To assess complications after ureteroscopy (URS) for upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) management and to assess its postoperative cumulative morbidity burden using the Comprehensive Complication Index (CCI).
Materials and methodsSingle center retrospective study including patients submitted to URS for UTUC suspicion. URSs were both diagnostic and operative. Postoperative complications were recorded according to the EAU Guidelines and graded according to Clavien-Dindo Classification (CDC). The cumulative postoperative morbidity burden developed by patients experiencing multiple events was assessed using the CCI. Multivariable logistic regression (MLR) analyses identified factors independently associated with the development of any grade and major postoperative complications.
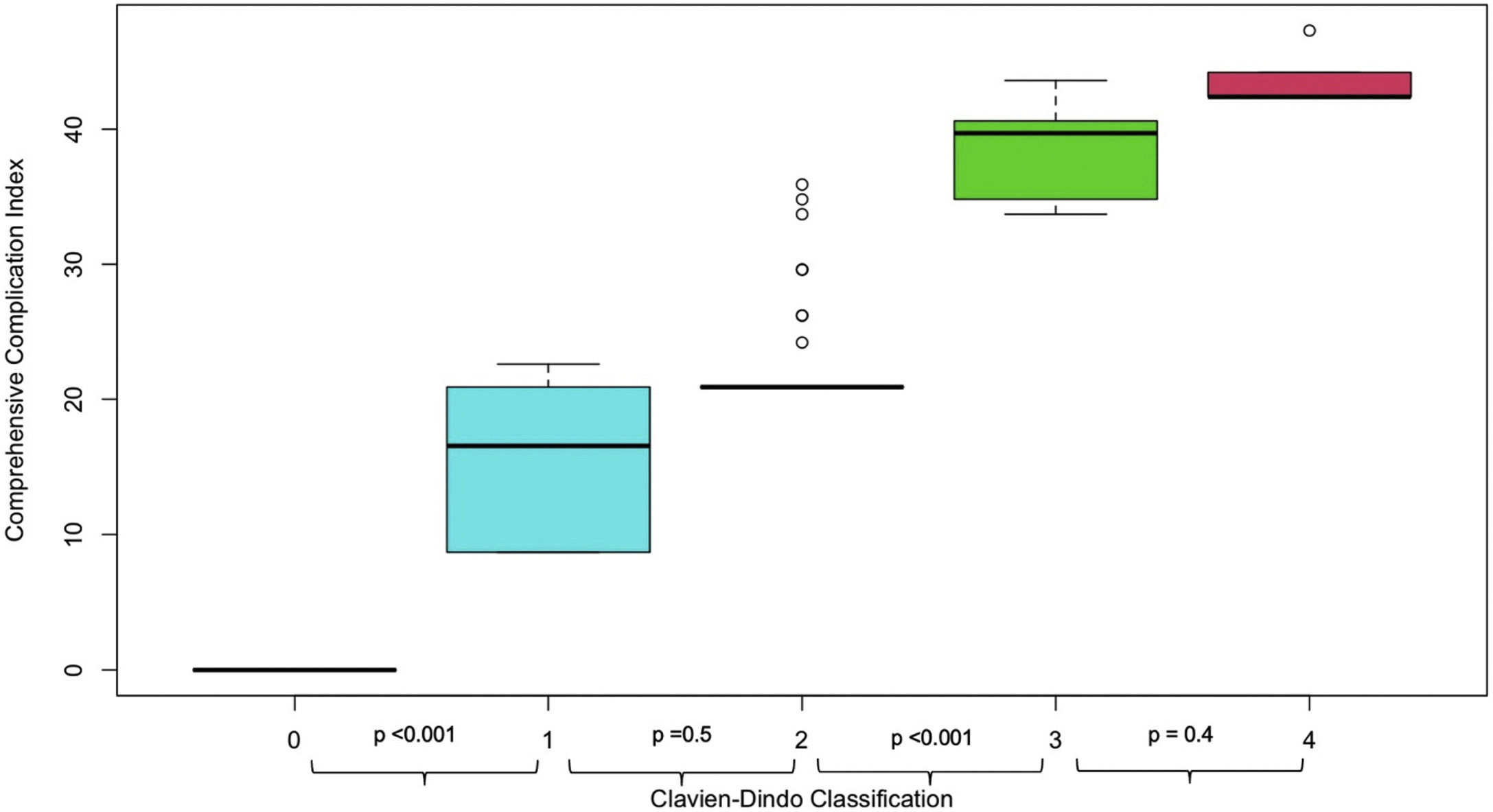
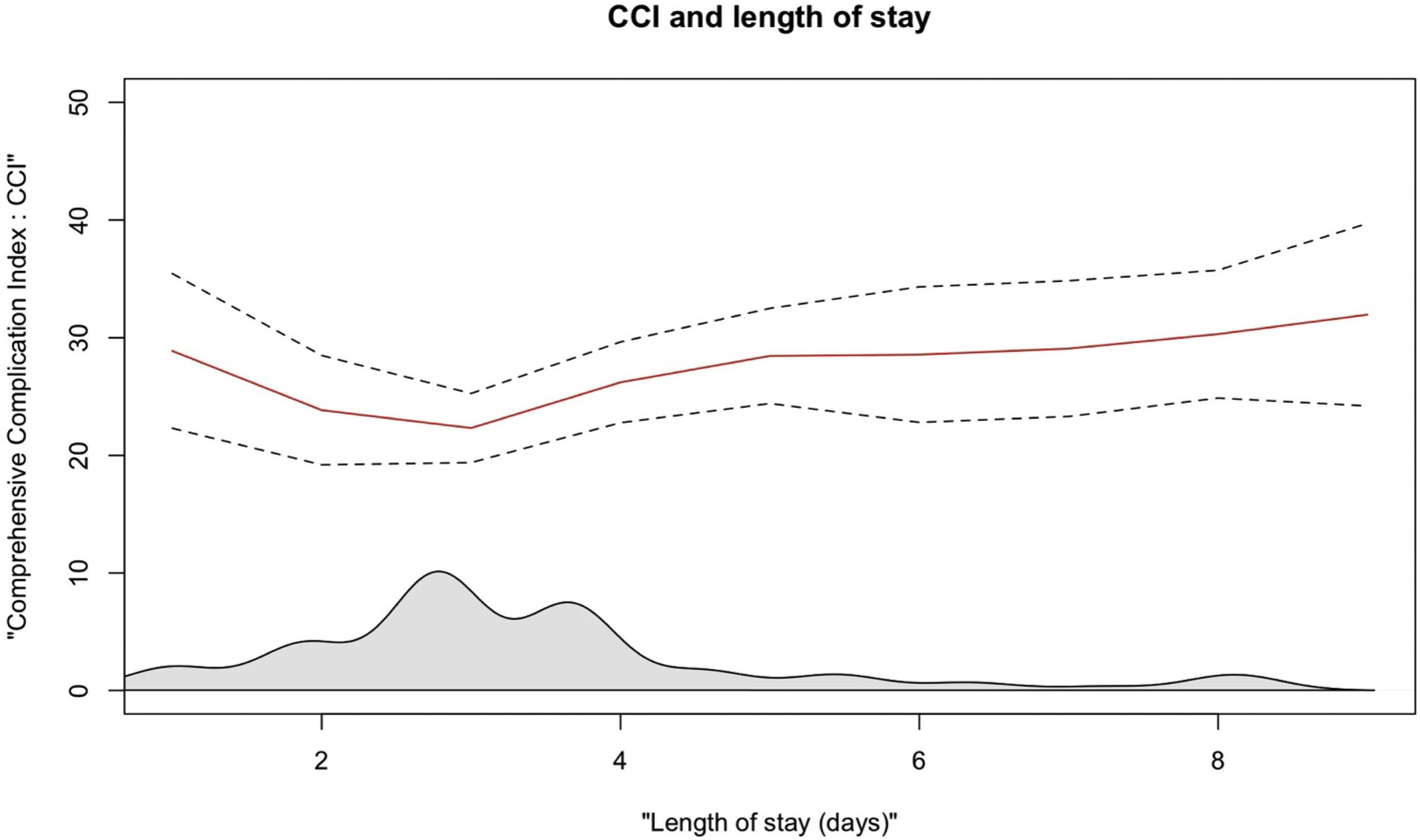
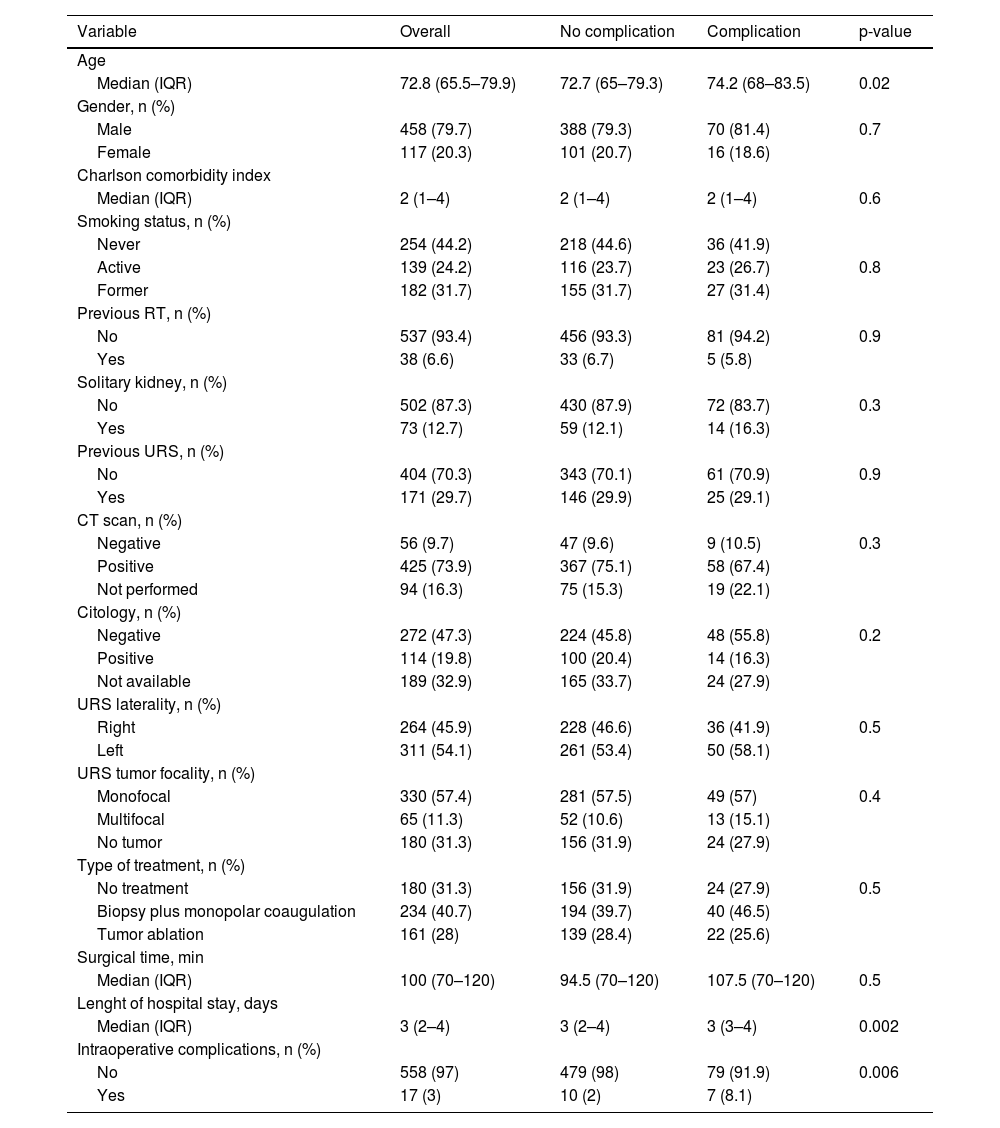
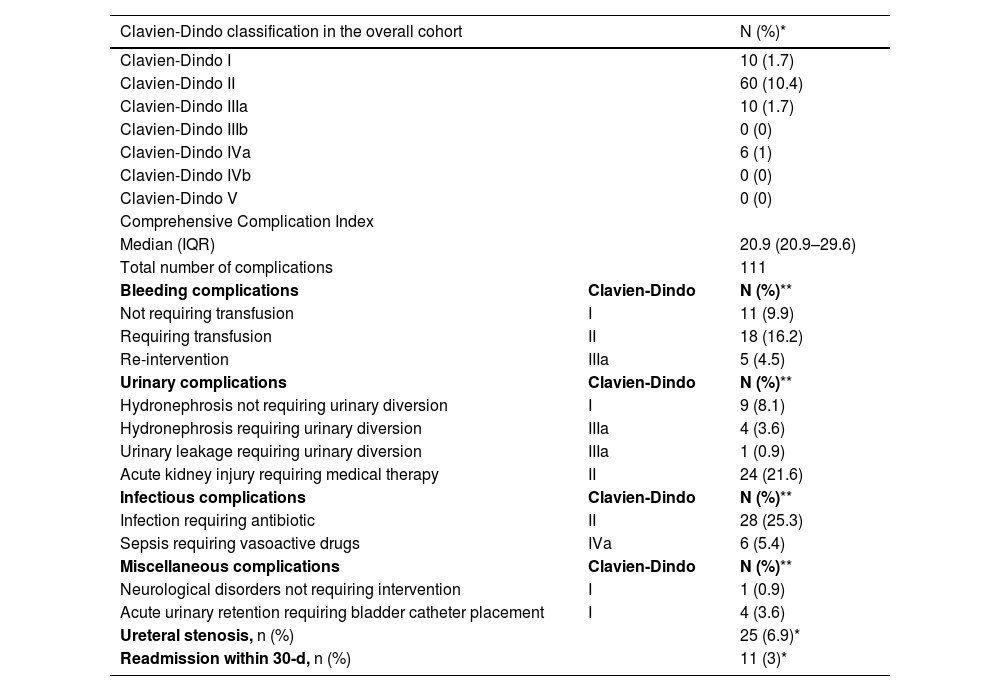
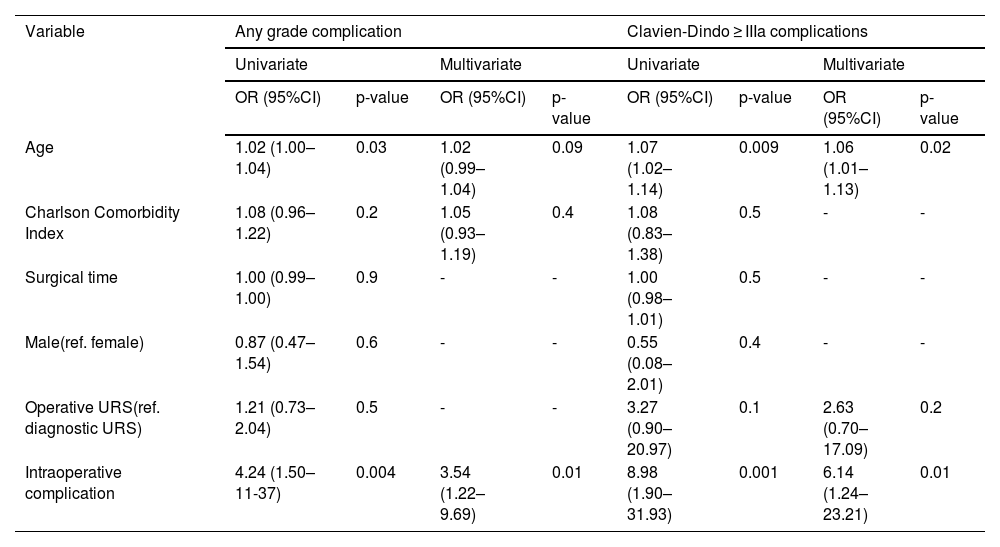
