The effectiveness of home non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIMV) is assessed by determining blood gas values in wakefulness, the evolution of their symptoms, and the monitoring of ventilation at night. The aim of our study is to evaluate whether defined values reached with outpatient monitoring by oximetry is related to the clinical, arterial gases and survival of a sample of patients with home NIMV.
Material and methodRetrospective observational cohort study of a series of patients receiving home NIMV treatment for different causes. Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and less than 3 months of follow-up were excluded. The evolution of the patient's symptoms, their baseline arterial blood gases in wakefulness, and home nocturnal oximetry records, are evaluated at each outpatient visit. Good maintained oximetry control (MOC) was defined when mean O2 saturation values were reached and maintained until the last revision. Patient groups were considered, according to whether or not a good MOC was achieved during follow-up.
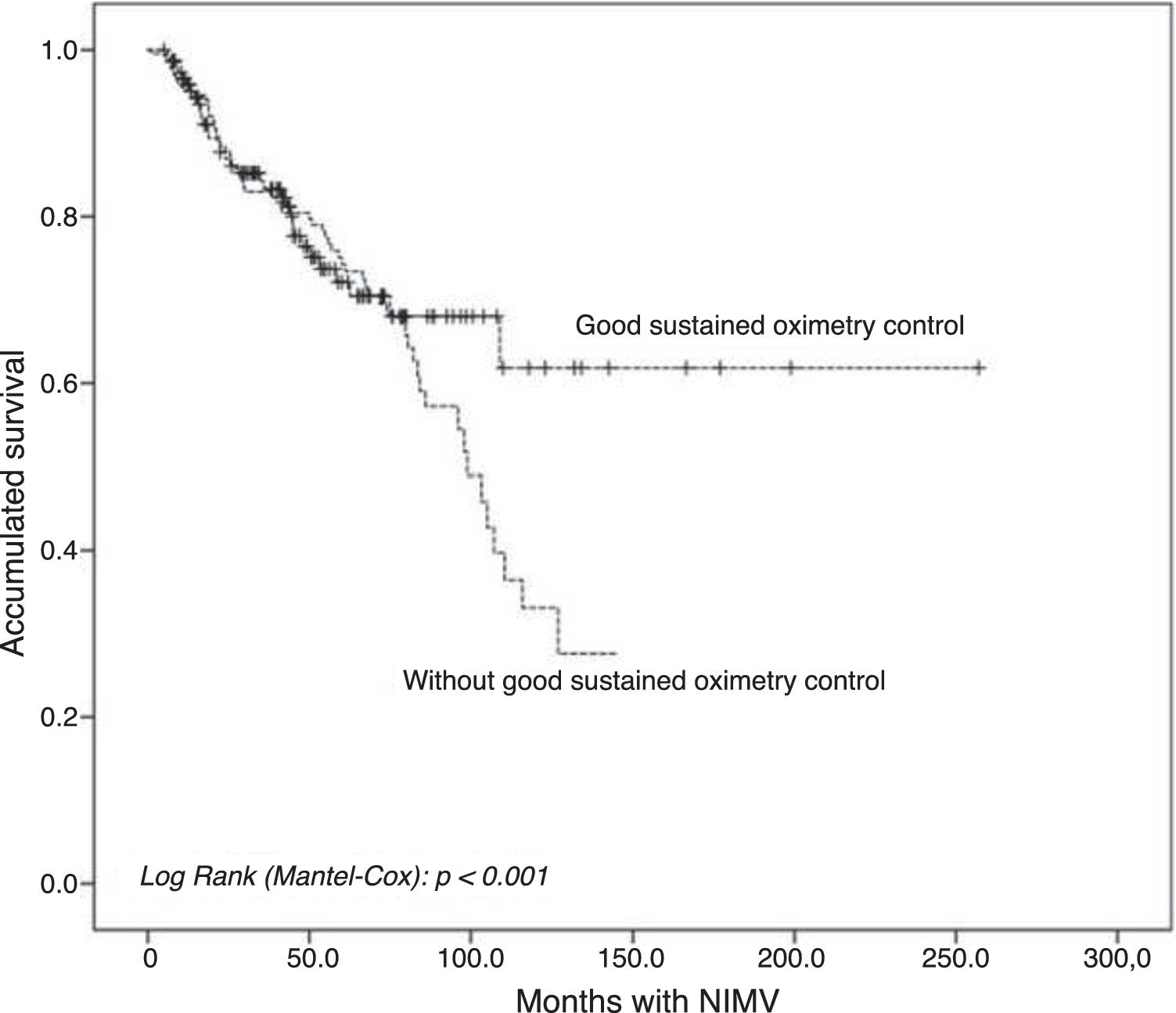
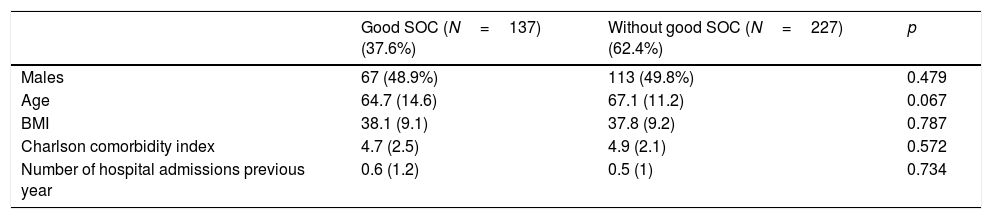
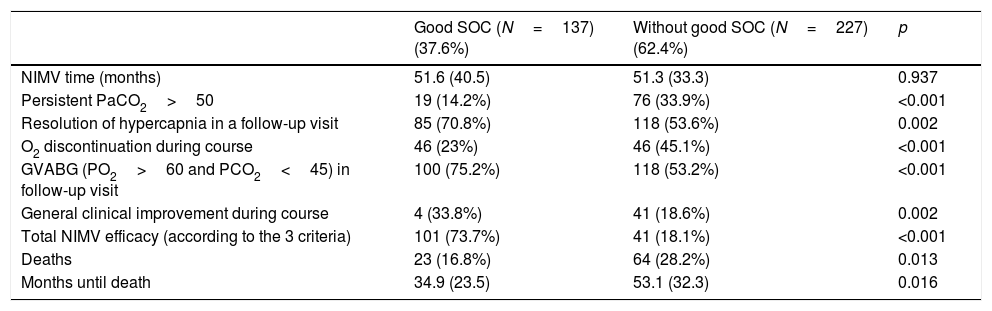
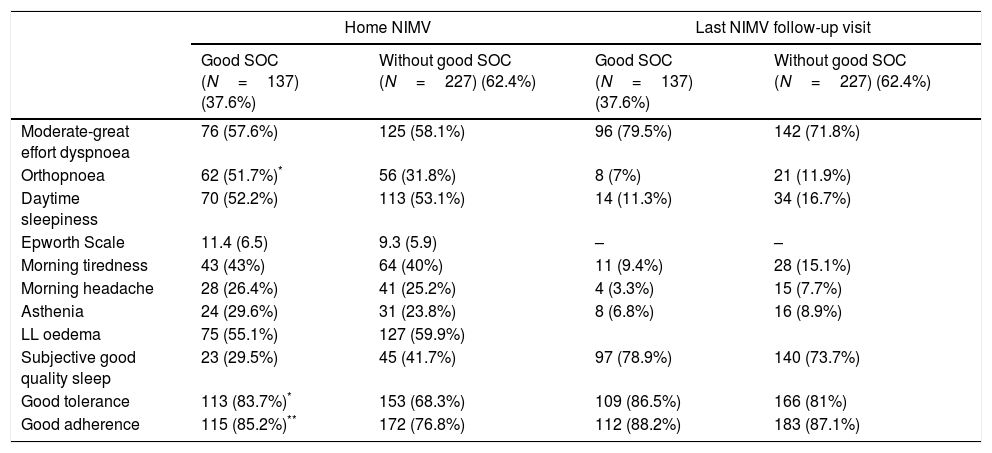
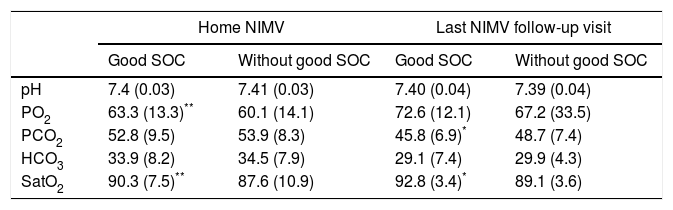
ResultFour hundred patients were evaluated. Three hundred and sixty four (91%) were included in the study; their median age was 68 years, 51% were male. 37.6% had a good MOC during follow-up. Compared to patients with not good MOC, a better long-term mortality was obtained (16.8% vs 28.2%, p=0.013), and an improvement in symptoms (33.8% vs 18.6%, p=0.002) and a lower proportion of patients with persistently >50mmHg PaCO2 (14.2% vs. 33.9%, p<0.001) was observed.
