Organ transplantation (TX) is currently a therapeutic alternative in the management of end-stage or lethal diseases and, in some cases, for improving the quality of life and reducing the complications of chronic conditions. The scarcity of organ grafts or donors due to the limited number of deceased donors or to a lack of compatible living donors is one of the main limitations for the execution of organ TX. In Brazil, there is a great disparity between the number of patients on waiting lists and TX procedures, especially for liver and kidney TX. As a result of this inequality, grafts from donors who are considered marginal or not ideal have been used, including those with higher risk of failure following TX or those with potentially transmissible infections, involving donors with positive serologic markers for the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
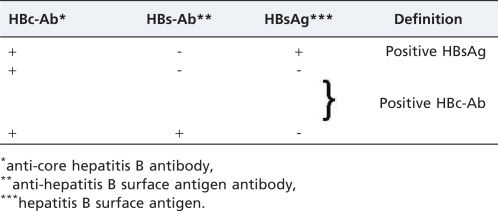
Donors who are positive for HBV markers have been routinely used in some TX centers. Four aspects should be considered for the assessment of the risk-benefit ratio of this procedure: 1. donor serologic profile, 2. recipient serologic profile, 3. TX variety and 4. the use of preventive therapy with human-specific HBV immunoglobulin and/or antiviral drugs. To establish recommendations, our group held discussions based on the data available in the medical literature and on the accumulated experience of the TX units at Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo. The definitions of serologic profiles for donors and recipients are described in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. The following transplants have been evaluated: liver, kidney, heart, lung, and hematopoietic stem cell transplants (HSCT). The IDSA (Infectious Diseases Society of America) rating system was used to assess the quality of evidence for graft acceptance and to identify the appropriate preventive strategy.
- 1.
Liver TX
HBsAg-positive donor: few reports are available, under particular circumstances, and there is a high risk of “de novo” HBV infection.
HBc-Ab-positive donor:
- •
HBsAg-positive recipient: regardless of the donor's serologic profile, this recipient must be administered combined prophylaxis with HBIG and an antiviral drug. The risk of viral reactivation does not seem to be increased by the involvement of an HBc-Ab-positive donor.
- •
Recipients who are positive for HBc-Ab and HBs-Ab: there are no reports of “de novo” HBV infection, with or without prophylaxis.
- •
Recipients with isolated HBc-Ab or a history of vaccination: the risk of “de novo” HBV is reduced in case series that described lamivudine and/or HBIG prophylaxis.
- •
Naïve recipient: group at highest risk; case series that described lamivudine and HBIG prophylaxis have demonstrated a reduction in risk.
- •
- 2.
Kidney TX
The largest case series of donors with positive serologic markers for HBV were published in kidney TX. However, some studies describe only the post-TX clinical course and fail to assess HBV serology.
HBsAg-positive donor: among 48 donors, “de novo” HBV infection has been detected in three recipients with variable pre-TX serologic profiles, while liver enzyme elevation has been detected in nine recipients.
HBc-Ab-positive donor:
- •
HBsAg-positive recipient: when lamivudine is used as preventive therapy, the clinical evolution is similar to that of recipients whose donors have negative HBV serology.
- •
Recipients with isolated HBc-Ab: without any prophylaxis, the seroconversion of HBsAg has been observed in 0.5% of recipients after TX. No reports have described seroconversion under lamivudine prophylaxis.
- •
Vaccinated or Naïve recipient: after TX, without any prophylaxis, seroconversion of HBc-Ab occurs in 2% of cases, and seroconversion of HBsAg occurs in less than 0.5% - without any impact on the clinical course. No reports have described seroconversion under lamivudine prophylaxis.
- •
- 3.
Heart TX
There are two case series on heart TX that report lamivudine prophylaxis in some recipients. Only one case of “de novo” HBV infection is reported in a naïve recipient with an HBsAg-positive donor.
- 4.
Lung TX
In two small case series of HBc-Ab-positive donors, no cases of recipient post-TX seroconversion were described. Among the two case series, one involved lamivudine prophylaxis.
- 5.
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant
In HSCT, the most relevant consideration is the risk of reverse seroconversion (loss of HBs-Ab after TX).
HBsAg-positive donor: in a study of HBsAg-negative recipients with a historical control group, the risk of “de novo” HBV was significantly reduced with lamivudine prophylaxis.
HBc-Ab-positive donor: when the bone marrow donor is naturally immunized (HBc-Ab and HBs-Ab positive), there is an unmistakable reduction in the risk of reverse seroconversion.
Recommendations:
- A.
General recommendations
- 1.
Potential TX recipients should receive HBV vaccination before TX, if possible (AII).
- 2.
HSCT donors should receive HBV vaccination before TX, if possible (BII).
- 3.
