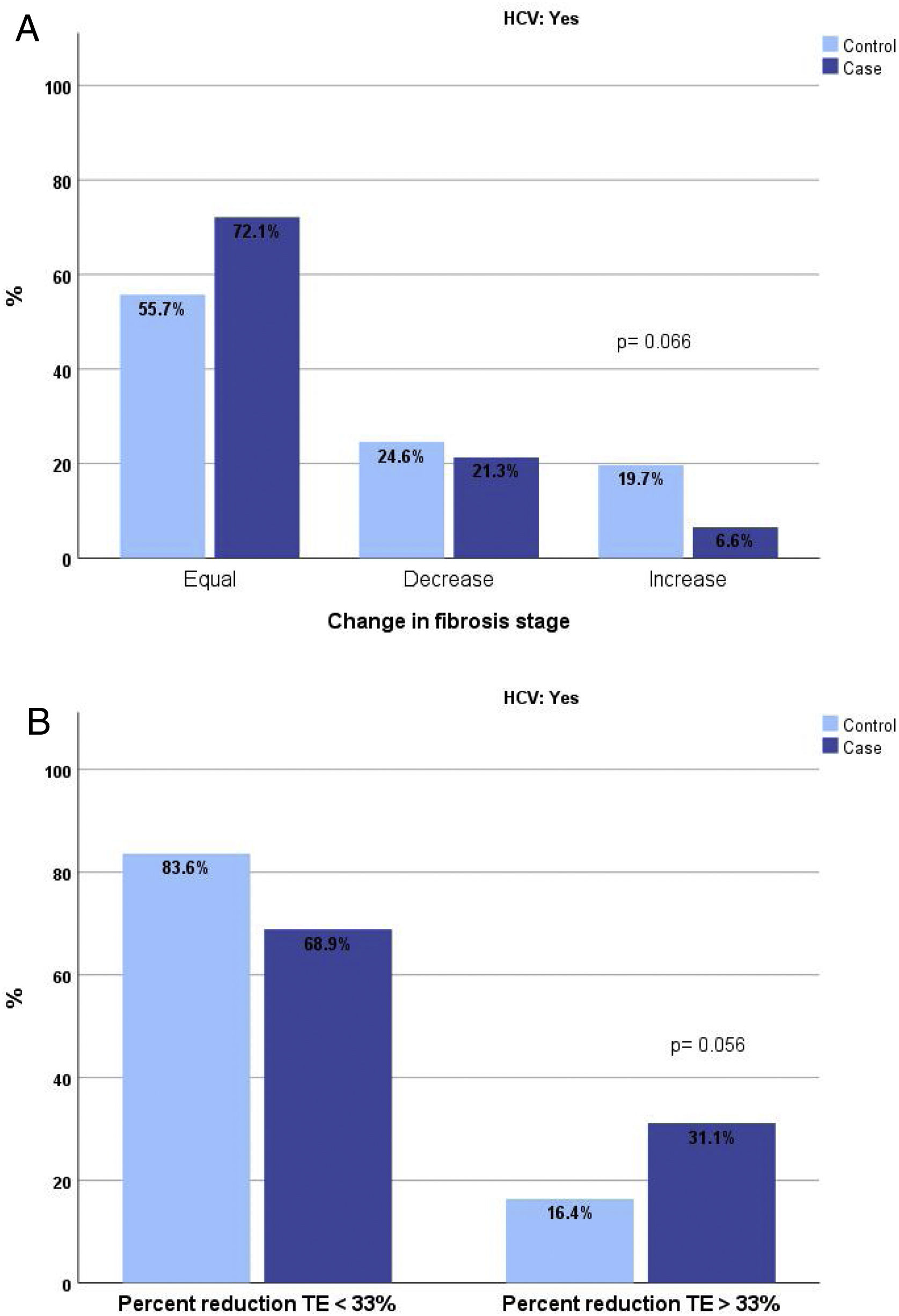
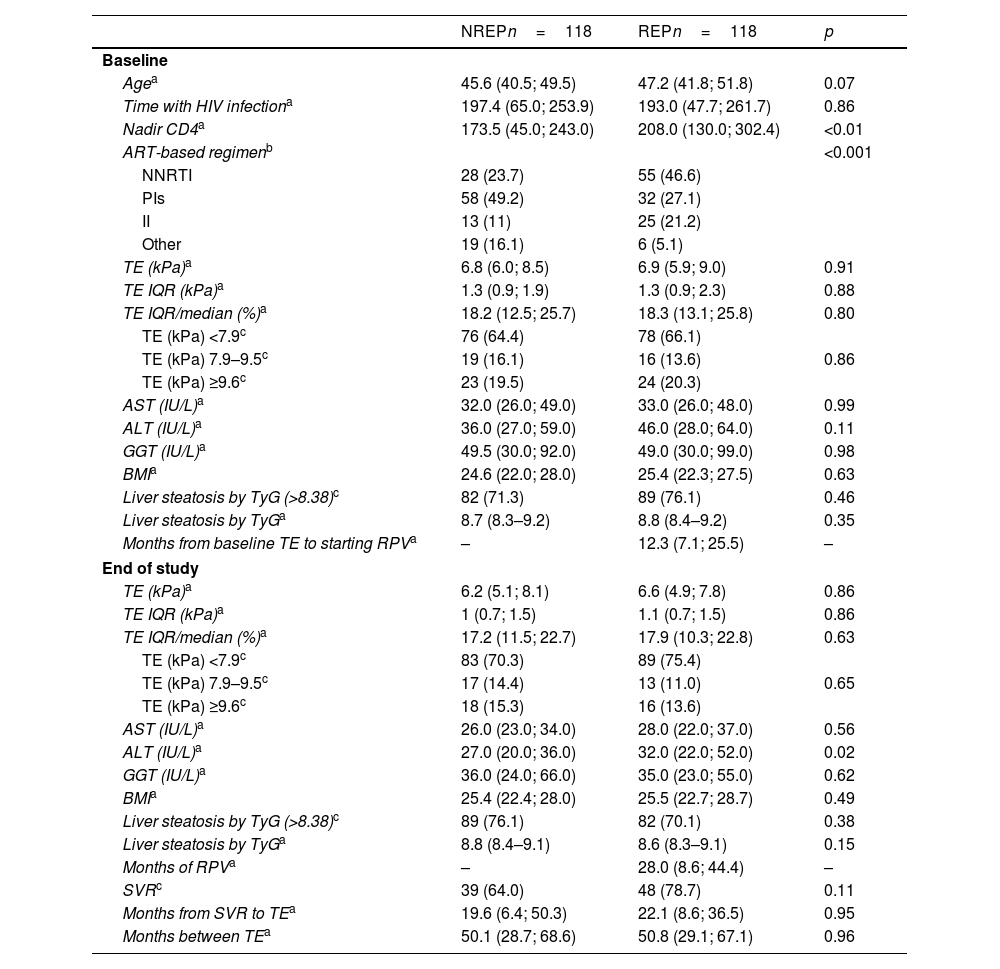
The analysis of the proportion of patients cured of HCV and exposed to RPV who changed fibrosis stage by TE revealed a higher proportion of patients who did not change or improved and a lower proportion of those who worsened. This difference was close to significance (p=0.066). If the analysis is performed by comparing patients whose reduction in TE measurement was greater than 33%, this proportion among REP was 31% compared with 16.4% among NREP (p=0.056). (Fig. 1A and B).
DiscussionThis study shows that liver stiffness was lower in treated HIV-infected patients cured of HCV infection who received an RPV-based ART regimen than in those who received other types of ART over a mean exposure period of 28 months. To our knowledge, this is the first report of such an effect associated with an ART regimen based on RPV in HIV-infected patients.
Elimination of HCV has a beneficial effect on liver stiffness, as demonstrated by the results of our study and those of other authors.9,10 However, our results reflect a greater reduction in liver stiffness with exposure to RPV, a proven long-term predictor of better liver outcomes. This reduction was mainly observed in HCV-coinfected patients who were cured, after adjustment for the main HIV-related factors, BMI, and time of exposure to RPV. In the subanalysis focusing on changes in TE stages and percentage reduction in the TE value, the reduction in liver stiffness tended to be greater in REP, although the differences were not statistically significant, probably owing to insufficient statistical power.
