Invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) is a major public health problem worldwide with high morbidity and mortality that causes a wide spectrum of diseases, from otitis media to sepsis and meningitis. In Catalonia, the universal immunization program with the 13-valent conjugated pneumococcal vaccine (Pn13 vaccine) began in 2016. The objective of this study was to analyse the impact of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13 vaccine) on the incidence of IPD during the years 2017−2018 compared to the years 2014−2015.
MethodRetrospective study of IPD cases notified by reporting laboratories to the Microbiological Reporting System of Catalonia (MRSC) from 2014 to 2018. Incidence rates (IR) and relative risk (RR) were calculated.
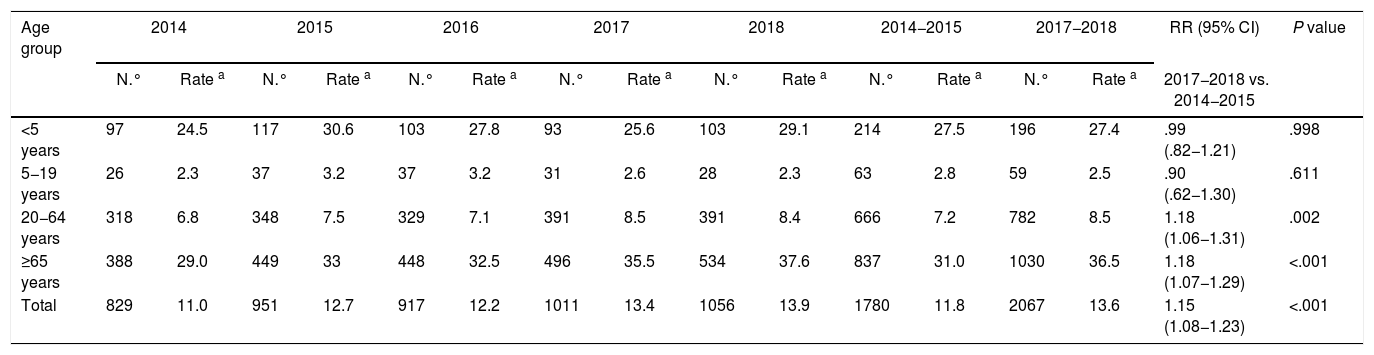
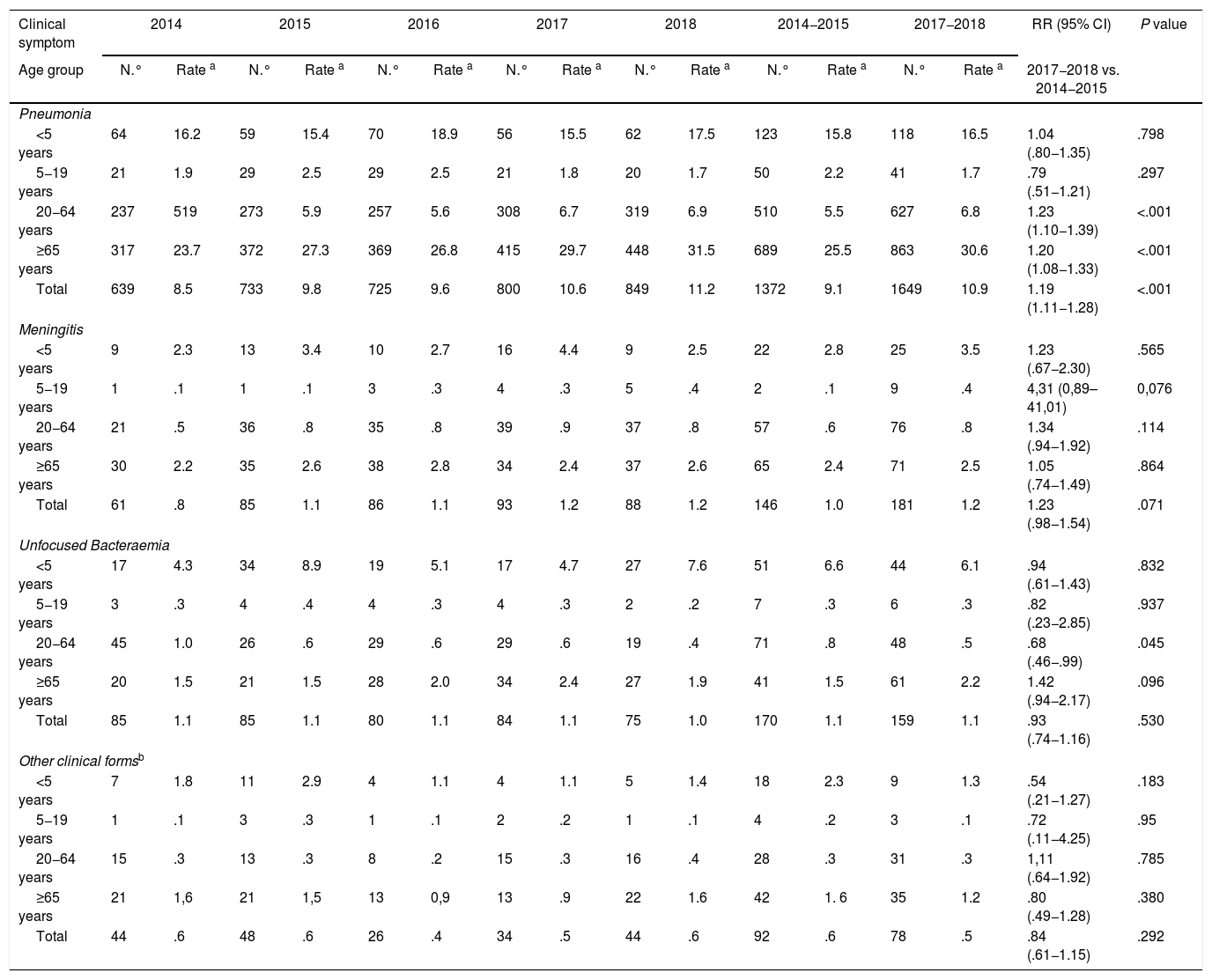
ResultsThe global incidence of IPD (2014–2018) was 12,6 cases per 100,000 persons/year. Comparing 2017−2018 vs 2014−2015, the incidence of IPD caused by the serotypes included in the PCV13 vaccine has decreased in children <5 years by 46% while it has remained stable in the rest of the groups. Serotype 3, despite being included in the PCV13 vaccine, remained a high incidence. In contrast, the incidence of IPD caused by non PCV13 serotypes increased in adults aged 20−64 years (35%) and ≥65 years (27%), mainly due to the increase of serotype 8.
ConclusionsPCV13 introduction is beneficial for both, vaccinated and non-vaccinated people (due to herd immunity). However, a precise and continuous epidemiological surveillance of IPD must be carried out to detect changes in the incidence of the disease and circulating serotypes.