HSCT recipients who are negative for HBsAg must be directed to HBV vaccination, starting six months after TX (BIII).
- 4.
Liver TX recipients who are HBsAg positive must be prescribed an antiviral drug and HBIG as preventive therapy, regardless of the donor's serologic profile, due to the risk of post-TX recurrence (AII).
- 5.
TX recipients (except for those undergoing liver TX) who are HBsAg positive must be prescribed an antiviral drug, due to the risk of viral replication following TX (AII).
- 6.
HSCT donors who are HBsAg positive with active viral replication (positive polymerase chain reaction) must start on antiviral treatment before TX (BIII).
- 1.
- B.
Specific recommendations:
- 1.
Liver TX (B1).
- 2.
Kidney TX (B2).
- 3.
Heart and Lung TX (B3).
- 4.
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation TX (B4).
- 1.
Liver TX: Specific Recommendations
| Donor | Recipient | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg + | HBc-Ab+ HBs-Ab+ | HBc-Ab- HBs-Ab+ | Isolated HBc-Ab+ | Naïve | |
| HBsAg+ | No (DII) | No (DII) | No (DII) | No (DII) | No (EI) |
| HBc-Ab+ | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BIII) | Yes (BIII) | No (DII) |
| Prophylaxis | LAM + HBIG∗ (AII) | LAM (BIII)∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗ | _ |
LAM = lamivudine
Kidney TX: Specific Recommendations
| Donor | Recipient | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg+ | HBc-Ab+HBs-Ab+ | HBc-Ab-HBs-Ab+ | IsolatedHBc-Ab+ | Naïve | |
| HBsAg+ | Exceptional circumstances∗) (CIII) | Exceptional circumstances∗) (CIII) | Exceptional circumstances∗) (CIII) | Exceptional circumstances∗) (CIII) | No (DIII) |
| Prophylaxis | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | - |
| HBc-Ab+ | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | No (DIII) |
| Prophylaxis | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗∗ | _ |
Heart and Lung TX: Specific Recommendations
| Donor | Recipient | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg+ | HBc-Ab+HBs-Ab+ | HBc-Ab-HBs-Ab+ | IsolatedHBc-Ab+ | Naïve | |
| AgHBs+ | Exceptional circumstances∗) (CIII) | Exceptional circumstances∗) (CIII) | Exceptional circumstances∗) (CIII) | Exceptional circumstances∗) (CIII) | No (DIII) |
| Prophylaxis | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | - |
| Anti-HBc+ | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | No (DIII) |
| Prophylaxis | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗ | - |
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Specific Recommendations
| Donor | Recipient | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBsAg+ | HBc-Ab+HBs-Ab+ | HBc-Ab-HBs-Ab+ | IsolatedHBc-Ab+ | Naïve | |
| HBsAg+ | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Special circumstances (CIII) |
| Prophylaxis | LAM (AII)∗) | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (AII)∗∗ |
| HBc-Ab+ HBs-Ab- | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) | Yes (BII) |
| Prophylaxis | LAM (AII)∗) | ∗∗∗ | ∗∗∗ | ∗∗∗ | ∗∗∗ |
| HBc-Ab+ HBs-Ab+ | Yes (AII) | Yes (AII) | Yes (AII) | Yes (AII) | Yes (AII) |
| Prophylaxis | LAM (AII) | # | - | - | - |
Abdala E wrote the manuscript (Portuguese), supervised the revision that addressed the recommendation for liver transplantation, participated in the discussion of the final recommendations and revised the English version of the text. Azevedo LSF presented the kidney transplantation recommendation and discussed the final recommendations. Avelino-Silva VI presented the liver transplantation recommendation and translated the text into English. Costa SF, Strabelli TMV, Caramori ML presented the recommendation for bone marrow, heart and lung transplantation, respectively, and discussed the final recommendations. Pierrotti L, Souza Marques HH, Lopes MH, Varkulja GF, Santos VA participated in the discussion of the recommendations. Shikanai-Yasuda MA coordinated the presentations and discussion of the recommendations, helped revise the final recommendations and to prepare the manuscript for submission.
We thank the Clinical Directors from Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo (Prof. José Otavio Costa Auler Junior, Prof. Tarcísio Eloi Pessoa de Barros Filho and Prof. Eloísa Bonfá) for all their support.
O transplante (tx) consiste, atualmente, em alternativa terapêutica para doenças terminais e fatais ou, em alguns casos, para melhoria da qualidade de vida e diminuição dos riscos de complicações de doenças crônicas. Uma das principais limitações atuais para a realização de tx é a escassez de órgãos ou de doadores, por dificuldades na captação de doadores falecidos ou pela indisponibilidade de doadores vivos compatíveis. Há, no Brasil, um grande número de pacientes em lista de espera, especialmente para tx de fígado e de rim, em relação ao número de procedimentos realizados. Como consequência destas limitações, doadores considerados não ideais têm sido utilizados, incluindo-se aqueles cujo enxerto apresenta maior risco de não funcionamento após o transplante e doadores com risco potencial de transmissão de alguma infecção. Entre estes últimos encontram-se aqueles com marcador sorológico para o vírus da hepatite B (VHB).
