The risk of bacterial meningitis increases in cochlear implant (CI) patients. Therefore, pneumococcal, influenza and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccination is indicated in this group. The aim of this study was to determine compliance with the vaccination calendar in patients implanted in a referral hospital.
Materials and methodsPatients with CI operated between 2005 and 2015 were included. Vaccine coverage for seasonal influenza, Hib and pneumococcal conjugate 13-serotypes (CNV13) and pneumococcal polysaccharide 23-serotypes (NPPV23) was evaluated. The sample was divided into two age groups (<14 years and ≥ 14 years). A univariate and bivariate analysis was performed.
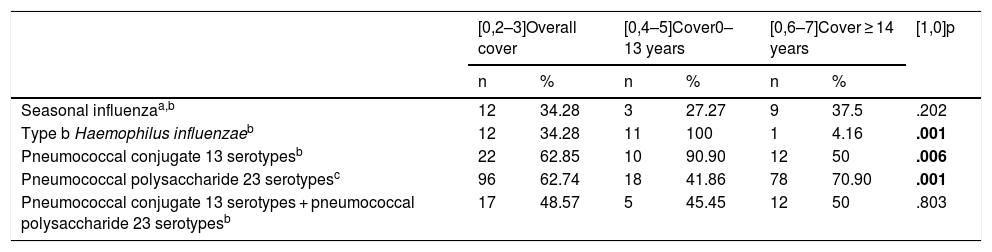
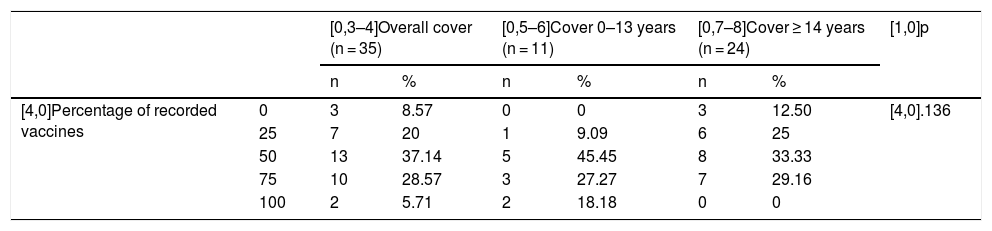
ResultsOf the 153 patients studied (28.01% 0–13 years old and 71.9% ≥ 14), only 2 (5.71%) had 100% adherence to the vaccination schedule, while 65.71% had compliance of 50% or less. Overall, vaccination coverage against the sequential pneumococcal pattern was 48.57%. The paediatric population exceeded 90% coverage for the vaccine against Hib and CNV13 while in those over 14 years of age it barely exceeded 50%. Influenza coverage was less than 40%. An inverse correlation was obtained between age and compliance, although not statistically significant.
ConclusionsVaccination coverage in patients with CI is lower than expected. Close collaboration between otolaryngology departments and the vaccination units is proposed as the main strategy for improvement.
El riesgo de meningitis bacteriana aumenta en los pacientes con implante coclear (IC). Por ello, se indica la vacunación antineumocócica, antigripal y contra Haemophilus influenzae tipo b (Hib) en este grupo. El objetivo del presente estudio es conocer el cumplimiento del calendario vacunal en los pacientes implantados en un hospital de referencia.
Materiales y métodosSe incluyeron los pacientes con IC intervenidos entre 2005 y 2015. Se evaluaron las coberturas vacunales frente a gripe estacional, Hib y neumococo conjugada 13-serotipos (VNC13) y neumococo polisacárida 23-serotipos (VNP23). Se dividió la muestra en dos grupos por edad (<14 años y ≥14 años). Se realizó un análisis univariante y bivariante.
ResultadosDe los 153 pacientes estudiados (28,01% 0-13 años y 71,9% ≥14), solo 2 (5,71%) tuvieron un 100% de adherencia al calendario vacunal, mientras que el 65,71% registró un cumplimiento del 50% o menor. Globalmente, la cobertura de vacunación frente a la pauta secuencial de neumococo fue 48,57%. La población pediátrica superó el 90% de cobertura para la vacuna frente a Hib y VNC13 mientras que en los mayores de 14 años apenas superó el 50%. La cobertura frente a gripe estacional fue inferior al 40%. Se obtuvo una correlación inversa entre la edad y el cumplimiento, aunque no estadísticamente significativa.
ConclusionesLas coberturas de vacunación en los pacientes con IC evaluados son más bajas de lo esperado. Se propone la colaboración estrecha entre los Servicios de Otorrinolaringología y las Unidades de Vacunas como principal estrategia para la mejora.