La enfermedad neumocócica invasiva (ENI) es un importante problema de salud pública a escala mundial con elevada morbilidad y mortalidad que causa un espectro amplio de enfermedades, desde otitis media hasta sepsis y meningitis. En Cataluña, el programa de inmunización universal con la vacuna antineumocócica conjugada 13-valente (vacuna Pn13) se inició en 2016. El objetivo de este estudio fue analizar el impacto de la vacuna Pn13 sobre la incidencia de ENI durante 2017−2018 respecto de 2014−2015.
MétodoEstudio retrospectivo de casos de ENI notificados por laboratorios participantes al sistema de notificación microbiológica de Cataluña del 2014 al 2018. Se calcularon las tasas de incidencia (TI) y riesgo relativo (RR).
ResultadosLa incidencia global de ENI (2014–2018) fue de 12,6 casos por 100,000 personas/año. Comparando 2017−2018 vs 2014−2015, la incidencia de ENI causada por serotipos incluidos en la vacuna Pn13 disminuyó en niños <5 años un 46% mientras que en el resto de grupos de edad permaneció estable. El serotipo 3, pesar a estar incluido en la vacuna Pn13, mantuvo una incidencia elevada. Por el contrario, la incidencia de ENI por serotipos no vacunales aumentó en adultos de 20−64 años (35%) y de ≥65 años (27%), principalmente debido al aumento del serotipo 8.
ConclusionesLa introducción de la vacuna Pn13 es beneficiosa tanto para la población vacunada como la no vacunada (por efecto indirecto o inmunidad de grupo). Debe llevarse a cabo una vigilancia epidemiológica precisa y continuada de la ENI para detectar cambios en la incidencia de la enfermedad y los serotipos circulantes.