ResultsOverall, 360 patients with UTUC suspicion were included with a total of 575 URSs performed. The cumulative number of all postoperative complications recorded was 111. In 86 (15%) procedures, patients experienced at least one postoperative complication, while 25 (4.3%) experienced more than one complication. Of these, 16 (14%) were severe (CDC ≥ IIIa). The most frequent type of complications were urinary (34%), bleeding (30%) and infectious (30%). The higher the CDC grade, the higher the median CCI, with a statistically significant increase in median CCI from CDC II to major complications. Patients who experienced intraoperative complications were at higher risk of developing any grade and major postoperative complications at MLR.
ConclusionsComplications after ureteroscopy for UTUC are relatively uncommon events. Patients who experience intraoperative complications are at higher risk of developing postoperative complications. The comprehensive complication index appeared more representative of the cumulative postoperative morbidity rather than the Clavien-Dindo classification.
Evaluar las complicaciones tras la ureteroscopia (URS) para el tratamiento del carcinoma urotelial del tracto superior (CUTS) y evaluar la morbilidad postoperatoria global mediante el Comprehensive Complication Index (CCI).
Materiales y métodosEstudio retrospectivo unicéntrico que incluye pacientes sometidos a URS por sospecha de CUTS. Las URS se realizaron con fines diagnósticos y de tratamiento. Las complicaciones postoperatorias se registraron según las directrices de la EAU y el grado de la clasificación Clavien-Dindo (CDC). La carga de morbilidad postoperatoria global desarrollada por los pacientes que presentaron múltiples eventos se evaluó mediante el CCI. Los análisis de regresión logística multivariable (RLM) identificaron factores independientes asociados al desarrollo de complicaciones postoperatorias de cualquier grado y mayores.
ResultadosEn total se incluyeron 360 pacientes con sospecha de CUTS y se realizaron 575 URS. Se registró un total de 111 complicaciones postoperatorias. En 86 (15%) procedimientos hubo pacientes con al menos una complicación postoperatoria, y 25 (4,3%) presentaron más de una complicación. De éstas, 16 (14%) fueron graves (CDC ≥ IIIa). Las complicaciones más frecuentes fueron las relaciones con el tracto urinario (34%), hemorrágicas (30%) e infecciosas (30%). Cuanto mayor era el grado CDC, mayor era la mediana de CCI, y se produjo un aumento estadísticamente significativo de la mediana de CCI de complicaciones CDC II a complicaciones mayores. Los pacientes que presentaron complicaciones intraoperatorias tenían mayor riesgo de desarrollar complicaciones postoperatorias de cualquier grado y mayores en la RLM.
ConclusionesLas complicaciones tras la ureteroscopia para el CUTS son relativamente infrecuentes. Los pacientes que sufren complicaciones intraoperatorias tienen un mayor riesgo de desarrollar complicaciones postoperatorias. El Comprehensive Complication Index parece representar mejor la morbilidad postoperatoria global que la clasificación de Clavien-Dindo.