This study aimed to determine if NOD2 gene polymorphisms are found in neonatal with early breastfeeding initiation and neonatal without early breastfeeding initiation.
MethodThis study used a Quasy Experiment type, with Non-equivalent Control Group Design. The sample in this study were 60 pregnant women; gestational age±34 and 36 weeks, normal delivery, and carried out early breastfeeding at the Siti Fatima maternal and child hospital and Public Health Center Bara-baraya. The sample was divided into two groups, i.e., the intervention group as many as 30 neonatal and the control group as many as 30 neonatal. Samples were taken from blood from the umbilical cord as much as three cc for the examination of NOD2 polymorphisms.
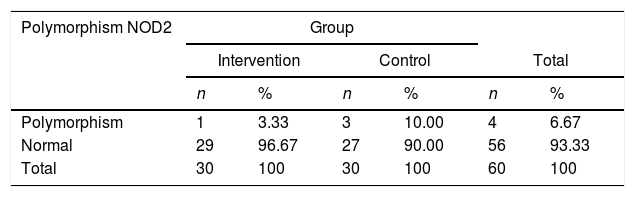
ResultsThe group that was given early breastfeeding initiation intervention had a polymorphism frequency of 1 person (3.33%), while the control group had a polymorphism frequency of 4 people (6.67%).
ConclusionThe control group, i.e., infants who did not get early breastfeeding initiation had a higher frequency of NOD2 gene mutations compared to the group that received early breastfeeding initiation.
Nucleotide oligomerization domain2 (NOD2) is a protein also known as the family recruitment domain caspase family, caspase recruitment domain protein 15 (CARDS 15) which plays an important role in the immune system.1 NOD2 in the infant is currently a concern of research because of its importance in the next phase of infant growth and development. The early neonatal period is a critical phase for the development of intestinal digestion and colonization by commensal microbiota, which will affect the development of the neonatal immune system. Continued efforts have been directed at understanding the growth process of the neonatal digestive tract that is influenced by the diet, especially by the components present in breastmilk.2
Early initiation of breastfeeding is strongly associated with neonatal survival.3 Mother and baby interactions during pregnancy and post-birth will be continued through breast milk, which has various immune modulation compounds such as IgM and IgA. The protective effect of breast milk shows that breast milk can function as a carrier of passive immunity in the baby's digestive tract, while the local immune system is still immature.4,5 This study aimed to determine if NOD2 gene polymorphisms are found in neonatal with early breastfeeding initiation and neonatal without early breastfeeding initiation.
MethodsThis study used a Quasy Experiment type, with Non-equivalent Control Group Design. The sample in this study were 60 pregnant women; gestational age±34 and 36 weeks, normal delivery, and carried out early breastfeeding at the Siti Fatima maternal and child hospital and Public Health Center Bara-baraya. The sample was divided into two groups, i.e., the intervention group as many as 30 people and the control group as many as 30 people. For the examination of NOD2 polymorphisms, samples were taken from blood from the umbilical cord as much as three cc.
ResultsThe group that was given early breastfeeding initiation intervention had a polymorphism frequency of 1 person (3.33%), while the control group had a polymorphism frequency of 4 people (6.67%) (Table 1).
