To offer a set of useful recommendations for urologists who are starting to provide treatment of overactive bladders with onabotulinumtoxinA.
MethodsA literature search to December 2013 was conducted, as well as a subsequent critical reading of the selected publications. The coordinators prepared a document that was submitted for review by the members of the Spanish Group for the use of Botulinum Toxin in Urology.
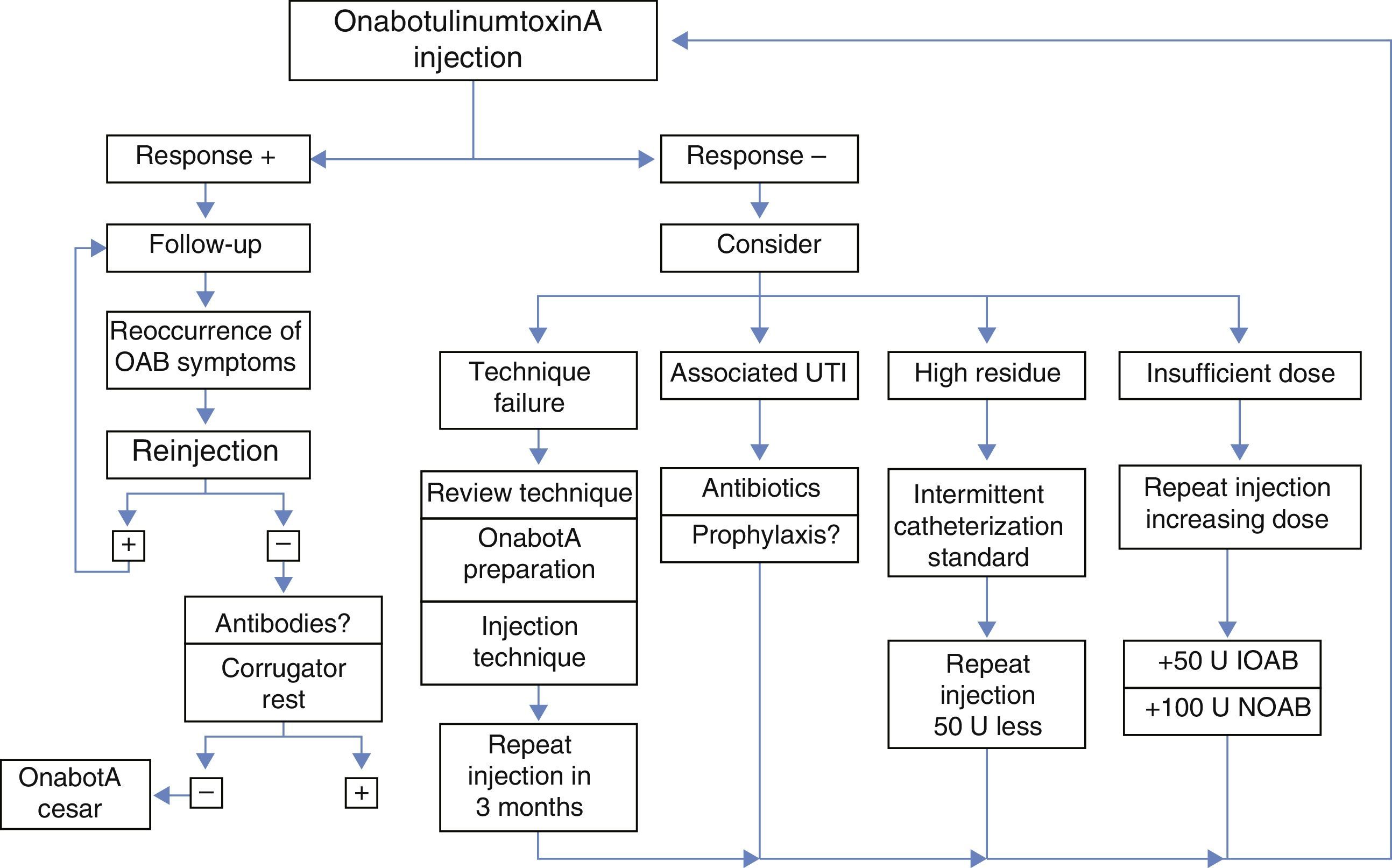
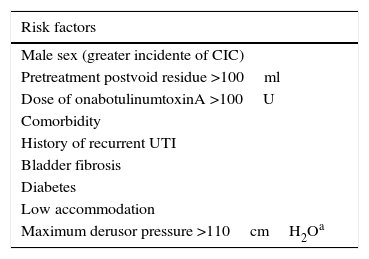
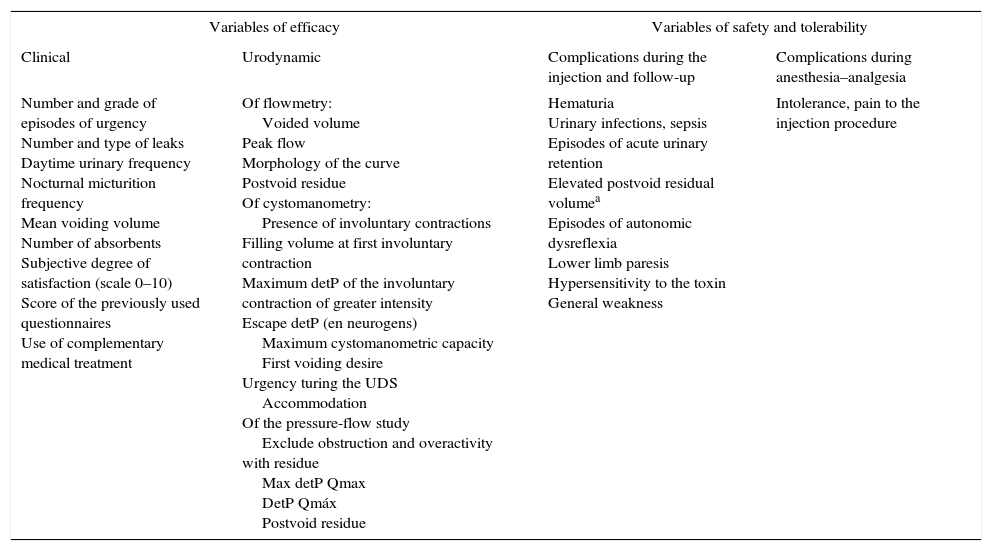
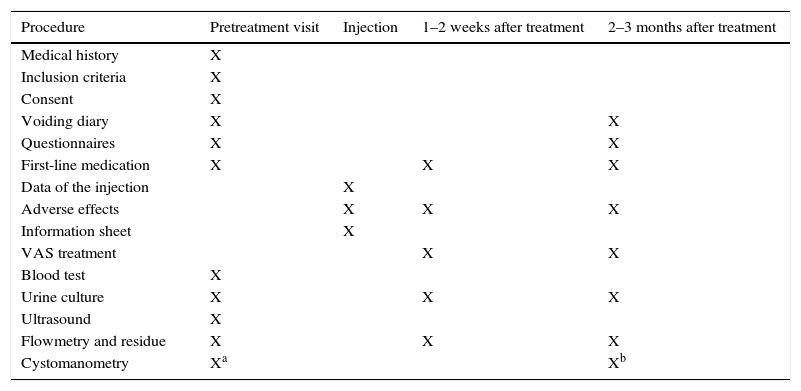
ResultsThe expert group considered that onabotulinumtoxinA may be used for overactive bladder syndrome with urinary urge incontinence secondary to neurogenic or idiopathic detrusor overactivity for patients for whom conservative treatment and first-line medical treatment has failed, is not tolerated or is contraindicated. Treatment in most cases was performed with local intravesical anesthesia, although it can also be performed under epidural or general anesthesia. Patients must be informed of the possibility of requiring self-catheterization or temporary catheterization. Clinicians should ensure that the patients are capable of performing this catheterization before the treatment is conducted. Patients must also be informed of the need for antibiotic prophylaxis to reduce the risk of urinary tract infections. At least 2 follow-up visits are recommended: the first at days 7–14 after the injection and the second at 2–3 months. Reinjection is indicated when the effect of the treatment decreases.
ConclusionThese guidelines can help clinicians in their daily decisions and limit the potential risks associated with the incorrect use of the drug.