Recent experimental data indicate that administration of RPV reduces fibrosis and progression of liver disease, irrespective of etiology. Signaling via the Janus kinase (JAK)-STAT-1 and JAK-STAT-3 pathways regulates liver regeneration and fibrosis. RPV could play a key role in this process via specific and selective STAT-1-mediated induction of apoptosis in HSCs, which release interleukin 6 and normalize STAT-3 in hepatocytes, thus favoring liver regeneration after chronic injury.6 This novel approach could prove highly effective for attenuating liver fibrosis and promoting hepatocyte regeneration in patients with liver damage. In fact, we found the greatest effect in the group of patients with chronic hepatitis C, because liver disease was more frequent in this group, and, therefore, as HSCs were more frequently activated, the effects of RPV on STAT-1 signaling pathways may have been more evident. The changes observed in patients who were not cured of hepatitis C and whose liver stiffness worsened suggest that liver damage secondary to chronic HCV infection is greater than the potential benefit of RPV.
The point from which RPV can exert its antifibrotic effect is unknown. However, taking into account previous studies on regression of liver fibrosis in HIV/HCV-coinfected patients and recent clinical trials with new antifibrotic drugs, regression of fibrosis was observed from 16-18 months after SVR or after starting antifibrotic treatment.10 Therefore, we set the time between TE measurements to be at least 24 months. Our results did not show a linear relationship between time of exposure to RPV and change in TE findings or in differences in the percentage of change in TE values by percentile. We believe that these results reinforce the observation that differences in RPV exposure times would not bias the conclusions of the study.
Although we observed a reduction in liver stiffness in non-HCV-infected patients (REP and NREP), this reduction was not significant, and this finding does not seem to be due to the effect of antiretroviral treatment or liver steatosis. In NREP, it could be associated with changes to regimens based on integrase inhibitors, mainly RAL, which have proven to reduce steatosis (as measured by the CAP) and favor a reduction in liver stiffness.11,12 However, application of a noninvasive serum marker, TyG, at baseline and at the end of the study to estimate liver steatosis did not reveal significant changes in either group. We analyzed the hypothetical impact of switching ART in this subgroup of patients. Again, we found no differences in changes in ART by family between baseline and the end of the study. Thus, it seems unlikely that the impact of switching ART on the greater reduction in the TE value could differ between non-HCV-infected individuals and others. Another potential explanation for the improvement in liver stiffness in non-HCV-coinfected patients could be the impact of four years of hepatitis B treatment in those with chronic hepatitis B.13 The observed effect on liver stiffness is maintained despite the adjustments made for other metabolic or clinically relevant inflammatory variables (such as BMI or alanine aminotransferase) included in the model of analysis.
Our study is limited by its retrospective design. Other uncontrolled covariates may be present despite our criteria for matching REP and NREP, and the analysis of means adjusted for covariates considerably affected liver fibrosis. Although heavy drinkers and regular drug users were excluded, light or moderate consumption of these toxic substances could not be controlled for. We highlight the low proportion of women included in the study cohort and the lack of evidence to generalize our conclusions to this population. However, given that the ratio of males to females in our clinic is 5:1, this cannot be considered an exclusion bias.
RPV is widely used in HIV-infected patients. It is very effective and well tolerated, with little liver or lipid toxicity. Data from clinical trials highlight its hepatic safety profile, and, to date, no cases of clinical hepatitis have been reported.14–19 Therefore, RPV is a drug of choice in patients with chronic liver disease. It would also be very interesting if it could help to improve liver fibrosis and thus reduce both the progression of chronic liver disease and its consequences. Improvement in liver stiffness has been associated with reduced frequency of decompensation, hepatocarcinoma, and liver-related and non-liver-related mortality.20,21 The use of RPV-based therapy in HIV-infected patients could help to reduce the burden of surveillance programs for specific liver complications.
ConclusionOur results show that administration of RPV-based ART to treat HIV/HCV-coinfected patients with chronic hepatitis C cured, is associated with a greater reduction in liver stiffness. Until further data are available, our results could support a role for RPV in liver regeneration, in addition to its antiretroviral effect. Further studies with different designs are needed to confirm the long-term impact of RPV-based ART on reducing liver stiffness.
Conflicts of interestNone to declare.
We acknowledge Ana Delgado as data manager and Lucía Serrano for the statistical analysis. We acknowledge Mr. Thomas O’Boyle for translation of the manuscript into English.
This work was supported by grants from Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII; grant number PI17/01218 as part of the Plan Nacional R + D + I) and was cofunded by the ISCIII.
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation manuscript.