ConclusionIn the follow-up of patients with home NIMV in our context, values defined in home nocturnal oximetry (good MOC) are positively associated with clinical, gasometric and longer-term survival.
Nuestro objetivo es evaluar si alcanzar unos valores definidos mediante la oximetría nocturna en la monitorización ambulatoria de la ventilación mecánica no invasiva (VMNI) se relaciona con la evolución clínica, gasométrica y la supervivencia de una muestra de pacientes con VMNI domiciliaria.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional de cohortes retrospectivo de una serie de pacientes en tratamiento con VMNI domiciliaria por diferentes causas. Se excluyeron los pacientes con esclerosis lateral amiotrófica y/o menos de 3 meses de seguimiento. Se valora la evolución de la sintomatología, la gasometría arterial basal en vigilia, y los registros oximétricos nocturnos domiciliarios, en cada visita ambulatoria. Se definió buen control oximétrico mantenido (COM) cuando se alcanzan unos valores y se mantienen hasta la última revisión. Se consideraron 2 grupos de pacientes, según alcanzaron o no un buen COM durante el seguimiento.
Resultadosse evaluaron 400 pacientes, fueron incluidos finalmente 364 (91%), con una edad mediana de 68 años, el 51% varones. El 37,6% presentaban buen COM a lo largo del seguimiento. Comparando los pacientes con vs. sin buen COM, se obtuvo una menor mortalidad a largo plazo (16,8 vs. 28,2%; p=0,013), mejoría en la sintomatología (33,8 vs. 18,6%; p=0,002), y una menor proporción de pacientes con una PaCO2 persistentemente>50mmHg (14,2 vs. 33,9%; p<0,001).
ConclusiónEn el seguimiento de pacientes con VMNI domiciliaria en nuestro medio, unos valores definidos en la oximetría nocturna domiciliaria (buen COM) se asocia de forma positiva con una mejoría clínica, gasométrica y una mayor supervivencia a largo plazo.