Ofrecer un conjunto de recomendaciones que sean de utilidad para aquellos urólogos que se inician en el tratamiento de la hiperactividad vesical con OnabotulinumtoxinA.
MétodosSe realizó una búsqueda bibliográfica, hasta diciembre del año 2013, y una posterior lectura crítica de las publicaciones seleccionadas. Los coordinadores elaboraron un documento que fue sometido a la revisión de los miembros del Grupo español para el uso de toxina botulínica en urología.
ResultadosEl grupo de expertos considera que OnabotulinumtoxinA puede ser utilizada en el síndrome de vejiga hiperactiva con incontinencia urinaria de urgencia secundaria a hiperactividad del detrusor neurógena o idiopática en los que el tratamiento conservador y médico de primera línea haya fracasado, no sea tolerado o exista contraindicación para su uso. El tratamiento en la mayoría de los casos se realiza con anestesia local intravesical, si bien también se puede realizar bajo anestesia epidural o general. Es obligatorio informar de la posibilidad de necesitar autosondaje o sondaje temporal y comprobar que serán capaces de hacerlo, si se precisa, antes de realizar el tratamiento, así como de la necesidad de efectuar una profilaxis antibiótica para disminuir el riesgo de infección urinaria. Se recomiendan al menos 2 visitas de seguimiento: a los días 7-14 tras la inyección y la segunda a los 2-3 meses. Se indicará la reinyección cuando el efecto del tratamiento disminuya.
ConclusiónEstas guías pueden ayudar al clínico en su toma de decisiones diaria y limitar los potenciales riesgos asociados con el uso incorrecto de este fármaco.