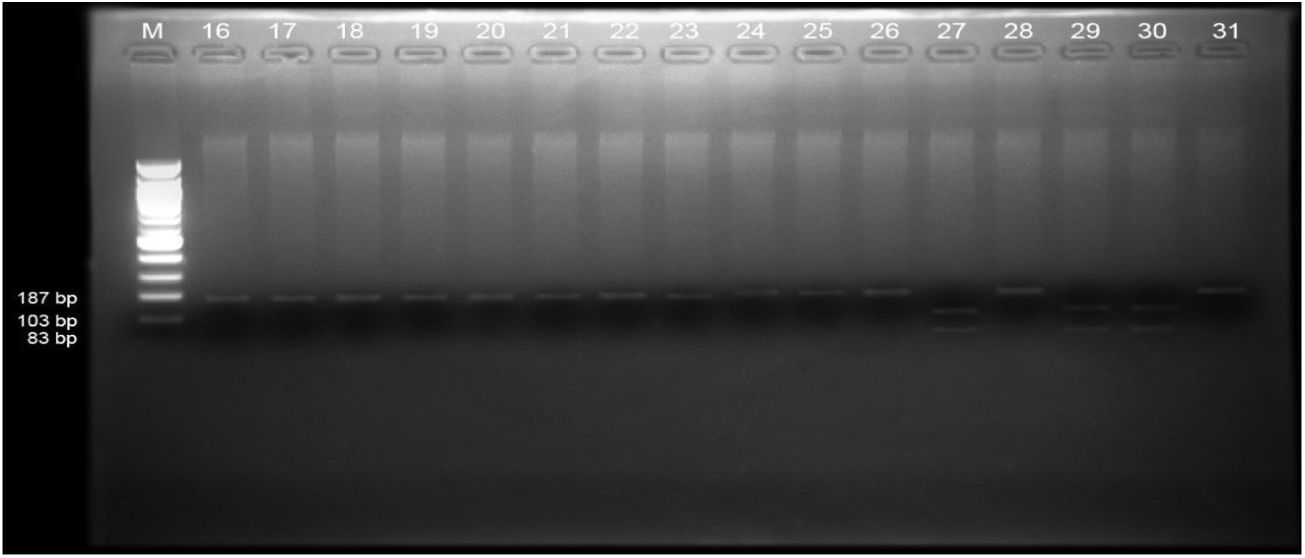
In Figs. 1 and 2, we can see the polymorphism of each of the sample numbers; 15, 27, 29, and 30, which appear at 103bp and 83bp. RFLP-PCR test results showed genetic variation in mutations, electrophoresis showed one band, homozygous mutations showed two bands. Electrophoretic readings that did not experience mutations showed a fixed restriction area at 187bp, whereas homozygous mutations showed restriction at 103bp and 83bp. The picture above shows the NOD2 gene in exon4, which was cut with the BamH1 enzyme and cut 103bp and 83bp, which showed mutations.
DiscussionThis study reveals that the control group, i.e., neonatal who did not get early breastfeeding initiation had a higher frequency of NOD2 gene mutations compared to the group that received early breastfeeding initiation. Neonatal which getting early breastfeeding initiation will get colostrum, which is rich in sIgA, lactoferrin, and lysozyme, which are components of the immune substance in the digestive tract.5–7 Several factors found in breast milk affect the expression of intestinal epithelial genes, especially genes associated with enterocyte differentiation. Breast milk contains epidermal growth factor (EFG) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF); both of these hormones increase the activity of the brush border enzyme.8 Polymorphisms are variants in DNA sequences that can cause changes in protein function in the body, gene polymorphisms can trigger various diseases such as cardiovascular, metabolic syndrome, and others if manifestations occur. NOD2 is a protein involved in the immune system that is associated with the development of digestive cancer.
As a result of this mutation has a different phenotype expression, namely a decrease in immune function that manifests causing infections, especially Chron Disease, intestinal failure, sarcoidosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, pulmonary tuberculosis. Thus it can be said that early breastfeeding initiation plays a role in reducing/preventing the occurrence of NOD2 polymorphisms in infants. Infants who have NOD2 gene polymorphisms have great potential to experience infectious diseases.9 NOD2 gene mutation can be an initial screening for prevention and alertness to diseases related to the digestive system.10–12
ConclusionThe control group, i.e., infants who did not get early breastfeeding initiation had a higher frequency of NOD2 gene mutations compared to the group that received early breastfeeding initiation.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the International Conference on Women and Societal Perspective on Quality of Life (WOSQUAL-2019). Full-text and the content of it is under responsibility of authors of the article.