The links between body weight and sexuality, notably sexual dysfunction (SD), are intricate and not yet fully understood. A more individual-focused evaluation of sexual difficulties, as recently provided by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), contributes to improve precision in SD diagnosis and has the potential to advance our knowledge on the association between body weight and SD.
ObjectivesTo identify gender differences in sexual behaviors and SD among Portuguese men and women within different classes of body mass index (BMI); and to explore the association between BMI and SD by using the new DSM-5 criteria.
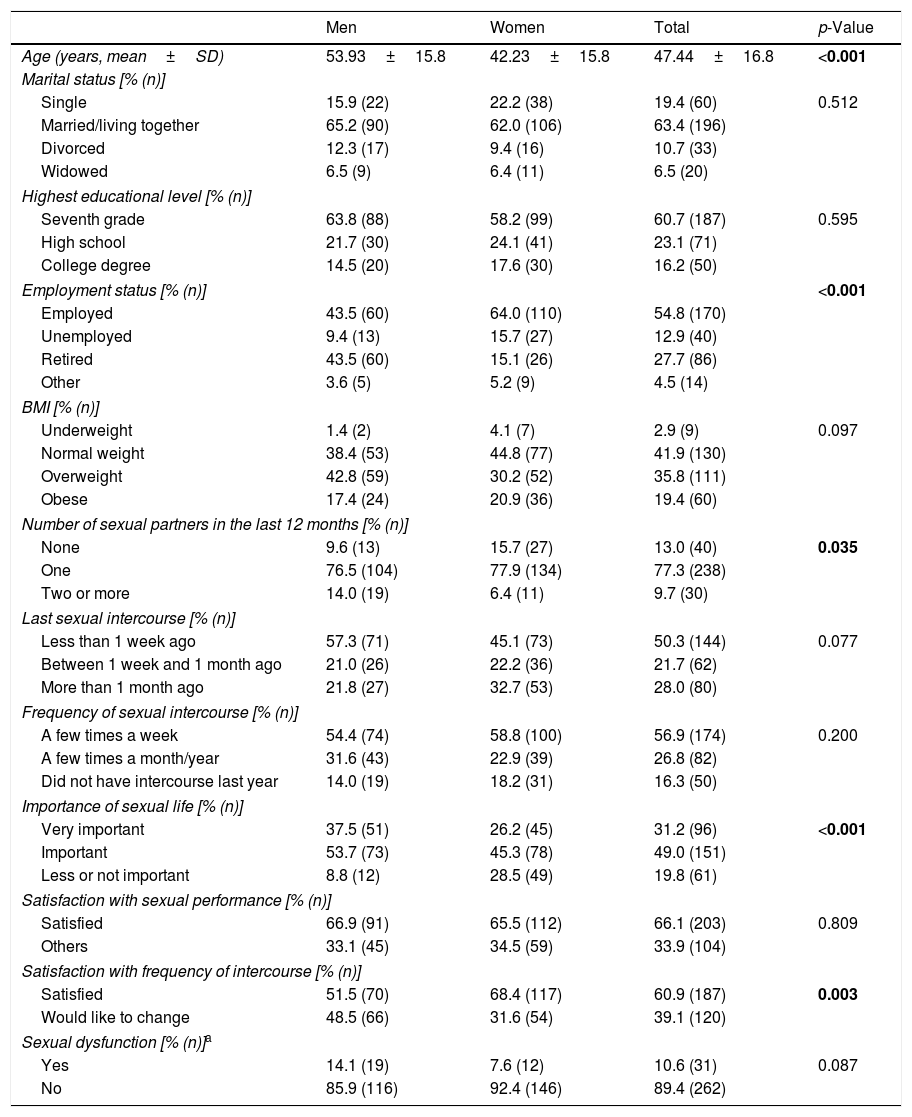
Material and methodsFace-to-face interviews followed by self-completed questionnaires of primary healthcare users in Portugal (n=323). Data on sociodemographic variables, BMI, sexual behaviors and SD were collected. DSM-5 criteria were used to assess sexual dysfunction. The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) and the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) for men and women, respectively, were used for comparison purposes.