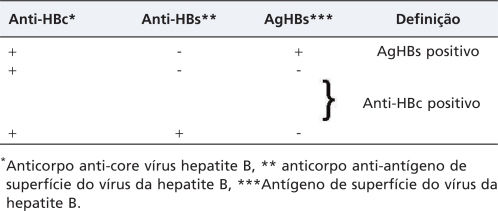
Doadores com algum marcador sorológico para VHB têm sido utilizados como rotina por alguns grupos. A relação risco-benefício desta medida é dependente de quatro fatores: 1. Estado sorológico do doador, 2. Estado sorológico do receptor, 3. Tipo de transplante e 4. Uso de profilaxia com imunoglobulina específica e/ou droga antiviral. Com o objetivo de estabelecer uma recomendação em nosso meio, realizamos discussões baseadas nos dados disponíveis na literatura e na experiência dos grupos de transplante do Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo. As definições dos perfis sorológicos possíveis para doador e receptor encontram-se nas Tabelas 1 e 2, respectivamente. Foram analisados os seguintes transplantes: fígado, rim, coração, pulmão e transplante de células-tronco hematopoiéticas (TCTH). Para a determinação dos níveis de evidência para aceitar o enxerto e indicar profilaxia foi utilizado o sistema da IDSA (Infectious Diseases Society of America).
Definições para perfis sorológicos para o vírus da hepatite B – Receptor.
| Anti-HBc | Anti-HBs | AgHBs | Definição |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | Naïve |
| + | - | + | AgHBs positivo |
| - | + | - | Anti-HBs isolado/Vacinado |
| + | - | - | Anti-HBc isolado |
| + | + | - | Anti-HBc e Anti-HBs |
∗Anticorpo anti-core vírus hepatite B, ∗∗ anticorpo anti-antígeno de superfície do vírus da hepatite B, ∗∗∗Antígeno de superfície do vírus da hepatite B.
- 1.
Transplante de Fígado
Doador AgHBs positivo: existem poucos relatos, sob circunstâncias especiais. Risco de desenvolvimento de hepatite B “de novo” muito alto.
Doador Anti-HBc positivo:
- •
Receptor AgHBs positivo: este receptor recebe, independentemente do estado sorológico do doador, profilaxia combinada com imunoglobulina específica (HBIG) e antiviral. Aparentemente, o risco de reativação não aumenta nos casos de doadores Anti-HBc positivos.
- •
Receptor Anti-HBc e Anti-HBs: não há casos de hepatite B “de novo” descritos, com ou sem profilaxia.
- •
Receptor vacinado ou Anti-HBc isolado: a ocorrência de hepatite B “de novo” é menor nas séries de casos em que foi utilizada profilaxia com lamivudina e/ou HBIG.
- •
Receptor naive: grupo de maior risco. Séries de casos sob profilaxia com lamivudina e HBIG demonstraram diminuição deste risco.
- •
- 2.
Transplante de Rim
As maiores séries de doadores com marcador sorológico para VHB são em tx de rim. Entretanto, em algumas delas é descrita apenas a evolução clínica pós-transplante, sem avaliação sorológica.
Doador AgHBs positivo: em um total de 48 doadores, detectou-se hepatite B “de novo” em 3 receptores (perfis sorológicos pré-tx variados) e aumento de enzimas hepáticas em 9.
Doador Anti-HBc positivo:
- •
Receptor AgHBs positivo: a evolução é semelhante aos caos de doadores sem marcador sorológico para o VHB, utilizando-se profilaxia com lamivudina.
- •
Receptor Anti-HBc isolado: soroconversão do AgHBs após o tx de 0,5% sem profilaxia. Não há relatos de soroconversão sob profilaxia com lamivudina.
- •
Receptor vacinado ou naive: após o tx, sem uso de profilaxia, soroconversão do Anti-HBc de 2% dos casos, e do AgHBs de menos de 0.5% - sem alteração na evolução clínica. Utilizando-se profilaxia com lamivudina, não há descrição de soroconversão.
- •
- 3.
Transplante de Coração
Existem duas séries de casos em tx de coração, utilizando-se profilaxia com lamivudina em alguns casos. Há apenas um relato de hepatite B “de novo”, em um receptor naive com doador AgHBs positivo.
- 4.
Transplante de Pulmão
Duas séries pequenas com doadores Anti-HBc positivos não demonstraram soroconversão do receptor após o tx. Lamivudina profilática foi utilizada em uma delas.