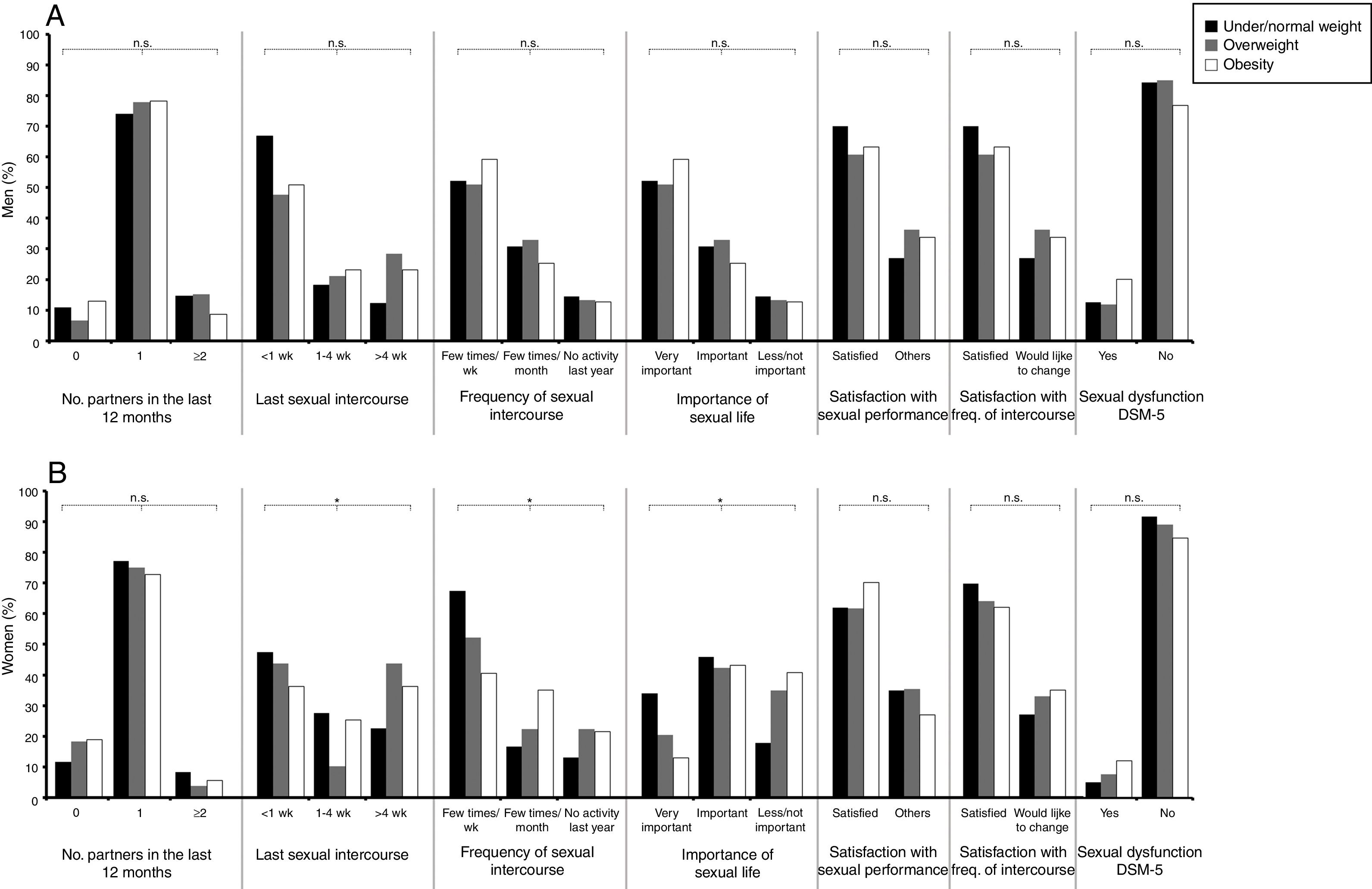
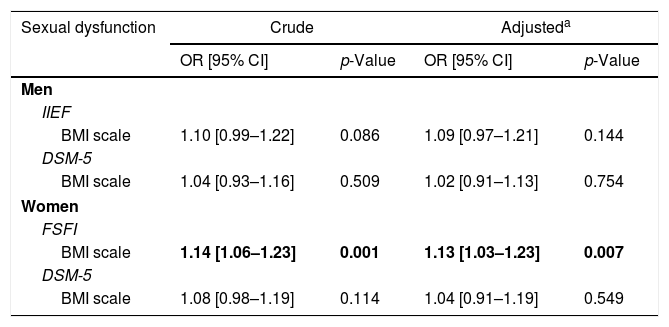
ResultsOverweight and obese women reported less sexual partners, less satisfaction with sexual frequency and rated sexual life as less important. These differences were not found among men. Normal weight men and women had a higher score of IIEF and FSFI, respectively, than those overweight and obese. No significant effects of BMI scale on SD following DMS-5 were detected.
ConclusionsWomen's sexual function is more impacted by BMI than men's. Individual-orientated approaches, as proposed in DSM-5, may allow a better understanding on the relation between body size and sexuality in both genders.
La relación entre el peso corporal y la sexualidad, en particular la disfunción sexual (DS), es compleja y aún no se entiende por completo. Una evaluación de las dificultades sexuales más centrada en el individuo, como la recientemente proporcionada por el Manual Diagnóstico y Estadístico de los Trastornos Mentales (DSM-5), contribuye a mejorar la precisión en el diagnóstico de la DS y tiene el potencial para avanzar en el conocimiento sobre la asociación entre el peso corporal y la DS.
ObjetivoIdentificar diferencias de género en conductas sexuales y DS entre varones y mujeres portuguesas con diferentes clases de índice de masa corporal (IMC), y explorar la asociación entre IMC y DS utilizando los nuevos criterios del DSM-5.
Material y métodosEntrevistas cara a cara con usuarios de atención primaria de salud en Portugal (n=323), seguidas de cuestionarios autocompletados. Se recogieron datos sobre variables sociodemográficas, IMC, conductas sexuales y DS. Los criterios del DSM-5 se utilizaron para evaluar la DS. El Índice Internacional de Función Eréctil (IIEF) y el Índice de Función Sexual Femenina (IFSF) se utilizaron con fines comparativos, para varones y mujeres, respectivamente.
ResultadosLas mujeres con sobrepeso y obesidad comunicaron menos parejas sexuales, menor satisfacción con la frecuencia sexual y calificaron la vida sexual como menos importante. Estas diferencias no se encontraron entre los varones. Los varones y mujeres de peso normal tuvieron una puntuación más alta de IIEF y IFSF, respectivamente, que los varones y las mujeres con sobrepeso y obesidad. No se detectaron efectos importantes de la escala del IMC en la DS según el DSM-5.
ConclusiónLa función sexual de las mujeres está más afectada por el IMC que la de los varones. Los enfoques orientados al individuo, como se propone en el DSM-5, pueden permitir una mejor comprensión de la relación entre el peso corporal y la sexualidad en ambos sexos.