- 5.
Transplante de Células-Tronco Hematopoiéticas (TCTH)
Em TCTH, a consideração mais significativa é o risco de soroconversão reversa (perda do Anti-HBs pós-tx).
Doador AgHBs positivo: estudo com controle histórico, em receptores AgHBs negativos, demonstrou diminuição significativa do risco de hepatite B “de novo” com profilaxia com lamivudina.
Doador Anti-HBc positivo: existe um evidente benefício sobre o risco de soroconversão reversa quando o doador é naturalmente imunizado (Anti-HBc e Anti-HBs positivos).
Recomendações:
A. Gerais
- 1.
Todo candidato a transplante de órgão sólido deve ser encaminhado para vacinação contra o VHB antes do transplante, se possível (AII).
- 2.
Todo doador de células-tronco hematopoiéticas deve ser encaminhado para vacinação contra o VHB antes do transplante, se possível (BII).
- 3.
Todo receptor de células-tronco hematopoiéticas que for AgHBs negativo deve ser encaminhado para vacinação contra o VHB, a partir de 6 meses do transplante (BIII).
- 4.
Todo receptor de transplante de fígado que for AgHBs positivo deve receber profilaxia com droga antiviral e HBIG, independentemente do estado sorológico do doador, pelo risco de recidiva pós-transplante (AII).
- 5.
Todo receptor de transplante (exceto fígado) que for AgHBs positivo deve receber profilaxia com droga antiviral, pelo risco de replicação após o transplante (AII).
- 6.
Todo doador de células-tronco hematopoiéticas que for AgHBs positivo e estiver com replicação viral (PCR positivo) deve iniciar tratamento com antiviral antes do transplante (BIII).
B. Específicas
- 1.
Transplante de Fígado: Recomendações Específicas (B1).
- 2.
Transplante de Rim: Recomendações Específicas (B2).
- 3.
Transplantes de Coração e Pulmão: Recomendações Específicas (B3).
- 4.
Transplante de Células Tronco-Hematopoiéticas: Recomendações Específicas (B4).
Transplante de Fígado: Recomendações Específicas
| Doador | Receptor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgHBs + | Anti-HBc+ Anti-HBs+ | Anti-HBc- Anti-HBs+ | Anti-HBc+ isolado | Naive | |
| AgHBs+ | Não (DII) | Não (DII) | Não (DII) | Não (DII) | Não (EI) |
| Anti-HBc+ | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BIII) | Sim (BIII) | Não (DII) |
| Profilaxia | LAM + HBIG∗) (AII) | LAM (BIII)∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗ | _ |
Transplante de Rim: Recomendações Específicas
| Doador | Receptor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgHBs + | Anti-HBc+ Anti-HBs+ | Anti-HBc- Anti-HBs+ | Anti-HBc+ isolado | Naive | |
| AgHBs+ | Situações excepc.∗) (CIII) | Situações excepc.∗) (CIII) | Situações excepc.∗) (CIII) | Situações excepc.∗) (CIII) | Não (DIII) |
| Profilaxia | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | - |
| Anti-HBc+ | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Não (DIII) |
| Profilaxia | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗∗ | _ |
Transplantes de Coração e de Pulmão: Recomendações Específicas
| Doador | Receptor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgHBs + | Anti-HBc+Anti-HBs+ | Anti-HBc-Anti-HBs+ | Anti-HBc+ isolado | Naive | |
| AgHBs+ | Situações excepc.∗) (CIII) | Situações excepc.∗) (CIII) | Situações excepc.∗) (CIII) | Situações excepc.∗) (CIII) | Não (DIII) |
| Profilaxia | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | LAM (BIII)∗∗∗ | - |
| Anti-HBc+ | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Não (DIII) |
| Profilaxia | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗∗ | LAM (CIII)∗∗∗∗ | _ |
Transplantes de Células Tronco-Hematopoiéticas: Recomendações Específicas
| Doador | Receptor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgHBs + | Anti-HBc+Anti-HBs+ | Anti-HBc-Anti-HBs+ | Anti-HBc+ isolado | Naive | |
| AgHBs+ | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Situações especiais (CIII) |
| Profilaxia | LAM (AII)∗) | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (AII)∗∗ | LAM (AII)∗∗ |
| Anti-HBc+ Anti-HBs- | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) | Sim (BII) |
| Profilaxia | LAM (AII)∗) | ∗∗∗ | ∗∗∗ | ∗∗∗ | ∗∗∗ |
| Anti-HBc+ Anti-HBs+ | Sim (AII) | Sim (AII) | Sim (AII) | Sim (AII) | Sim (AII) |
| Profilaxia | LAM (AII) | # | - | - | - |